
What is ISO 22000:2018 Food Safety Management?
ISO 22000:2018 is an internationally recognized standard for food safety management systems. It specifies the requirements for a food safety management system and is designed to help organizations ensure that they control food safety hazards and consistently provide safe food products.
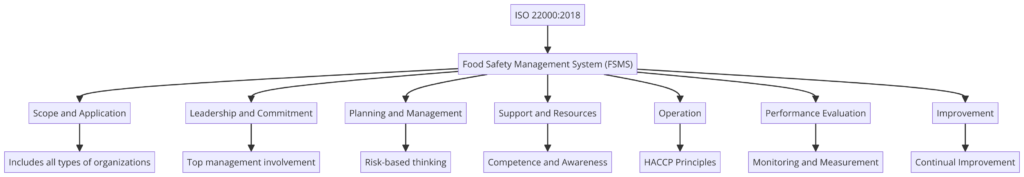
What are the Key Elements of ISO 22000:2018
- Scope and Applicability
- Management System Approach
- Risk-Based Thinking
- Prerequisite Programs (PRPs)
- Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP)
- Communication
- Documentation and Record Keeping
- Continual Improvement
Structure of ISO 22000:2018 – Clause Wise:
Clause 4: Context of the Organization
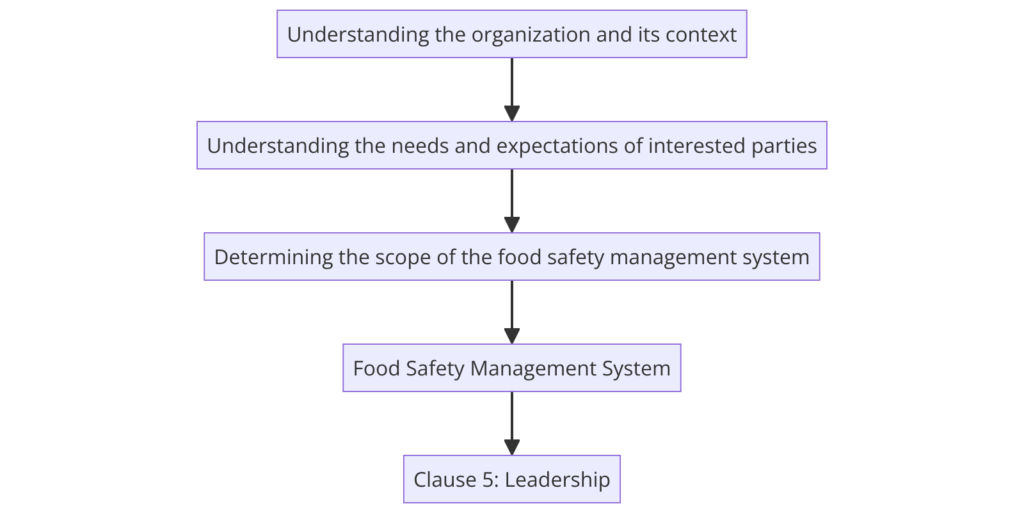
- 4.1 Understanding the organization and its context: Identifies external and internal issues relevant to the FSMS.
- 4.2 Understanding the needs and expectations of interested parties: Identifies stakeholders and their requirements.
- 4.3 Determining the scope of the FSMS: Defines the boundaries and applicability of the FSMS.
- 4.4 FSMS and its processes: Establishes, implements, maintains, and continually improves the FSMS.
Clause 5: Leadership

- 5.1 Leadership and commitment: Top management must demonstrate leadership and commitment to the FSMS.
- 5.2 Policy: Establishes a food safety policy that is appropriate for the organization.
- 5.3 Organizational roles, responsibilities, and authorities: Assigns and communicates roles and responsibilities.
Clause 6: Planning
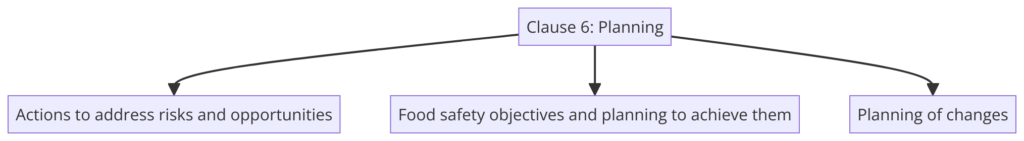
- 6.1 Actions to address risks and opportunities: Identifies and addresses risks and opportunities.
- 6.2 Objectives of the FSMS and planning to achieve them: Establishes food safety objectives and plans to achieve them.
- 6.3 Planning of changes: Plans changes to the FSMS in a controlled manner.
Clause 7: Support
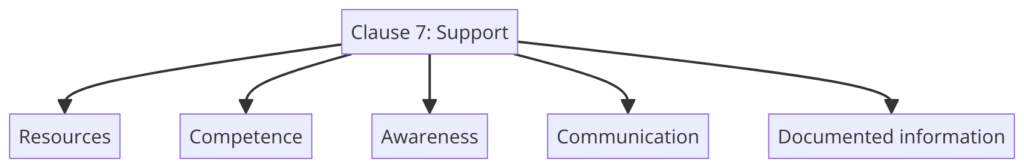
- 7.1 Resources: Determines and provides the resources needed for the FSMS.
- 7.2 Competence: Ensures personnel are competent based on appropriate education, training, or experience.
- 7.3 Awareness: Ensures that employees are aware of the food safety policy and their contributions to the FSMS.
- 7.4 Communication: Establishes internal and external communication processes relevant to the FSMS.
- 7.5 Documented information: Manages documented information required for the FSMS.
Clause 8: Operation

- 8.1 Operational planning and control: Plans, implements, and controls processes needed to meet FSMS requirements.
- 8.2 Prerequisite programs (PRPs): Establishes and maintains PRPs.
- 8.3 Traceability system: Establishes a traceability system for identification and tracking of products.
- 8.4 Emergency preparedness and response: Prepares for and responds to emergency situations.
- 8.5 Hazard control:
- 8.5.1 Preliminary steps to enable hazard analysis: Collects and evaluates data to facilitate hazard analysis.
- 8.5.2 Hazard analysis: Conducts hazard analysis to determine control measures.
- 8.5.3 Validation of control measure(s) and combinations of control measures: Validates control measures.
- 8.5.4 Hazard control plan (HACCP/OPRP plan): Develops and implements the hazard control plan.
- 8.6 Updating the information specifying the PRPs and the hazard control plan: Keeps information up-to-date.
- 8.7 Control of monitoring and measuring: Controls monitoring and measuring devices.
- 8.8 Verification related to PRPs and the hazard control plan: Verifies PRPs and hazard control plan effectiveness.
- 8.9 Control of product and process nonconformities: Controls nonconforming products and processes.
Clause 9: Performance Evaluation
- 9.1 Monitoring, measurement, analysis, and evaluation: Monitors, measures, analyzes, and evaluates FSMS performance.
- 9.2 Internal audit: Conducts internal audits to verify FSMS compliance.
- 9.3 Management review: Top management reviews the FSMS for effectiveness and suitability.
Clause 10: Improvement
- 10.1 General: Continually improves the suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness of the FSMS.
- 10.2 Nonconformity and corrective action: Manages nonconformities and takes corrective actions.
- 10.3 Continual improvement: Implements improvements based on the results of analysis and evaluation.
Each clause provides a structured approach to managing food safety hazards, ensuring organizations can produce safe food products consistently and effectively.
If you are looking for ISO 22000:2018, contact us today at support@pacificcert.com.
Clause wise Audit Checklist for ISO 22000:2018
Below is a comprehensive audit checklist broken down by each clause of the standard:
Clause 4: Context of the Organization
- 4.1 Understanding the organization and its context:
- Has the organization identified internal and external issues relevant to its purpose and that affect its ability to achieve the intended outcome(s) of the FSMS?
- 4.2 Understanding the needs and expectations of interested parties:
- Has the organization determined the interested parties that are relevant to the FSMS?
- Are their needs and expectations considered?
- 4.3 Determining the scope of the FSMS:
- Is the scope of the FSMS documented and consistent with the context and strategic direction of the organization?
- 4.4 FSMS and its processes:
- Are the FSMS and its processes established, implemented, maintained, and continually improved?
Clause 5: Leadership
- 5.1 Leadership and commitment:
- Does top management demonstrate leadership and commitment with respect to the FSMS?
- 5.2 Policy:
- Is there a food safety policy that is appropriate to the purpose of the organization?
- Is the policy communicated, understood, and applied within the organization?
- 5.3 Organizational roles, responsibilities, and authorities:
- Are roles, responsibilities, and authorities defined, documented, and communicated?
Clause 6: Planning
- 6.1 Actions to address risks and opportunities:
- Are risks and opportunities determined and addressed to ensure the FSMS can achieve its intended outcome(s)?
- 6.2 Objectives of the FSMS and planning to achieve them:
- Are measurable food safety objectives established and plans in place to achieve them?
- 6.3 Planning of changes:
- Are changes to the FSMS planned and carried out in a controlled manner?
Clause 7: Support
- 7.1 Resources:
- Are resources determined and provided for the establishment, implementation, maintenance, and continual improvement of the FSMS?
- 7.2 Competence:
- Are personnel competent based on education, training, or experience?
- 7.3 Awareness:
- Are personnel aware of the food safety policy and their contribution to the effectiveness of the FSMS?
- 7.4 Communication:
- Are internal and external communication processes established?
- 7.5 Documented information:
- Is documented information required by the FSMS controlled and maintained?
Clause 8: Operation
- 8.1 Operational planning and control:
- Are processes needed for the FSMS planned, implemented, and controlled?
- 8.2 Prerequisite programs (PRPs):
- Are PRPs established, implemented, and maintained?
- 8.3 Traceability system:
- Is a traceability system in place for identification and tracking of products?
- 8.4 Emergency preparedness and response:
- Are emergency preparedness and response plans established?
- 8.5 Hazard control:
- 8.5.1 Preliminary steps to enable hazard analysis:
- Are data collected and evaluated to enable hazard analysis?
- 8.5.2 Hazard analysis:
- Is a hazard analysis conducted to determine control measures?
- 8.5.3 Validation of control measure(s) and combinations of control measures:
- Are control measures validated?
- 8.5.4 Hazard control plan (HACCP/OPRP plan):
- Is a hazard control plan developed and implemented?
- 8.5.1 Preliminary steps to enable hazard analysis:
- 8.6 Updating the information specifying the PRPs and the hazard control plan:
- Is information kept up-to-date?
- 8.7 Control of monitoring and measuring:
- Are monitoring and measuring devices controlled?
- 8.8 Verification related to PRPs and the hazard control plan:
- Is the effectiveness of PRPs and the hazard control plan verified?
- 8.9 Control of product and process nonconformities:
- Are nonconforming products and processes controlled?
Clause 9: Performance Evaluation
- 9.1 Monitoring, measurement, analysis, and evaluation:
- Are methods established to monitor, measure, analyze, and evaluate FSMS performance?
- 9.2 Internal audit:
- Are internal audits conducted at planned intervals to verify FSMS compliance?
- 9.3 Management review:
- Does top management review the FSMS for effectiveness and suitability?
Clause 10: Improvement
- 10.1 General:
- Is the FSMS continually improved to ensure its suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness?
- 10.2 Nonconformity and corrective action:
- Are nonconformities managed and corrective actions taken?
- 10.3 Continual improvement:
- Are improvements implemented based on the results of analysis and evaluation?
Additional Points to Consider
- Verification Records:
- Are records of verification activities maintained and reviewed?
- Supplier and Raw Material Controls:
- Are controls in place for suppliers and raw materials to ensure food safety?
- Hygiene and Sanitation:
- Are hygiene and sanitation procedures documented and followed?
- Training and Competence:
- Are training programs effective and documented?
Pacific Certifications is accredited by ABIS, if you need support with ISO 22000 certification for your business, please contact us at support@pacificcert.com or +91-8595603096.
Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) Explained: ISO 22000:2018
The Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle is a key element in ISO 22000:2018, providing a framework for continuous improvement of the Food Safety Management System.
Here is a detailed explanation of each phase of the PDCA cycle and how it applies to ISO 22000:
Application of PDCA in ISO 22000:2018
- Plan: Establish objectives, processes, policies, and procedures required to achieve safe food products.
- Do: Implement the planned processes, ensuring resources are available and properly managed.
- Check: Monitor and measure processes, conduct internal audits, and perform management reviews to ensure the FSMS is effective and meets requirements.
- Act: Take corrective and preventive actions based on performance evaluation and audit results, striving for continuous improvement.
Plan
Context of the Organization (Clause 4):
- Understanding the organization and its context, identifying internal and external issues.
- Determining the needs and expectations of interested parties.
- Defining the scope of the FSMS.
- Establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving the FSMS and its processes.
Leadership (Clause 5):
- Ensuring top management demonstrates leadership and commitment to the FSMS.
- Establishing a food safety policy.
- Defining roles, responsibilities, and authorities.
Planning (Clause 6):
- Identifying risks and opportunities that need to be addressed to achieve intended outcomes.
- Setting food safety objectives and planning to achieve them.
- Planning for changes to the FSMS.
Do
Support (Clause 7):
- Determining and providing the necessary resources.
- Ensuring competence, awareness, and communication within the organization.
- Managing documented information required for the FSMS.
Operation (Clause 8):
- Planning and controlling operational processes to meet the FSMS requirements.
- Implementing prerequisite programs (PRPs) to maintain a hygienic environment.
- Establishing a traceability system.
- Preparing for and responding to emergency situations.
- Conducting hazard analysis and developing a hazard control plan (HACCP/OPRP plan).
- Updating information related to PRPs and the hazard control plan.
- Controlling monitoring and measuring devices.
- Verifying the effectiveness of PRPs and the hazard control plan.
- Managing nonconformities in products and processes.
Check
Performance Evaluation (Clause 9):
- Monitoring, measuring, analyzing, and evaluating the performance of the FSMS.
- Conducting internal audits to verify compliance with FSMS requirements.
- Reviewing the FSMS by top management to ensure its continuing suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness.
Act
Improvement (Clause 10):
- Continually improving the FSMS to enhance overall food safety performance.
- Addressing nonconformities and taking corrective actions to prevent recurrence.
- Implementing changes and improvements based on the results of monitoring, measurement, and analysis.
The PDCA cycle helps organizations maintain a dynamic FSMS that adapts to changes, identifies and mitigates risks, and ensures the production of safe food products, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction and regulatory compliance.
Global Trends on ISO 22000:2018 and How Companies Gained Benefits
ISO 22000:2018 applies to organizations involved in any aspect of the food chain. The standard ensures that companies implement robust food safety management practices, thus improving food safety, quality, and customer trust.
This year, several trends are shaping the landscape of ISO 22000 certification, bringing significant benefits to companies that adopt these practices.
The graph below shows how companies have gained advantages from ISO 22000 from the year 2017 to 2024:
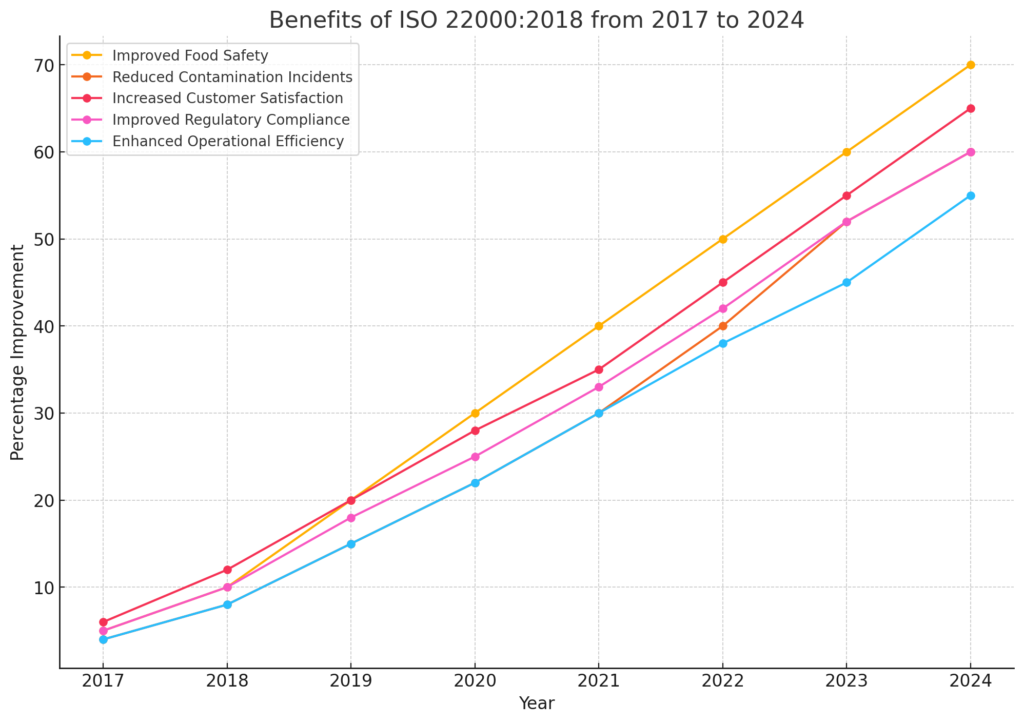
- More companies in developing nations are seeking ISO 22000 certification to gain access to global markets. This trend is driven by increasing consumer demand for safe and high-quality food products, as well as stringent import regulations in developed countries.
- Organizations are increasingly integrating ISO 22000 with other management systems such as ISO 9001 (Quality Management) and ISO 14001 (Environmental Management). This integrated approach helps streamline processes, reduce redundancy, and improve overall efficiency.
- There is a growing emphasis on sustainability within the food industry. Companies are aligning their ISO 22000 certification efforts with sustainable practices, such as reducing food waste, optimizing resource use, and minimizing environmental impact.
- Increasing consumer awareness about food safety issues is driving companies to adopt ISO 22000. Consumers are more informed and demand higher standards of food safety, which in turn compels companies to maintain ISO 22000 certification.
Case Studies and External References
ISO 22000:2018 certification has been very useful among the companies dealing in food products, below are some case studies of popular ones which gained benefits from implementing ISO 22000:
Nestlé, a global food and beverage leader, has integrated ISO 22000 into its operations to enhance food safety and quality, Nestlé ensures that its products meet stringent safety standards, thereby maintaining consumer trust and market leadership.
Danone has implemented ISO 22000:2018 across its supply chain to ensure consistent food safety practices. This has helped Danone improve product quality, enhance traceability, and reduce the risk of food safety incidents.
Tetra Pak, a leading packaging solutions provider, has adopted ISO 22000:2018 to improve food safety and operational efficiency. The certification has enabled Tetra Pak to meet regulatory requirements and enhance customer satisfaction.
ISO 22000:2018 certification is becoming increasingly important for companies involved in the food industry. By adopting ISO 22000, companies can enhance food safety, improve operational efficiency, and gain access to new markets.
Feel free to reach out to us at support@pacificcert.com for further assistance with ISO 22000 certification and to learn more about how we can help your organization achieve its food safety management goals.
ISO 22000:2018 Certification Requirements: Implementing ISO 22000:2018
ISO 22000:2018 helps organizations in the food chain ensure that food is safe for consumption. Implementing ISO 22000:2018 involves understanding and meeting specific requirements, from planning and executing the FSMS to achieving certification. Below is a detailed guide to implementing ISO 22000:
Understand the Standard
Before starting the implementation, thoroughly understand the ISO 22000 requirements. The standard is structured around the High-Level Structure (HLS) and includes:
- Context of the Organization
- Leadership
- Planning
- Support
- Operation: Planning and controlling operations, establishing prerequisite programs (PRPs), hazard control plan (HACCP/OPRP), and traceability systems.
- Performance Evaluation
- Improvement
Gap Analysis
Conduct a gap analysis to identify the differences between the current food safety management practices and the ISO 22000:2018 requirements
Project Planning
Develop a detailed project plan that includes:
- Objectives and goals
- Timeline and milestones
- Responsibilities and resources
- Training and awareness programs
Top Management Commitment
Ensure top management is fully committed to the implementation of ISO 22000. Their involvement is crucial for providing direction, resources, and support. They should establish a food safety policy and integrate FSMS into the organization’s processes.
Establish a Food Safety Team
Form a food safety team comprising members with the necessary knowledge and expertise in food safety management, the team will be responsible for developing, implementing, and maintaining the FSMS.
Documentation
Develop the required documentation, including:
- Food safety policy and objectives
- Procedures and work instructions
- HACCP plan and PRPs
- Records and forms
Ensure the documentation is controlled and accessible to relevant personnel.
Training and Awareness
Provide training to all employees on ISO 22000:2018 requirements, food safety principles, and their specific roles in the FSMS.
Hazard Analysis and Risk Assessment
Conduct a thorough hazard analysis to identify potential food safety hazards. Perform risk assessments to evaluate the severity and likelihood of these hazards. Establish control measures, including PRPs and a HACCP plan, to mitigate the identified risks.
Implementation of PRPs and HACCP Plan
Implement prerequisite programs (PRPs) that provide basic conditions for food safety, such as hygiene practices, pest control, and maintenance. Develop and implement a HACCP plan to control significant hazards.
Internal Audits
Conduct internal audits to evaluate the effectiveness of the FSMS and ensure compliance with ISO 22000 requirements. Internal audits help identify nonconformities and areas for improvement.
Management Review
Perform regular management reviews to assess the performance of the FSMS. Top management should review audit results, feedback from interested parties, performance against food safety objectives, and opportunities for improvement.
Continual Improvement
Implement a process for continual improvement of the FSMS. Address nonconformities through corrective actions and strive to enhance food safety performance.
Certification Audit
Once the FSMS is fully implemented and functioning effectively, schedule a certification audit with a certification body. The audit process typically involves:
- Stage 1 Audit: Review of documentation and readiness for certification.
- Stage 2 Audit: On-site/online audit to verify compliance with ISO 22000 requirements.
Steps to Achieve ISO 22000:2018 Certification
Achieving ISO 22000 certification involves a comprehensive approach to developing and implementing a food safety management system (FSMS) that meets the standard’s requirements. Below are the detailed steps to guide you through the certification process:
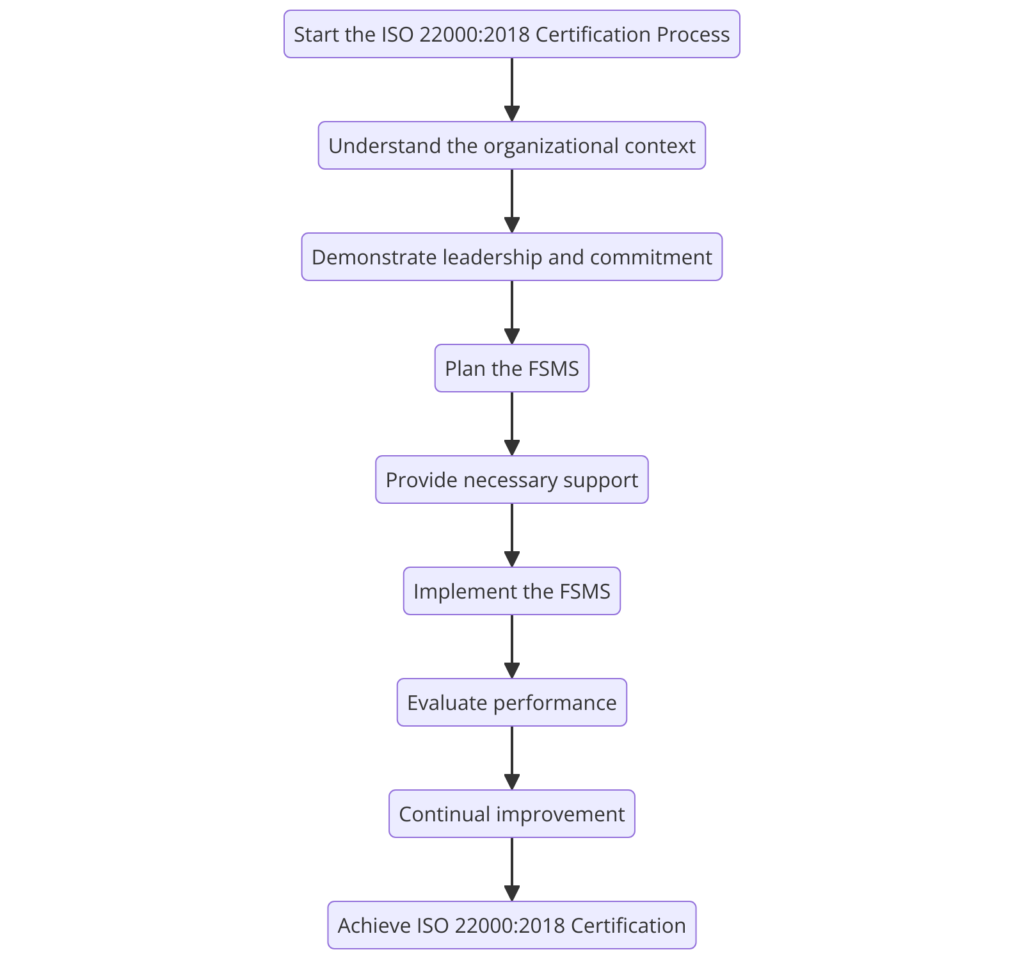
- Step 1: Understanding the ISO 22000:2018 Standard
- Step 2: Conduct a Gap Analysis
- Step 3: Develop a Project Plan
- Step 4: Obtain Top Management Commitment
- Step 5: Form a Food Safety Team
- Step 6: Training and Awareness
- Step 7: Develop Documentation
- Step 8: Implement Prerequisite Programs (PRPs)
- Step 9: Conduct Hazard Analysis and Risk Assessment
- Step 10: Implement the FSMS
- Step 11: Internal Audits
- Step 12: Management Review
- Step 13: Continual Improvement
- Step 14: Certification Audit
- Step 15: Achieving Certification
These steps help organizations to develop an effective FSMS, achieve certification, and ensure the safety of their food products. This certification enhances food safety and improves customer confidence and opens up new market opportunities.
What are the Benefits of ISO 22000 Certification
ISO 22000 certification offers several benefits, including:
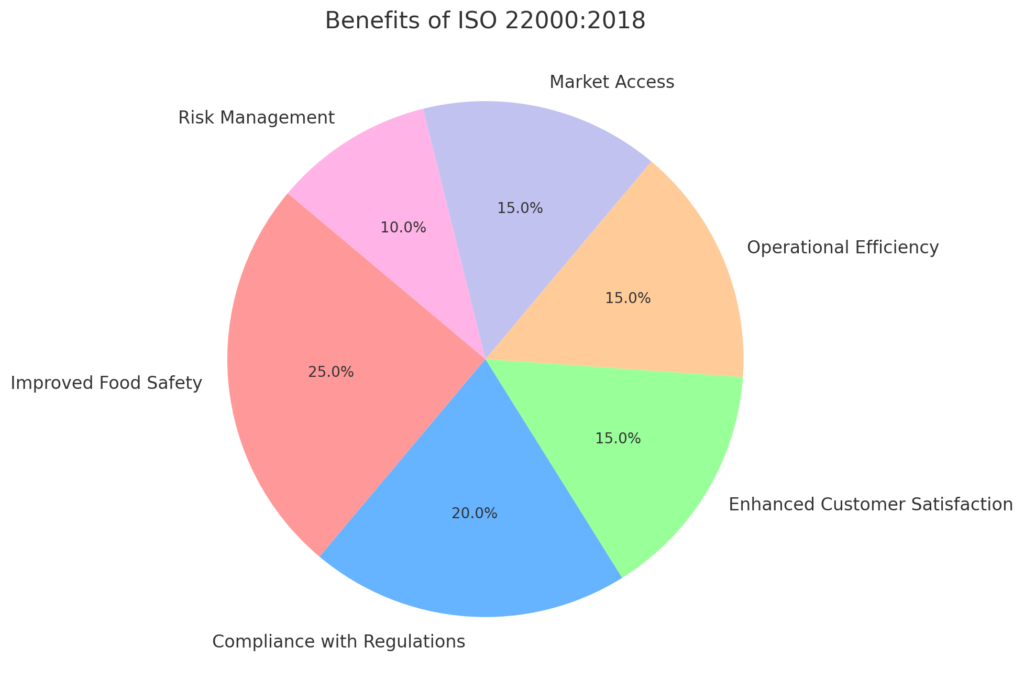
- Ensures the implementation of a robust food safety management system, reducing the risk of foodborne illnesses.
- Meets international regulatory and customer requirements, ensuring compliance with global food safety standards.
- Facilitates entry into international markets by demonstrating adherence to globally recognized food safety standards.
- Identifies and manages food safety risks effectively, leading to improved operational efficiency.
- Increases customer trust and satisfaction by consistently delivering safe and high-quality food products.
- Encourages a culture of continuous improvement in food safety practices and processes.
- Differentiates the company from competitors by showcasing a commitment to food safety and quality.
- Enhances coordination and communication within the supply chain, promoting better food safety management.
- Raises awareness and training among employees regarding food safety practices and standards.
- Protects and enhances the company’s reputation by preventing food safety incidents and recalls.
Who Needs ISO 22000:2018 Food Safety Management Systems
- Food Manufacturers: Companies involved in the processing of raw food materials to produce consumable products.
- Food Packaging Companies: Businesses that produce packaging materials that come into direct contact with food.
- Food Distributors: Organizations that handle the storage and transportation of food products.
- Food Retailers: Supermarkets, grocery stores, and other retail outlets that sell food products to consumers.
- Food Service Providers: Restaurants, catering services, and any business involved in preparing and serving food.
- Farms and Primary Producers: Agricultural businesses and farms that grow or produce food items, including livestock.
- Feed Producers: Companies that manufacture feed for animals that are part of the food supply chain.
- Food Ingredient Suppliers: Businesses that supply raw or processed ingredients used in food production.
- Food Logistics Companies: Providers of transportation, warehousing, and other logistics services for food products.
- Importers and Exporters of Food Products: Companies involved in the international trade of food items.
How is ISO 22000:2018 related to HACCP?
ISO 22000:2018 and HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) are both crucial components of food safety management systems, yet they serve different roles and have unique attributes.
HACCP Overview
HACCP is a systematic approach to food safety that focuses on preventing biological, chemical, and physical hazards in food production processes. It involves the following key steps:
- Identify potential hazards that could occur in the food production process.
- Identify points in the process where hazards can be prevented, eliminated, or reduced to acceptable levels.
- Set maximum or minimum limits for CCPs to ensure that the hazard is controlled.
- Implement procedures to monitor CCPs and ensure they remain within critical limits.
- Define actions to be taken when monitoring indicates that a CCP is not within the established limits.
- Verify that the HACCP system is working effectively.
- Maintain records of the HACCP plan and its implementation.
Relationship Between ISO 22000:2018 and HACCP
ISO 22000:2018 builds on the principles of HACCP and integrates them into a broader management system framework. Here’s how they are related:
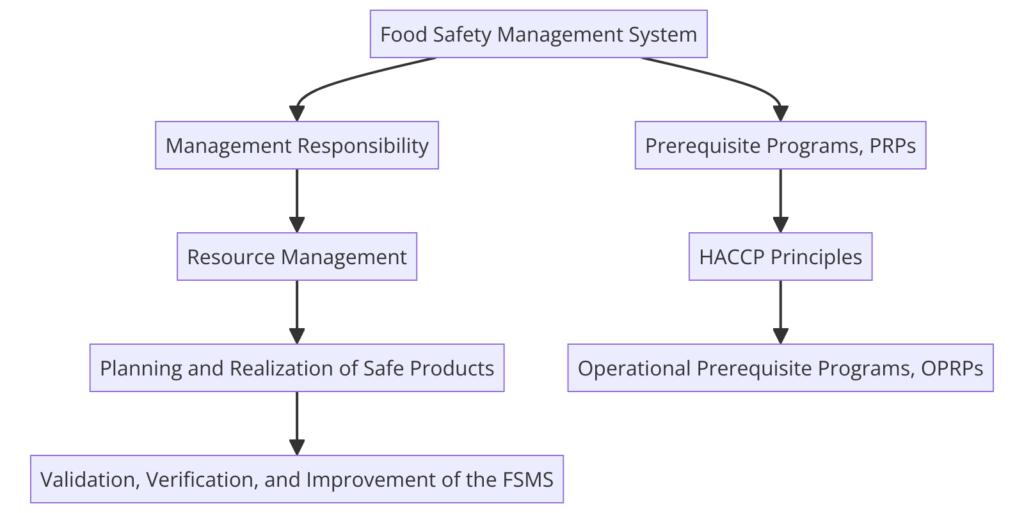
ISO 22000 incorporates all HACCP principles, making them part of the broader FSMS. Organizations implementing ISO 22000 must also adhere to HACCP principles. While HACCP focuses specifically on controlling hazards, ISO 22000 provides a more comprehensive framework, addressing management responsibilities, resource management, planning and realization of safe products, and validation, verification, and improvement of the FSMS.
Both require extensive documentation and record-keeping, but ISO 22000 expands this to include documentation of the entire FSMS, not just the HACCP plan.
Differences Between ISO 22000:2018 and HACCP
While they are related, there are distinct differences between the two:
- HACCP is specifically a system for controlling food safety hazards, whereas ISO 22000 is a full-fledged FSMS that includes HACCP as one of its components.
- ISO 22000 includes additional requirements related to the overall management system, such as management review, continual improvement, and internal audits, which are not part of HACCP.
- ISO 22000 requires a risk-based approach to the entire food safety management system, whereas HACCP is specifically focused on hazard analysis and control.
ISO 22000:2018 and HACCP are complementary tools in ensuring food safety. HACCP forms the foundation of the hazard control component within ISO 22000, while ISO 22000 provides a broader framework for managing food safety across the entire food supply chain.
Contact us today at support@pacificcert.com to discuss your certification related requirements!
Pacific Certifications is accredited by ABIS, Click here to apply for ISO 22000:2018 or get in touch with us at +91-8595603096 or support@pacificcert.com
Suggested Certifications –









