
What is ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018 Information Technology – Service Management System
ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018 is an international standard for IT Service Management (ITSM). It specifies the requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving a service management system (SMS). The standard ensures that service providers deliver effective, efficient, and reliable services that meet both customer and organizational needs.
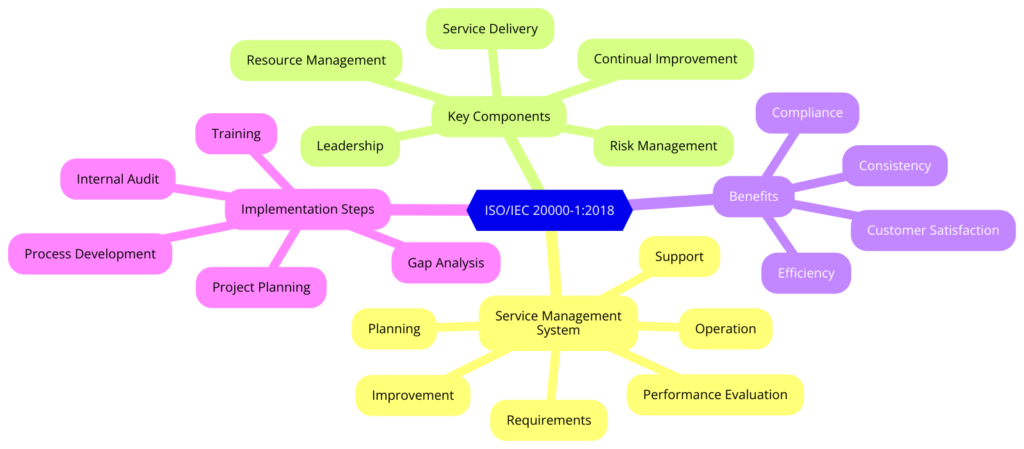
What are the Key elements of ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018
The standard is structured into several clauses, each addressing different aspects of service management:
- Service Management System (SMS)
- Context of the Organization
- Leadership and Commitment
- Planning
- Support
- Operation
- Performance Evaluation
- Improvement
If your company needs ISO/IEC 20000-1 certification, reach out to us today at support@pacificcert.com!
Structure of ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018 Clause Wise
ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018 is structured into ten main clauses, each addressing different aspects of a Service Management System (SMS). Here’s a detailed breakdown of each clause that is important for the implementation:
Clause 4: Context of the Organization
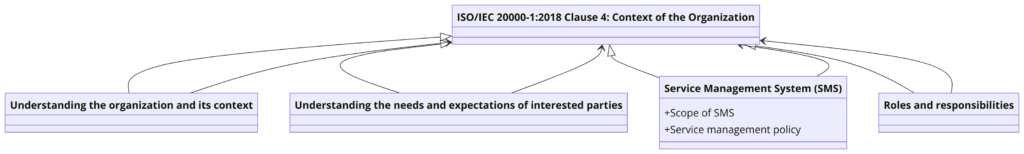
- 4.1 Understanding the Organization and Its Context: Requires the organization to determine external and internal factors that affect the SMS.
- 4.2 Understanding the Needs and Expectations of Interested Parties: Identifies stakeholders and their requirements relevant to the SMS.
- 4.3 Determining the Scope of the SMS: Establishes the scope of the SMS considering the organization’s context and stakeholders’ needs.
- 4.4 Service Management System: Defines the boundaries of the SMS.
Clause 5: Leadership
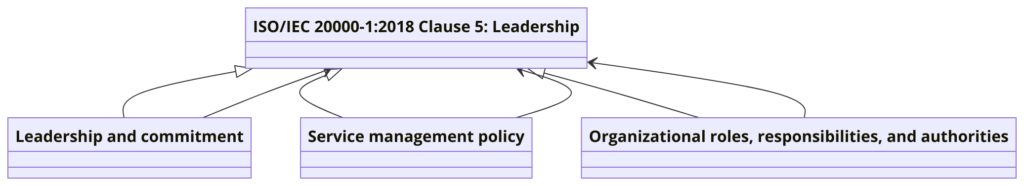
- 5.1 Leadership and Commitment: Top management must demonstrate leadership and commitment to the SMS.
- 5.2 Policy: Establishes a service management policy aligned with the organization’s strategic direction.
- 5.3 Organizational Roles, Responsibilities, and Authorities: Assigns roles, responsibilities, and authorities for the SMS.
Clause 6: Planning
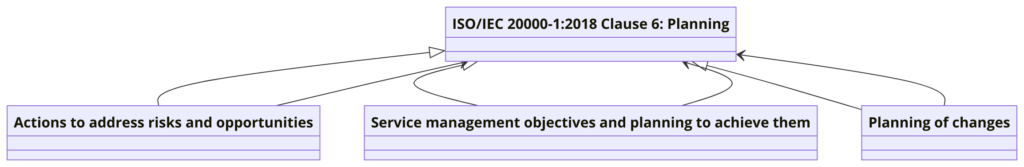
- 6.1 Actions to Address Risks and Opportunities: Identifies and plans actions to address risks and opportunities.
- 6.2 Service Management Objectives and Planning to Achieve Them: Sets objectives for service management and plans to achieve them.
- 6.3 Planning of Changes: Ensures changes to the SMS are planned and implemented systematically.
Clause 7: Support
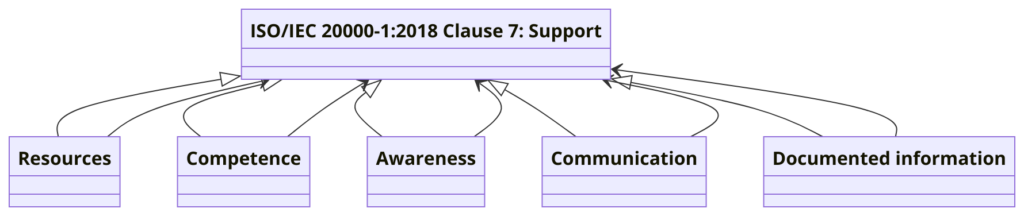
- 7.1 Resources: Determines and provides necessary resources for the SMS.
- 7.2 Competence: Ensures personnel are competent based on education, training, and experience.
- 7.3 Awareness: Ensures personnel are aware of the SMS and their contribution to its effectiveness.
- 7.4 Communication: Establishes internal and external communication relevant to the SMS.
- 7.5 Documented Information: Manages documented information required for the SMS.
Clause 8: Operation
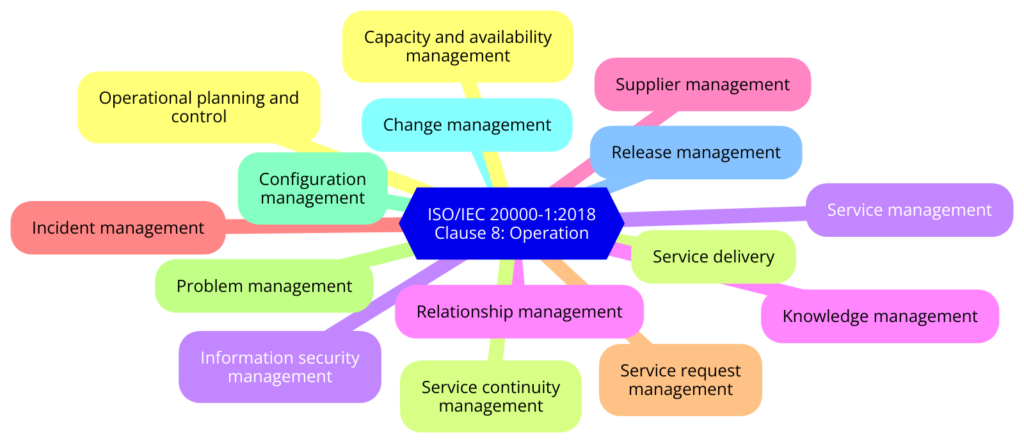
- 8.1 Operational Planning and Control: Plans, implements, and controls the processes needed to meet SMS requirements.
- 8.2 Service Delivery: Ensures effective service delivery processes are in place.
- 8.3 Relationship and Agreement Management: Manages relationships and agreements with stakeholders.
- 8.4 Supply Chain Management: Ensures effective management of suppliers and their impact on the SMS.
- 8.5 Incident and Service Request Management: Manages incidents and service requests to restore service operation.
- 8.6 Service Continuity and Availability Management: Ensures service continuity and availability are maintained.
- 8.7 Service Level Management: Manages service levels to meet agreed requirements.
- 8.8 Capacity and Performance Management: Ensures sufficient capacity and performance of services.
- 8.9 Information Security Management: Protects information security in service management.
- 8.10 Knowledge Management: Manages knowledge to support the SMS.
Clause 9: Performance Evaluation
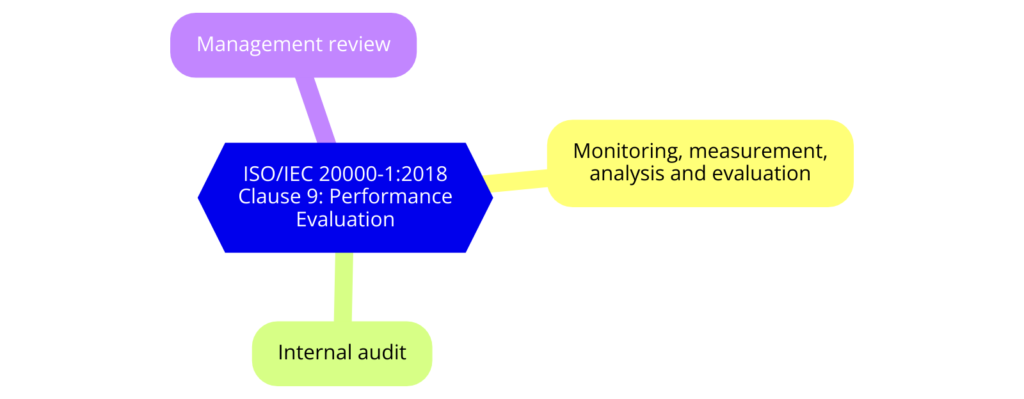
- 9.1 Monitoring, Measurement, Analysis, and Evaluation: Monitors, measures, analyzes, and evaluates SMS performance.
- 9.2 Internal Audit: Conducts internal audits to ensure SMS compliance.
- 9.3 Management Review: Reviews the SMS at planned intervals to ensure its continuing suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness.
Clause 10: Improvement

- 10.1 Nonconformity and Corrective Action: Addresses nonconformities and implements corrective actions.
- 10.2 Continual Improvement: Continually improves the suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness of the SMS.
Each clause is designed to ensure that the service management system is comprehensive, covering all critical areas of service delivery, from leadership and planning to operation and continual improvement.
Seeking ISO/IEC 20000-1 for your organization? Contact us now at support@pacificcert.com!
Audit Checklist for ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018: Clause-wise
An effective audit checklist helps ensure that all requirements of ISO/IEC 20000-1 are met. Below is a clause-wise audit checklist for ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018.
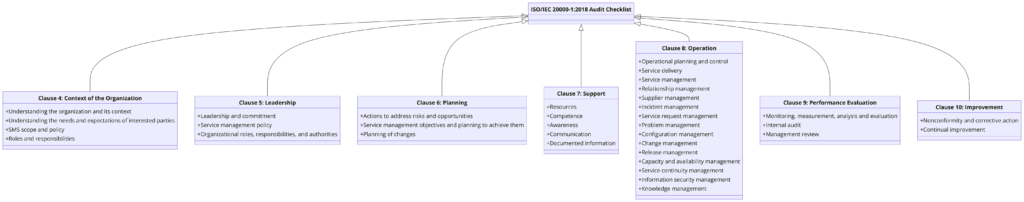
Clause 4: Context of the Organization
- Has the organization identified internal and external issues that affect its ability to achieve the intended outcomes of the SMS?
- Has the organization determined the needs and expectations of interested parties relevant to the SMS?
- Are these needs and expectations documented and reviewed regularly?
- Is the scope of the SMS documented, including boundaries and applicability?
- Does the scope consider the organization’s context and interested parties’ requirements?
- Is the SMS established, implemented, maintained, and continually improved?
- Are the boundaries of the SMS clearly defined and documented?
Clause 5: Leadership
- Is top management demonstrating leadership and commitment to the SMS?
- Are there records of top management’s involvement in SMS activities?
- Is there a service management policy in place?
- Is the policy aligned with the organization’s strategic direction and communicated within the organization?
- Are roles, responsibilities, and authorities for the SMS clearly defined and documented?
- Is there evidence of communication of these roles and responsibilities?
Clause 6: Planning
- Has the organization identified risks and opportunities relevant to the SMS?
- Are there plans in place to address these risks and opportunities?
- Are service management objectives established and documented?
- Are there plans to achieve these objectives, and are they monitored and reviewed?
- Is there a documented process for planning changes to the SMS?
- Are changes reviewed and approved before implementation?
Clause 7: Support
- Are sufficient resources allocated for the establishment, implementation, maintenance, and continual improvement of the SMS?
- Are personnel performing work under the SMS competent based on education, training, or experience?
- Is there a process for evaluating and maintaining competence?
- Are employees aware of the SMS and their contribution to its effectiveness?
- Is there a communication plan for internal and external communication relevant to the SMS?
- Is documented information required by the SMS created, updated, and controlled?
- Are there procedures for managing documented information?
Clause 8: Operation
- Are operations planned, implemented, and controlled to meet SMS requirements?
- Is there evidence of operational controls?
- Are effective service delivery processes in place and documented?
- Are relationships and agreements with stakeholders managed effectively?
- Is there documentation of agreements and their management?
- Are suppliers managed to ensure their impact on the SMS is controlled?
- Are incidents and service requests managed effectively to restore service operations?
- Are there plans to ensure service continuity and availability?
- Are these plans tested and reviewed regularly?
- Are service levels managed to meet agreed requirements?
- Is there evidence of service level agreements and their management?
- Is capacity and performance of services managed to meet customer and organizational needs?
- Is information security maintained in service management?
- Is knowledge relevant to the SMS managed and maintained?
Clause 9: Performance Evaluation
- Are processes in place to monitor, measure, analyze, and evaluate SMS performance?
- Are there records of performance evaluations?
- Are internal audits conducted to ensure the SMS conforms to planned arrangements and the requirements of the standard?
- Is there evidence of audit plans, reports, and follow-up actions?
- Is the SMS reviewed by top management at planned intervals?
- Are there records of management reviews and actions taken as a result?
Clause 10: Improvement
- Are nonconformities identified and corrective actions taken to eliminate their causes?
- Is there evidence of nonconformity reports and corrective actions?
- Are there processes in place for the continual improvement of the SMS?
- Is there evidence of continual improvement activities?
Above is a structured approach to auditing an organization’s compliance with ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018, ensuring all requirements are systematically evaluated and documented.
Is your business looking to achieve ISO/IEC 20000-1 certification? Email us today at support@pacificcert.com!
Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) Explained: ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018
The Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle is a four-step iterative method used for continuous improvement of processes. In ISO/IEC 20000-1, helps organizations establish, implement, maintain, and continually improve their Service Management System (SMS). Here’s how PDCA is applied within the context of ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018:
- Plan: Establish service management objectives and processes.
- Do: Implement and operate the SMS.
- Check: Monitor and review SMS performance.
- Act: Take corrective actions and make improvements based on performance evaluation.
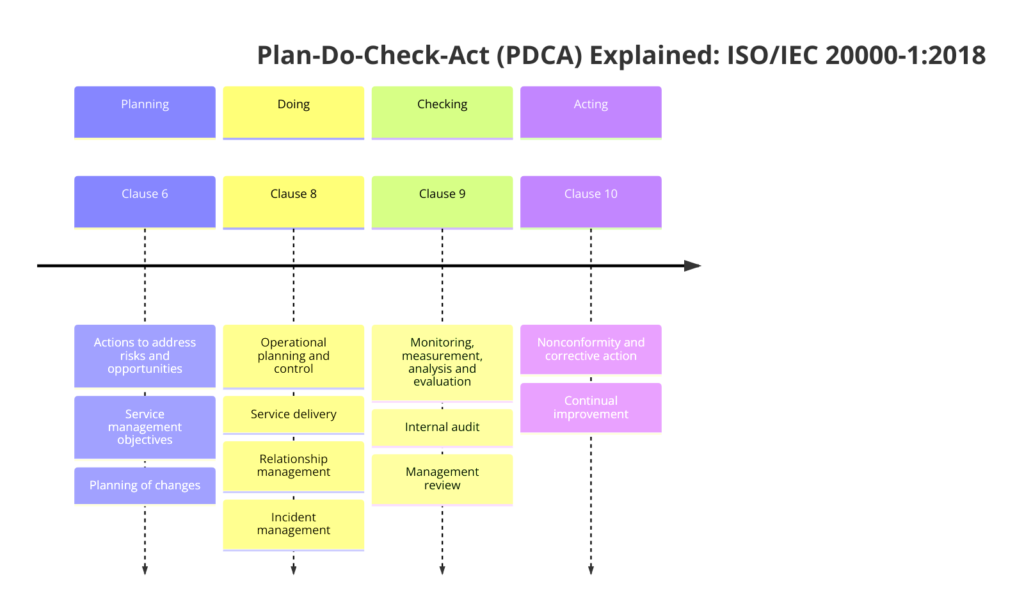
Plan: Establish objectives and processes necessary to deliver results in accordance with the organization’s service management policy.
- Identify external and internal issues that affect the SMS.
- Identify and document stakeholders and their requirements.
- Define the boundaries of the SMS based on the organization’s context and stakeholder needs.
- Develop a service management policy that aligns with the organization’s strategic direction.
- Establish specific, measurable objectives to achieve desired outcomes.
- Identify and plan actions to address potential risks and opportunities.
- Plan changes to the SMS systematically to ensure consistency and reliability.
Do: Implement the processes as planned.
- Ensure the availability of necessary resources for implementing the SMS.
- Ensure personnel are competent, aware of their roles, and communication is effective.
- Create, update, and control documented information required for the SMS.
- Plan, implement, and control service management processes.
- Ensure effective service delivery processes are in place and followed.
- Manage relationships and agreements with customers and other stakeholders.
- Manage suppliers to ensure they meet SMS requirements.
- Effectively manage incidents and service requests to restore service operation promptly.
- Ensure service continuity and availability are maintained.
- Manage service levels to meet agreed requirements.
- Ensure sufficient capacity and performance of services.
- Protect information security in service management.
- Manage and maintain knowledge relevant to the SMS.
Check: Monitor and measure processes and services against the service management policy, objectives, and requirements and report the results.
Monitor and measure SMS performance against planned objectives and criteria.
Conduct internal audits to ensure the SMS conforms to the requirements of ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018 and is effectively implemented and maintained.
Top management reviews the SMS at planned intervals to ensure its continuing suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness. This includes reviewing audit results, feedback, and performance data.
Act: Take actions to continually improve performance.
- Address nonconformities identified through audits and other reviews. Implement corrective actions to eliminate the root causes of nonconformities.
- Continuously improve the SMS by identifying opportunities for improvement, implementing changes, and ensuring the changes are effective.
The PDCA cycle is integrated into the structure of ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018 to ensure a systematic approach to managing and improving service management processes. This continuous loop ensures that the SMS remains effective, efficient, and capable of delivering high-quality services that meet customer and organizational needs.
Need ISO/IEC 20000-1 certification for your company? Contact us at support@pacificcert.com today!
Global Trends in ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018 Adoption and Benefits for Companies
The adoption of ISO/IEC 20000-1 has been on the rise globally, driven by the need for organizations to enhance their IT service management systems (SMS) and improve service delivery.
Below is the chart which compares companies implemented ISO 20000-1 from 2017 to 2024:
ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018 is widely recognized as an international standard for IT service management. The 2018 update aligned ISO/IEC 20000-1 with the High-Level Structure (HLS) used by other management system standards, such as ISO 9001 and ISO/IEC 27001. This alignment facilitates easier integration and management of multiple standards within an organization, promoting a more unified and efficient approach to service management.
ITG highlights how the standard fosters a positive cultural change within organizations, encouraging employees to take ownership of services and comply with relevant laws, ultimately leading to improved service delivery and customer satisfaction (ITG Consulting).
Schellman & Company discusses the strategic benefits of adopting an SMS, including better visibility, centralized control of services, and continual improvement, which collectively contribute to greater effectiveness and efficiency (Schellman Compliance).
Overall, the global adoption of ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018 continues to grow as organizations recognize the value it brings in enhancing service management capabilities, improving customer satisfaction, and gaining a competitive edge in the market.
For ISO/IEC 20000-1 certification services, get in touch with us at support@pacificcert.com!
ISO 20000-1 Certification Requirements: Implementing ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018
Below is a guide to implementing ISO/IEC 20000-1, ensuring your organization is prepared for certification.
Understand the Standard
Define the Scope and Objectives
- Determine the boundaries and applicability of your Service Management System (SMS).
- Document the scope considering the services provided, the customer base, and the organizational context
- Establish clear, measurable objectives for your SMS aligned with your organization’s strategic goals.
Leadership and Commitment
- Ensure top management demonstrates commitment to the SMS.
- Develop and communicate a service management policy that supports the SMS and aligns with organizational objectives.
Conduct a Gap Analysis
- Perform a gap analysis to identify areas where your current practices do not meet ISO/IEC 20000-1 requirements.
- Use the results to develop an implementation plan addressing the identified gaps.
Plan the Implementation
- Develop an action plan detailing the steps required to implement the SMS.
- Include timelines, resources needed, and responsibilities.
Establish Support and Resources
- Ensure sufficient resources (personnel, budget, tools) are allocated for implementing and maintaining the SMS.
Training and Competence:
- Provide training to ensure staff are competent and understand their roles within the SMS.
- Promote awareness of the SMS throughout the organization.
Develop and Document Processes
Develop and document the necessary processes as per ISO/IEC 20000-1 requirements. Key processes include:
- Service Level Management
- Incident and Problem Management
- Change Management
- Configuration Management
- Service Continuity and Availability Management
- Supplier Management
Documentation Control:
- Establish a system for controlling and maintaining documented information related to the SMS.
Implement the SMS
- Implement the processes and practices as planned.
- Ensure effective operational control and monitoring of service management activities.
Monitor and Measure Performance
- Monitor and measure the performance of the SMS against the set objectives.
- Conduct regular internal audits to assess compliance and effectiveness.
Management Review and Continual Improvement
- Conduct regular management reviews to evaluate the SMS and identify opportunities for improvement.
- Address nonconformities and implement corrective actions.
- Promote continual improvement by regularly reviewing and updating the SMS based on performance data and feedback.
Certification Audit
- Once the SMS is implemented and operational, prepare for the certification audit by an accredited certification body.
- Ensure all documentation, processes, and records are in place and ready for review.
- The certification body will conduct an audit to verify that your SMS complies with ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018 requirements.
- Address any findings from the audit to achieve certification.
After the completion of the audit, certification body will make a decision on the certificate issue, if your system complies with the requirements of the standard, you shall be granted a certificate
Contact us at support@pacificcert.com to start your certification journey!
Steps to achieve ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018 Certification
Below are the general steps to start and complete the ISO 20000 process:
- Understanding the Standard
- Conduct a Gap Analysis
- Secure Management Commitment
- Define Scope and Objectives
- Establish a Project Plan
- Assign Roles and Responsibilities
- Develop and Document Processes
- Implement the SMS
- Train and Educate Staff
- Monitor and Measure Performance
- Management Review
- Conduct Reviews:
- Continual Improvement
- Implement Improvements:
- Prepare for Certification Audit
- Certification Audit: Undergo Certification Audit:
- Maintain Certification
By following these steps, organizations can effectively implement an SMS that meets ISO/IEC 20000-1 requirements and achieve certification, demonstrating their commitment to high-quality IT service management.
Benefits of ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018 Certification
Achieving certification to ISO 20000 offers numerous benefits for organizations, enhancing their service management capabilities and overall efficiency.
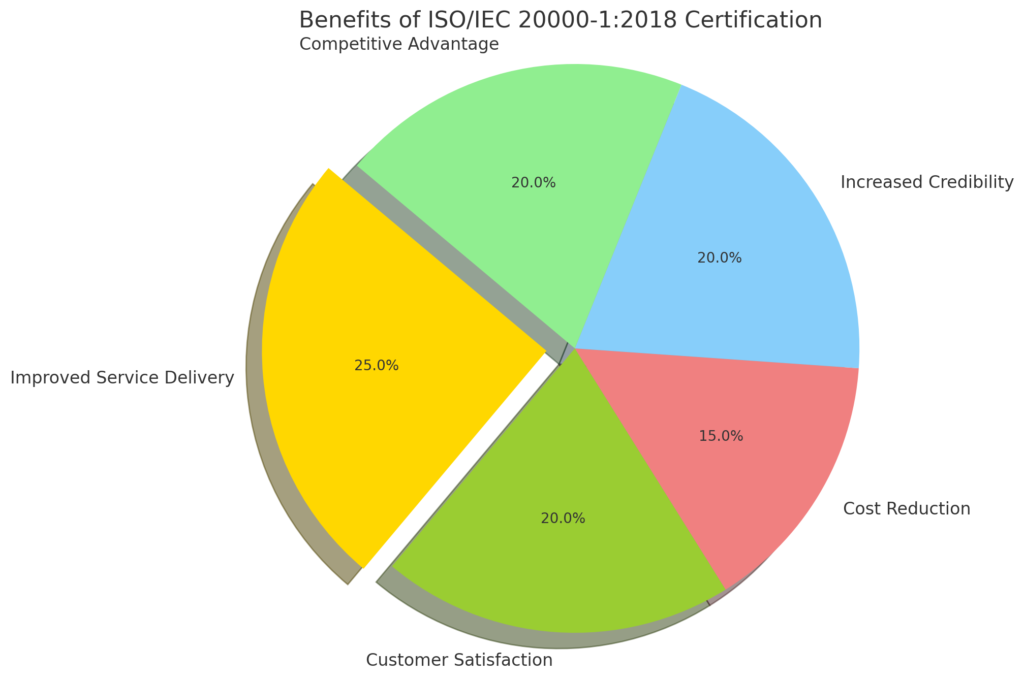
Here are the key benefits of ISO/IEC 20000-1 certification:
- The standard helps ensure that IT services are delivered consistently and meet agreed-upon service levels.
- Helps to gain customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- ISO/IEC 20000-1 promotes the adoption of best practices in IT service management
- The standard helps in optimizing the use of resources and improving productivity.
- Organizations can better identify, assess, and mitigate risks related to IT services, minimizing disruptions and downtime.
- The standard helps organizations comply with relevant legal and regulatory requirements.
- Certification demonstrates a commitment to quality and excellence in IT service management, differentiating the organization from competitors.
- Being certified enhances the organization’s reputation and credibility in the market.
- Efficient use of resources & reduces costs.
- The standard encourages a culture of continuous improvement, ensuring that IT service management processes are regularly reviewed and enhanced.
- It helps in defining clear roles and responsibilities, reducing ambiguity
- With improved processes and risk management, organizations can respond more effectively to changes in the business environment.
- Certification can facilitate business expansion into new markets by meeting international standards and gaining trust from global customers.
Achieving ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018 certification can bring substantial benefits to an organization, enhancing the quality, efficiency, and reliability of its IT services.
The commitment to continuous improvement and international recognition associated with this certification can drive long-term success and growth.
If your business is looking to achieve ISO/IEC 20000-1 certification? Contact us today at support@pacificcert.com!
Who needs ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018 Information Technology?
ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018 can be beneficial for a wide range of organizations, particularly those that provide IT services or rely heavily on IT to support their operations. Here are some examples:
- IT Service Providers: This includes IT companies, managed service providers (MSPs), cloud service providers, and any organization offering IT services to external customers. ISO/IEC 20000-1 helps such providers ensure the quality and reliability of their services.
- Internal IT Departments: Organizations with in-house IT departments can use ISO/IEC 20000-1 to improve the management and delivery of IT services to their internal customers and end-users. This is particularly valuable for large enterprises and government agencies.
- Outsourcing Service Providers: Companies that outsource their IT services to third-party providers can benefit by requiring their service providers to be ISO/IEC 20000-1 certified. This ensures a higher level of service quality and compliance with industry best practices.
- Government Organizations: Government agencies, at various levels, often rely heavily on IT services to deliver public services efficiently. ISO/IEC 20000-1 can help government organizations enhance the quality of their IT services and ensure compliance with regulations.
- Healthcare Providers: Healthcare organizations, including hospitals and clinics, depend on IT systems for patient care, record keeping, and administrative tasks. ISO/IEC 20000-1 can help them ensure the reliability and security of their IT services.
- Financial Institutions: Banks, insurance companies, and other financial institutions use IT extensively for transactions, customer interactions, and data management. ISO/IEC 20000-1 can help them maintain the integrity and availability of their IT services.
- Educational Institutions: Universities, colleges, and schools rely on IT for administration, online learning, and research. ISO/IEC 20000-1 can assist educational institutions in delivering dependable IT services to students and staff.
- Retail and E-commerce Companies: Retailers and e-commerce businesses often rely on IT for point-of-sale systems, online shopping platforms, and supply chain management. ISO/IEC 20000-1 can help ensure the availability and performance of these systems.
- Manufacturers: Manufacturers use IT for production control, supply chain management, and quality assurance. Implementing ISO/IEC 20000-1 can help them optimize IT processes and reduce downtime.
- Transportation and Logistics Companies: Organizations in the transportation and logistics sector depend on IT for tracking shipments, managing fleets, and optimizing routes. ISO/IEC 20000-1 can enhance the reliability and efficiency of these IT services.
- Nonprofit Organizations: Nonprofits often use IT for fundraising, donor management, and program delivery. ISO/IEC 20000-1 can help them ensure that their IT services support their missions effectively.
- Any Organization with IT Dependencies: In today’s digital age, virtually every organization relies on IT services to some extent. ISO/IEC 20000-1 can benefit any entity looking to enhance the management and performance of its IT services.
Moreover, the specific needs and objectives may vary among these organizations, ISO/IEC 20000-1 provides a framework for establishing, implementing, and continually improving IT service management processes, which can lead to improved service quality, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency. Organizations interested in ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018-Information technology should carefully assess their IT service management needs and align the standard’s requirements with their goals.
Lastly, Pacific Certifications is accredited by ABIS, If you need more support with ISO 20000-1, please contact us at +91-8595603096 or support@pacificcert.com
Suggested Certifications –









