What is RoHS?

RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substance) is a European Union directive that limits the use of specific hazardous materials in electrical and electronic equipment (EEE). First introduced under Directive 2002/95/EC and later replaced by Directive 2011/65/EU (RoHS 2) and its amendment 2015/863 (RoHS 3), the standard applies to products placed on the EU market. RoHS restricts the presence of substances like lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, and certain flame retardants used in plastics.
Manufacturers to distributors across electronics, medical devices, consumer appliances and telecommunications rely on RoHS to meet material safety expectations. The directive ensures that products do not pose environmental or health risks during production.
To begin your RoHS certification process or learn more, contact us at support@pacificcert.com
What is the Purpose of RoHS Certificate?
The primary goal of RoHS Certificate is to reduce environmental and health impacts caused by hazardous substances in electronics. It guides manufacturers in eliminating restricted chemicals from their supply chain and encourages safer product design. RoHS aligns with broader waste management and recycling goals across the EU.
What is Scope and Applicability of RoHS Certificate?
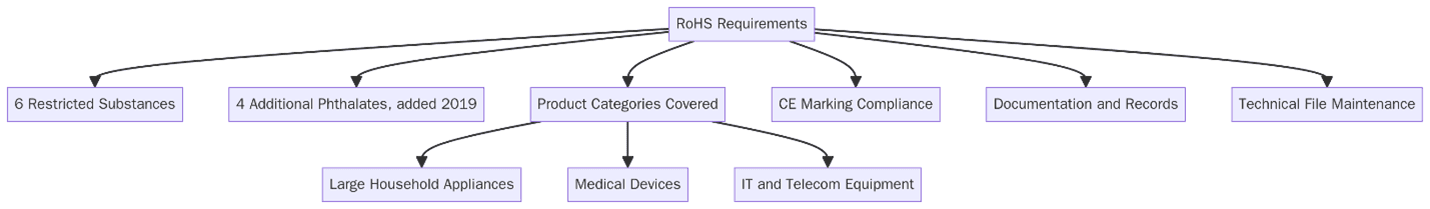
RoHS Certificate applies to a wide range of electrical and electronic equipment, including:
- Consumer electronics such as mobile phones, TVs and laptops
- Household appliances including refrigerators, vacuum cleaners and microwaves
- Lighting equipment like LED lamps and luminaires
- Medical devices and in-vitro diagnostic equipment
- Industrial monitoring and control instruments
- Toys, leisure and sports equipment with electronic functionality
The directive covers finished products and their components. Even imported goods must meet RoHS obligations before entering the EU market. Companies outside the EU supplying EEE or subassemblies must also comply if their products are sold within EU member states.
Key Definitions
EEE (Electrical and Electronic Equipment): Devices that require electric current or electromagnetic fields to function and are designed for use with voltages below 1000V AC or 1500V DC.
Restricted Substances: As of RoHS 3, the list includes 10 materials: lead, cadmium, mercury, hexavalent chromium, PBB, PBDE, DEHP, BBP, DBP and DIBP.
Homogeneous Material: Material that cannot be mechanically separated into different materials. Restrictions apply at this level.
Declaration of Conformity (DoC): A self-declared statement from the manufacturer confirming the product meets RoHS.
CE Marking: Indicates compliance with all applicable EU directives including RoHS.
Structure of the RoHS Directive
Section | Title | Description |
1 | Scope | Defines the categories of EEE covered by RoHS |
2 | Definitions | Clarifies terms used in the directive |
3 | Substances Restricted | Lists prohibited substances and allowable thresholds |
4 | Conformity Assessment | Outlines steps to verify RoHS conformity |
5 | CE Marking | Requirements for labeling and declarations |
6 | Obligations of Manufacturers | Duties related to product design, testing and documentation |
7 | Market Surveillance | Describes checks and enforcement procedures |
8 | Annexes | Contains details on exemptions, categories and technical documentation |
What are the RoHS Certification Requirements?
To get a RoHS Certificate, organizations must take measurable steps during design, sourcing and production. Below are the main RoHS Certification requirements:
- Identify and classify products as electrical and electronic equipment (EEE).
- Eliminate or reduce restricted substances to below maximum concentration values (MCVs).
- Conduct material testing or obtain supplier declarations confirming substance content.
- Maintain technical documentation proving compliance including bills of materials and lab reports.
- Prepare and sign a Declaration of Conformity (DoC).
- Affix the CE mark to the product, packaging and user manuals.
- Monitor changes in design or suppliers that may affect substance content.
- Review exemptions regularly to ensure ongoing validity.
What are the Benefits of RoHS Certificate?
RoHS certificate allows companies to validate that their products are safe for users and suitable for sale in the European market. It supports brand credibility and market growth.
Key RoHS benefits include:
- Opens access to EU and global markets with aligned material rules
- Builds buyer confidence across retail, B2B and procurement sectors
- Reduces risks related to hazardous waste management
- Encourages safer product development and innovation
- Protects users from exposure to toxic materials
- Supports compliance during customs checks and import declarations
- Helps avoid product recalls or market rejections
- Aligns with environmental sustainability goals
RoHS product certification is seeing stricter enforcement across the EU with increased inspections and a push for more detailed technical files backed by lab test results. Recent updates also include new exemptions like limited use of cadmium and lead in recycled PVC, while others are set to expire soon. China RoHS has aligned its substance list with the EU version, expanding its global impact.
Eligibility Criteria
RoHS applies to all businesses that manufacture, import or distribute electrical and electronic products in the EU. This includes OEMs, contract manufacturers, component suppliers and e-commerce sellers. Firms must show they control material sourcing and product design to ensure that hazardous substances are not present above legal limits. Companies already certified to ISO 14001 or ISO 9001 may benefit from existing documentation systems during RoHS implementation.
What is RoHS Certificate Process?
- Initial Gap Assessment – Review of existing product designs, material declarations and internal controls
- Material Verification – Testing of high-risk components and subassemblies through certified labs
- Technical File Compilation – Creation of documentation covering product schematics, testing data, and supplier declarations
- Drafting the DoC – Preparation of the legally required Declaration of Conformity
- CE Marking – Product packaging and labeling updates based on RoHS conformity
- Audit (Optional) – Third-party audits may be requested by buyers or required under supplier qualification programs
- Ongoing Surveillance – Internal audits or retesting after design changes or supplier shifts
What is RoHS Timeline?
For most companies, RoHS Timeline can be 4 to 8 weeks. This depends on the number of products, the availability of material test reports and whether previous assessments were done. For organizations with multiple product lines, a phased approach may be used. Changes in suppliers or formulations may require retesting or technical file updates. Timely recordkeeping supports faster approvals.
What is the RoHS Certification Cost?
The RoHS certification cost depends on the type of product, complexity of design, number of components requiring lab testing and the amount of technical documentation to be developed. Companies with access to supplier declarations or prior testing records may lower their costs. Additional expenses may arise from laboratory analysis, translation of technical files and CE labeling adjustments.
How can Pacific Certifications Help?
Pacific Certifications conducts RoHS assessments and certification audits. We support manufacturers and suppliers across all electronics categories to meet RoHS expectations. Our team works closely with technical managers, product designers and quality staff to ensure all material safety steps are taken before CE marking.
Our services include:
- Initial assessment of product materials and technical files
- Coordination with accredited labs for substance testing
- Review and validation of supplier material declarations
- Guidance on drafting Declaration of Conformity
- Audit and surveillance services to ensure continuous conformity
- Combined audits with ISO 9001 or ISO 14001 for added value
We are accredited by ABIS and recognized for helping electronics and medical device brands maintain material control across their product lifecycle.
Training and Courses
Lead Auditor Training
Covers internal and supplier audits against RoHS criteria and technical documentation review.
Lead Implementer Training
Focuses on setting up procedures for product design, supplier vetting and CE documentation under RoHS.
Internal Auditor Training
Designed for quality teams to conduct material verification and product reviews within an organization.
Pacific Certifications provides accredited training programs. If your organization is looking for RoHS training, our team is equipped to help you. Contact us at support@pacificcert.com
FAQs
Is RoHS mandatory for all electronics?
Yes. Any electronic product placed on the EU market must meet RoHS unless listed under specific exemptions.
What substances are restricted under RoHS 3?
RoHS 3 restricts 10 substances including lead, cadmium, mercury, chromium VI, PBB, PBDE, DEHP, BBP, DBP and DIBP.
Can RoHS and CE marking be done together?
Yes. RoHS is a requirement under CE for most electronic products, and the DoC must reference RoHS.
Do we need lab tests for every product?
Not always. If supplier declarations and existing records confirm RoHS content, testing may not be needed unless risks are high.
What happens if a product fails RoHS?
Products exceeding substance limits cannot carry the CE mark and must be redesigned or replaced before market entry.
Ready to get ISO certified?
Contact Pacific Certifications to begin your certification journey today!
Suggested Certifications –
Read more: Pacific Blogs






