What is ISO 14067?
ISO 14067:2018 is the internationally recognized standard that defines the principles, requirements, and guidelines for the quantification and reporting of the carbon footprint of products (CFP). It is part of the ISO 14000 environmental management family and provides a standardized methodology to calculate the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions associated with the life cycle of products, from raw material extraction to end-of-life disposal.
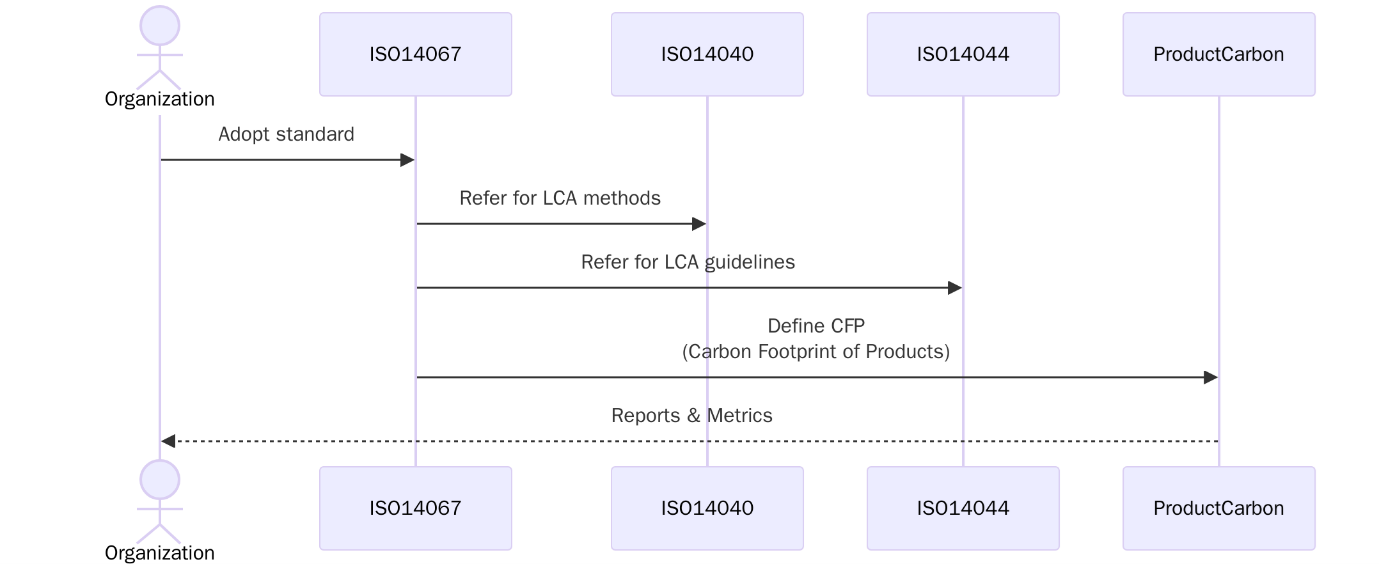
The standard is based on life cycle assessment (LCA) principles as laid out in ISO 14040 and ISO 14044, but it focuses exclusively on climate change impacts in terms of CO₂ equivalents (CO₂e). ISO 14067 supports organizations in identifying key emission hotspots, reducing environmental impact, and enhancing sustainability disclosures.
Need to measure or verify the carbon footprint of your products? Contact us at support@pacificcert.com
Scope and Applicability
ISO 14067 applies to any organization, regardless of industry, size, or geography, that:
- Manufactures or designs physical goods or products
- Supplies raw materials or intermediate components
- Offers product-based services (packaging, logistics)
- Participates in carbon labeling, eco-design, or EPD (Environmental Product Declaration) schemes
- Is involved in ESG reporting, green marketing, or sustainable procurement
The standard is applicable to individual products or product systems, enabling consistent quantification of GHG emissions for a single unit of product or service.
Unsure if ISO 14067 is suitable for your product line? Contact support@pacificcert.com for a suitability review.
Purpose and Objectives
The main objective of ISO 14067:2018 is to provide a consistent and transparent approach for:
- Quantifying GHG emissions and removals associated with a product’s life cycle
- Identifying emission hotspots across supply chains
- Supporting eco-design and sustainable innovation
- Facilitating credible carbon footprint claims
- Providing a foundation for carbon offsetting and neutrality programs
It serves as the cornerstone for product-level climate impact assessments, helping businesses demonstrate environmental responsibility and support global climate goals.
How to Implement ISO 14067 in Your Organization?
Implementing ISO 14067 involves a step-by-step approach grounded in life cycle thinking:
- Identify the product, its function, and boundaries (cradle-to-gate, cradle-to-grave, etc.). Choose between partial or full CFP studies depending on the use case.
- Collect data on inputs (raw materials, energy, transport) and outputs (waste, emissions). Both direct and indirect emissions must be considered.
- Convert all GHG emissions into CO₂ equivalents using IPCC characterization factors. This forms the quantitative basis of the carbon footprint.
- Evaluate results, assess uncertainties, and prepare documentation that clearly presents the assumptions, exclusions, and final CFP results.
- Third-party verification can enhance credibility. CFP results may be communicated in marketing materials, labels, or stakeholder reports.
Need support, contact support@pacificcert.com!
What is the documentation required?
ISO 14067 requires thorough documentation to ensure transparency and consistency:
- Definition of goal, scope, and functional unit
- System boundary and cut-off criteria
- GHG inventory and data sources
- Allocation procedures and modeling methods
- Impact assessment results (expressed in CO₂e)
- Assumptions, limitations, and uncertainty analysis
- CFP study report and, if applicable, verification statement
Eligibility Criteria
ISO 14067 can be implemented by:
- Manufacturers and product designers
- Retail brands conducting environmental product assessments
- Agribusiness, food & beverage producers, and FMCG companies
- Logistics, packaging, and construction material suppliers
- Technology and electronics providers
- Companies participating in carbon offset or neutrality schemes
If your product has a significant carbon impact or is part of a sustainability strategy, ISO 14067 is essential.
Still unsure about eligibility? Schedule a readiness consultation at support@pacificcert.com.
What is the cost of ISO 14067 certification?
The cost of ISO 14067 implementation and verification depends on:
- Product complexity and supply chain length
- Availability and quality of data
- Number of variants or functional units being assessed
- Scope of the CFP study (cradle-to-gate vs cradle-to-grave)
- Requirement for third-party verification or certification
- Integration with ISO 14001 or LCA software tools
Certification Timeline
Week | Activities |
Week 1 | Scoping session and boundary definition |
Week 2 | Data collection and life cycle inventory development |
Week 3 | Impact assessment and CO₂e calculations |
Week 4 | Documentation, reporting, and review of uncertainties |
Week 5 | Optional: Third-party verification and final CFP disclosure |
We help streamline this timeline based on your internal readiness—contact support@pacificcert.com.
Clauses and Structure
Here is a table summarizing the Clauses of ISO 14067:
Clause Number | Clause Title | Description |
1 | Scope | Defines the scope of the standard, focusing on the quantification and communication of CFP (Carbon Footprint of a Product). |
2 | Normative references | Lists documents that are indispensable for the application of this standard (mainly ISO 14040 and ISO 14044). |
3 | Terms and definitions | Provides definitions for key terms such as carbon footprint, life cycle, GHG emissions, and more. |
4 | Principles | Establishes guiding principles such as transparency, consistency, completeness, accuracy, and relevance. |
5 | Methodological framework | Outlines the overall approach and framework for CFP quantification including life cycle assessment (LCA) principles. |
6 | CFP quantification | Describes specific requirements and options for quantifying the carbon footprint of products. |
7 | CFP study report | Specifies the content and structure required for CFP reports to ensure credibility and transparency. |
8 | Communication of CFP results | Provides guidance on the communication of CFP results, ensuring clarity and avoiding misinterpretation. |
What are the requirements of ISO 14067?
Organizations applying ISO 14067 must:
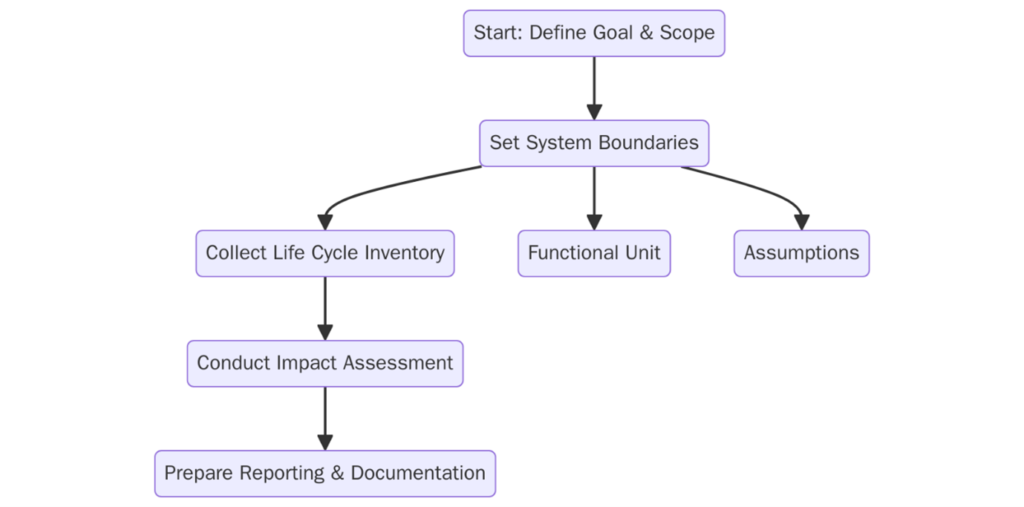
- Clearly define the functional unit and system boundaries for each product
- Conduct a life cycle inventory to quantify energy and material flows
- Convert GHG emissions into CO₂ equivalents using global warming potentials (GWP)
- Use consistent allocation rules when products share inputs or outputs
- Document assumptions, exclusions, and modeling choices
- Maintain data quality through transparency, representativeness, and completeness
- Provide full CFP reports with optional third-party review or verification
- Continuously update CFP values based on new data, methods, or design changes
Need a detailed breakdown of each requirement? Email us at support@pacificcert.com.
What are the benefits of ISO 14067?
Below are the key benefits of implementing ISO 14067 standard:
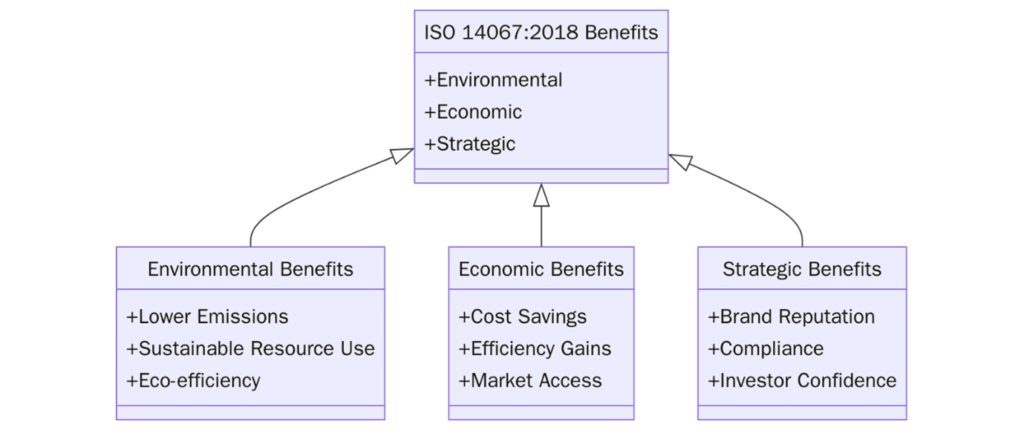
- Provides a rigorous, internationally accepted framework for assessing climate impacts.
- Establishes the baseline required to pursue credible carbon offsetting and neutrality labeling.
- Enhances transparency and trust in environmental disclosures for investors and regulators.
- Helps identify carbon hotspots and guides sustainable redesign of products or packaging.
- Improves brand reputation and access to eco-conscious consumers and B2B clients.
- Supports conformance with carbon disclosure laws, government procurement standards, and supply chain requirements.
- Supports alignment with the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDG 13: Climate Action) and national GHG reduction commitments.
- Reinforces lifecycle thinking and end-of-life considerations in carbon management.
This year, the demand for product-level carbon transparency is surging due to regulatory drivers such as the EU Green Deal, CBAM (Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism), and SEC climate disclosures and:
- Corporate ESG strategies requiring Scope 3 emission quantification
- Growing consumer demand for carbon-labelled products and sustainable packaging
- The rise of green procurement policies by governments and multinational corporations
According to the World Economic Forum (2024), over 65% of global companies are integrating ISO 14067-aligned product assessments into their sustainability strategy.
With the voluntary carbon market projected to exceed USD 50 billion by 2030, ISO 14067 is becoming a prerequisite for trustworthy offset claims and product-level emissions benchmarking.
Want to future-proof your sustainability claims? Contact support@pacificcert.com.
How Pacific Certifications Can Help?
We offer comprehensive support for ISO 14067:2018, including:
- CFP implementation and LCA-based calculation support
- Gap analysis and GHG inventory modeling
- Documentation templates and verification readiness
- Supplier engagement strategies for Scope 3 data
- Integration with ISO 14001, ISO 50001, and ESG frameworks
- Support for carbon neutrality, carbon labeling, and ecolabeling programs
From consumer goods to industrial products, we help quantify, reduce, and communicate your carbon footprint. Start your ISO 14067 journey today, email support@pacificcert.com!
FAQ on ISO 14067
Is ISO 14067 a certifiable standard?
ISO 14067 provides guidance, CFP studies can be verified by third-party certification bodies.
Can ISO 14067 be applied to services?
It’s primarily for products, but service-based systems can also be modeled using equivalent methods.
Does ISO 14067 replace ISO 14040/14044?
No. ISO 14067 is based on those standards but focuses solely on carbon footprints.
Is ISO 14067 required by law?
Not mandatory globally, but it is widely referenced in voluntary and regulatory frameworks.
How often should a CFP study be updated?
Ideally every 2–3 years or when major changes occur in the product design or supply chain.
Ready to get ISO 14067 certified?
Contact Pacific Certifications to begin your certification journey today!
Suggested Certifications –
Read more: Pacific Blogs






