What is ISO 9001:2015 – Quality Management Systems?

ISO 9001:2015 is the world’s most recognized standard for Quality Management Systems (QMS). It is the most widely implemented quality standard globally. ISO 9001 applies to all types of organizations, regardless of size or industry and is designed to help businesses consistently deliver products and services that meet customer and regulatory requirements
At its core, ISO 9001 is about making sure an organization is efficient, customer-focused, and committed to continuous improvement. It doesn’t dictate how your business should operate but instead provides flexible and universal principles that you can tailor to your specific operations. It acts as a blueprint for running your business more effectively to actually improve how you work every day.
If your organization is looking to implement or get certified for ISO 9001:2015, contact us at support@pacificcert.com!
What is PDCA Cycle in ISO 9001?
ISO 9001:2015 is based on the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) methodology, which supports continuous improvement and effective process control.
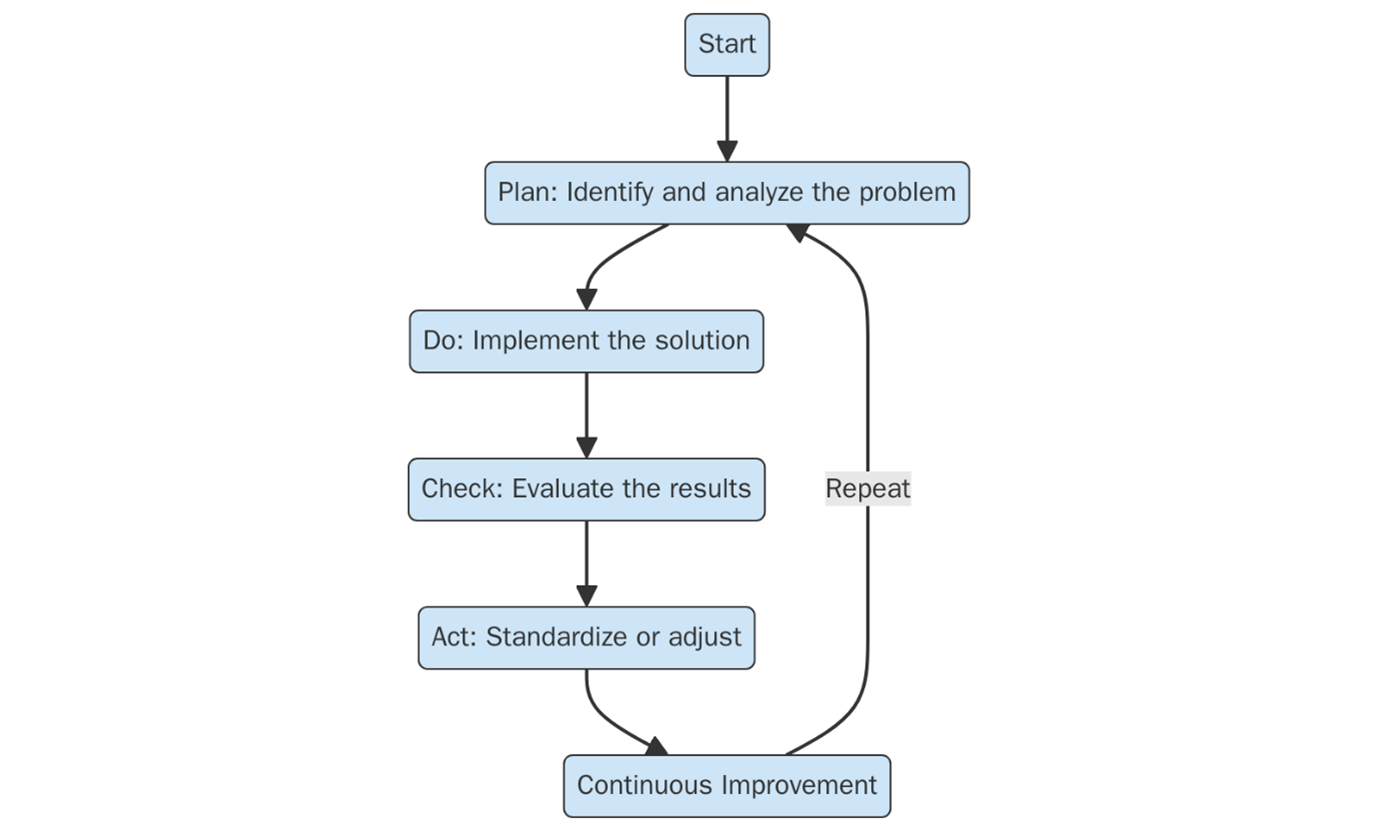
Plan – Define objectives, identify risks and opportunities, and plan the necessary processes.
Do – Implement the processes as planned and manage the associated resources.
Check – Monitor and measure process performance and outcomes against policies and objectives.
Act – Take actions to continually improve process efficiency and effectiveness.
Key Changes in ISO 9001:2015 vs ISO 9001:2008
ISO 9001:2015 introduced several changes compared to the previous version:
- Adoption of the Annex SL structure for easy integration with other standards.
- Greater emphasis on risk-based thinking to identify and mitigate potential failures.
- Strengthened top management commitment and leadership responsibilities.
- Increased flexibility in documented information.
- Requirement to understand the context of the organization and expectations of interested parties.
What are the 7 Principles of ISO 9001:2015?
- Customer Focus – Meeting and exceeding customer expectations is the primary objective.
- Leadership – Establishing unity of purpose and strategic direction through top management commitment.
- Engagement of People – Involving all employees enhances the organization’s capability.
- Process Approach – Managing processes as a system improves consistency and efficiency.
- Improvement – Emphasizing continuous performance enhancement.
- Evidence-Based Decision Making – Making informed decisions using accurate data.
- Relationship Management – Building strong relationships with suppliers and stakeholders.
Clause-wise Structure of ISO 9001:2015
ISO 9001:2015 is structured into 10 clauses. Clauses 4 through 10 are the core requirements of the standard.
Clause | Title | Description |
4 | Context of the Organization | Define internal and external factors affecting the QMS. |
5 | Leadership | Establish leadership roles and demonstrate top management commitment. |
6 | Planning | Address risks and opportunities, set objectives, and manage changes. |
7 | Support | Provide resources, competence, awareness, and documented information. |
8 | Operation | Execute processes that meet product and service requirements. |
9 | Performance Evaluation | Monitor, analyze, and evaluate QMS effectiveness through audits and data. |
10 | Improvement | Drive continuous improvement and address nonconformities. |
If your organization is looking for ISO 9001:2015 certification, contact us at support@pacificcert.com, our team is available 24×7 for your certification related needs!
What are the requirements of ISO 9001:2015?
To implement ISO 9001:2015 effectively, organizations must translate the standard’s clauses into actionable internal practices. It requires strategic alignment and an organizational culture that embraces quality. Below are the requirements you need to meet:
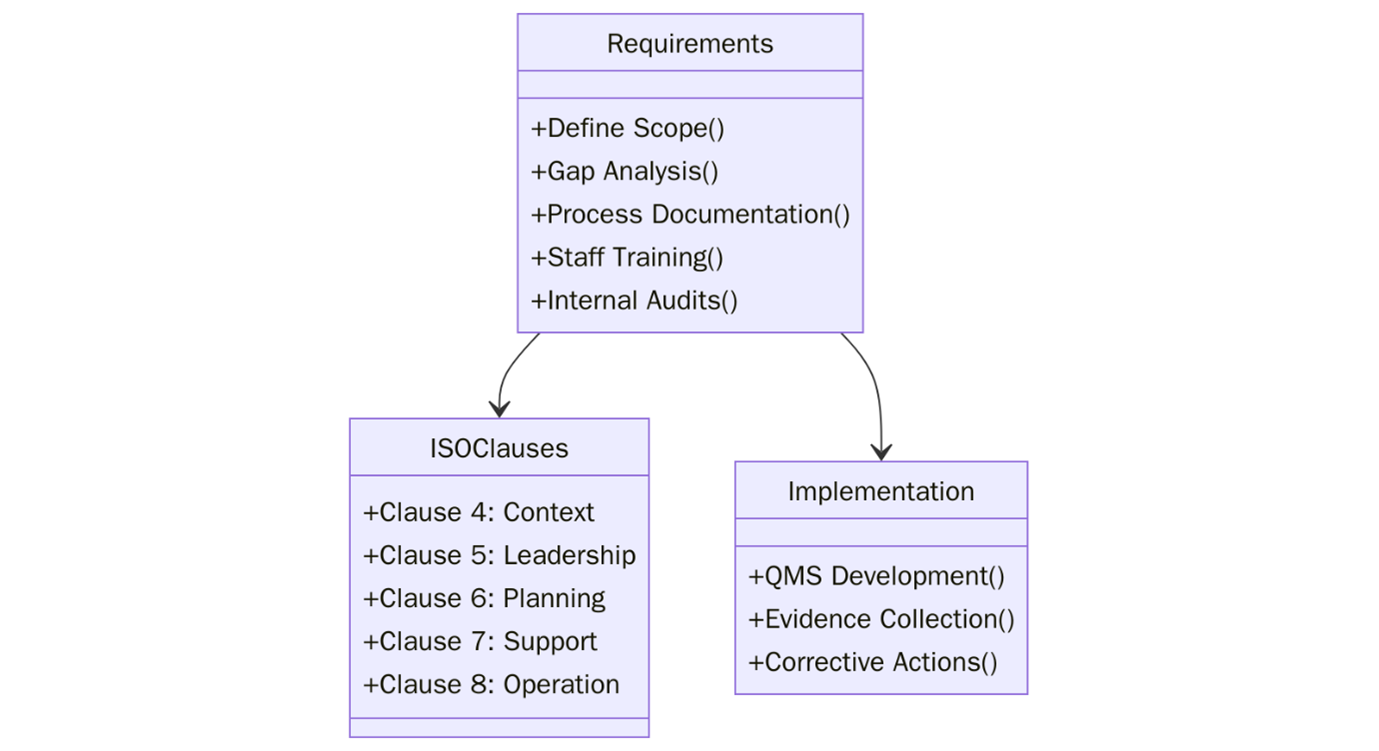
- Identify internal and external issues relevant to your QMS.
- Understand the needs and expectations of interested parties.
- Define the scope of the QMS and its applicability.
- Develop a documented quality policy and measurable objectives.
- Ensure top management commitment and assign roles and responsibilities.
- Conduct risk and opportunity assessments and integrate them into planning.
- Determine and control all required documented information.
- Train employees and raise awareness of QMS objectives.
- Monitor and measure key processes for effectiveness.
- Perform internal audits and management reviews at planned intervals.
ISO 9001:2015 Certification: Audit Checklist
The audit checklist helps to verify that processes are functioning as intended and contributing to customer satisfaction. It provides clarity on what to expect during the audit, and which areas require more attention or improvement. Below are the mandatory requirements:
- Has the organization defined the scope of its Quality Management System, including boundaries and applicability?
- Are the documented processes and procedures aligned with ISO 9001:2015 clause requirements?
- Can the organization demonstrate evidence of continual improvement across its processes?
- Is management review conducted regularly and do minutes reflect data-driven decisions?
- Are nonconformities identified, documented, and corrected with proper corrective actions?
- Are there clear methods to monitor, measure, and analyze performance indicators?
- Is customer satisfaction measured, and are results used to improve performance?
- Are competence, training, and awareness adequately managed and documented for all staff?
- Does the organization follow a consistent method for supplier evaluation and performance monitoring?
- Are products and services verified for quality before delivery to the customer?
- Are all statutory and regulatory requirements identified and complied with?
- Are internal audits conducted as per plan, and are results followed up effectively?
- Is there evidence of risk-based thinking integrated into operational and strategic planning?
- Does top management actively engage in and support the quality management system?
- Are customer complaints tracked and addressed systematically with root cause analysis?
What are the benefits of ISO 9001:2015 Certification?
ISO 9001:2015 certification is an official recognition that an organization has implemented a Quality Management System (QMS), it proves that your organization can consistently deliver products or services that meet customer expectations. Below are some key benefits:
- Improved operational control through standardized processes and procedures.
- Increased customer satisfaction resulting from consistent product and service quality.
- Enhanced market credibility and eligibility for government and international contracts.
- Better risk management through preventive measures and risk-based thinking.
- Stronger leadership engagement and organizational alignment with business goals.
- Efficient resource management leading to reduced costs and waste.
- Continual improvement culture supported by internal audits and reviews.
Overall, ISO 9001 remains one of the most sought-after management system certifications. With over one million certificates issued worldwide in 2025, it continues to evolve alongside digital transformation and sustainability goals. Organizations are integrating QMS platforms with ERP systems, automating compliance tracking, and aligning their QMS with ESG objectives.
If you want to get your ISO 9001 process started, please contact us at support@pacificcert.com today!
Certification Process: ISO 9001:2015
Below are the steps to start the certification process:
- Submit an application with organizational details and scope.
- Undergo a Stage 1 audit to evaluate documentation and preparedness.
- Proceed to Stage 2 audit for full QMS implementation assessment.
- Close nonconformities and receive the certification.
- Participate in annual surveillance audits to maintain certification.
- Complete recertification audits every three years.
Timeline – ISO 9001:2015 Certification
Week | Activity |
1 | Application and requirement analysis |
2 | Optional gap analysis and planning |
3-4 | Document review and Stage 1 audit |
5-6 | Implementation and gap closure |
7-8 | Stage 2 audit and nonconformity review |
9 | Final decision and certification |
10 | Certification issued |
What is ISO 9001 Certification Cost?
ISO 9001 certification cost varies depending on several key factors unique to your organization. The cost reflects the depth, scope, and complexity of your operations.
Some of the main factors that influence ISO 9001 certification cost include:
- Number of employees and operational sites
- Industry complexity and regulatory environment
- Whether you already have a QMS in place or are starting from scratch
- The readiness level of your documentation and processes
- Integration with other standards like ISO 14001, ISO 45001 etc
To get a quote for ISO 9001 certification cost or any other ISO standard, contact us at support@pacificcert.com
Why ISO 9001 Certification is Important in 2025?
In 2025, ISO 9001 holds greater importance as organizations face increasing pressure to deliver consistent quality. Businesses today must respond quickly, adapt seamlessly, and continuously improve, not just to grow, but to survive.
ISO 9001:2015 provides a strong and flexible framework that helps organizations to implement well-defined processes and integrate risk-based thinking into everyday decision-making. This is particularly valuable in a post-pandemic world where resilience and agility are non-negotiable.
Additionally, ISO 9001-certified companies are increasingly favored in global supply chains, government tenders, and B2B contracts because of the credibility and trust the certification brings. With the surge in automation and customer-centric business models, ISO 9001:2015 is a strategic tool for sustainable growth and excellence in 2025 and beyond.
Ready to begin your certification journey? Contact us at Pacific Certifications for audit and certification support at support@pacificcert.com.
Who Needs ISO 9001:2015 Certification?
ISO 9001:2015 certification is essential for any organization—regardless of its size or sector, is particularly valuable for companies looking to streamline operations and improve market credibility. Manufacturers, service providers, IT firms, healthcare institutions, educational organizations, construction companies, and even non-profits benefit from ISO 9001 by ensuring their internal processes are consistent and customer-focused.
Moreover, for businesses seeking to expand into regulated industries, supply chains or government tenders, ISO 9001:2015 certification is often a mandatory requirement. It sends a clear message to clients that your organization is professionally managed and serious about long-term performance.
ISO 9001 Training and Courses
ISO 9001 training is designed to equip individuals and teams with a deep understanding of Quality Management System (QMS) principles, structure and how to implement or audit these systems effectively within an organization. There are several levels of training available:
- Lead Auditor Training – Equips professionals to conduct external third-party audits.
- Lead Implementer Training – For those responsible for planning and executing QMS implementation.
- Internal Auditor Training – Designed for employees who will audit the QMS internally.
Pacific Certifications provides accredited training programs. If your organization is looking for ISO 9001 training, our team is equipped to help you, contact us at support@pacificcert.com!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is ISO 9001:2015?
ISO 9001 is a global standard that specifies requirements for a quality management system to consistently provide products and services that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
Who can apply for ISO 9001:2015?
Any organization, regardless of its size, industry, or type, can implement ISO 9001 and apply for certification.
How much does ISO 9001 certification cost?
The cost depends on factors such as the number of employees, locations, and the complexity of operations. Contact us for a personalized quote.
How long is the certificate valid?
The certificate is valid for 3 years, with annual surveillance audits.
Can ISO 9001:2015 certification be integrated with other standards?
Is training required for ISO 9001:2015 certification?
Training is not mandatory but highly recommended for successful implementation and audit readiness.
What if we fail the ISO 9001:2015 audit?
Nonconformities will be issued, and you will have time to correct them before re-evaluation.
How do I become ISO 9001 certified?
Build a QMS that meets ISO 9001, train your team, run internal audits and a management review, then hire an accredited certification body for a two-stage audit. Note that ISO itself does not certify—independent bodies do.
How much does it cost to get ISO 9001 certification?
Costs vary with headcount, sites and scope. Public examples show certification fees running a few thousand dollars, with total project budgets (prep + audits) for small firms often in the mid-thousands to low tens of thousands.
What is the difference between ISO 45001 and ISO 9001?
ISO 9001 focuses on product and service quality; ISO 45001 focuses on occupational health and safety. They share the same high-level structure and some clauses, but their objectives and controls are different. Many companies run them together.
How long does it take to get ISO 9001 certification?
A realistic window is 3–12 months depending on size and readiness. Some well-prepared SMEs complete in a few months, while larger or multi-site organizations take longer. Also expect to show about three months of QMS records before the certification audit.
What are the 7 principles of ISO 9001?
Customer focus, leadership, engagement of people, process approach, improvement, evidence-based decision making and relationship management. These are the quality management principles behind ISO 9001.
Ready to get ISO 9001:2015 certified?
Contact Pacific Certifications to begin your certification journey today!
Suggested Certifications –
Read more: Pacific Blogs






