Introduction to GHP- Good Hygiene Practices
Good hygiene practices (GHP) are essential for maintaining personal health, preventing the spread of diseases, and ensuring safety in homes, workplaces, food production environments, etc. These practices form the first line of defense against harmful microorganisms, contaminants, and public health risks.

Consistent hygiene routines contribute to overall well-being and form the backbone of public health policies and compliance standards around the world. In many industries, particularly food processing, hospitality, and healthcare, Good Hygiene Practices are part of regulatory frameworks and certification schemes.
Looking to align your business with hygiene certification standards such as GHP, HACCP, or ISO 22000? Contact Pacific Certifications at support@pacificcert.com for audit and certification services!
What Are Good Hygiene Practices?
Good Hygiene Practices refer to systematic behaviors and procedures implemented to maintain cleanliness, prevent infection and minimize contamination risks. These practices can be applied at the individual level (personal hygiene) or institutional level (organizational hygiene management).
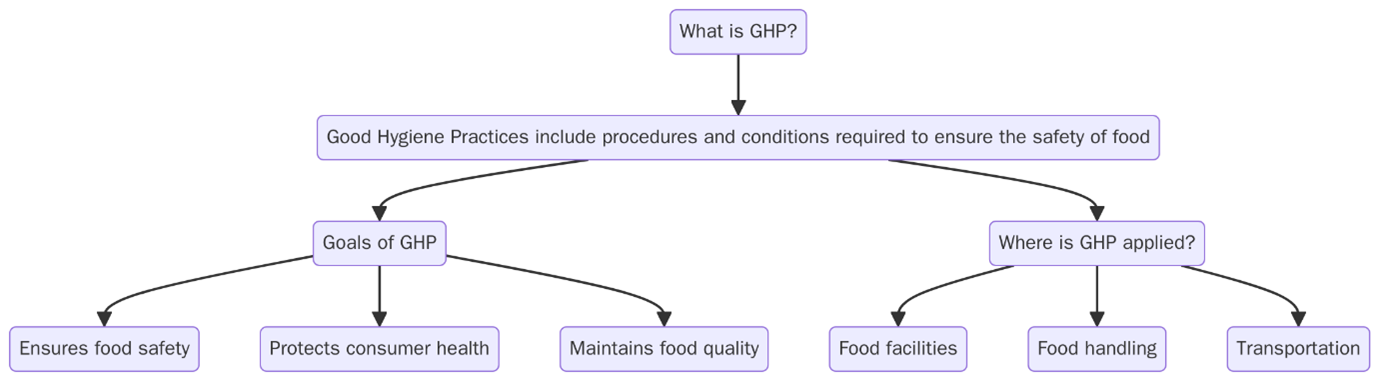
In regulated industries, GHP is a formalized set of procedures typically aligned with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP), Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP), or ISO 22000 standards, particularly in food safety, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics.
At its core, GHP includes:
- Hand hygiene (washing, drying, sanitizing)
- Clean and safe food handling
- Sanitary equipment and surfaces
- Pest control measures
- Waste disposal protocols
- Personal protective equipment (PPE) use
- Regular cleaning and disinfection procedures
Safe water supply and storage
Importance of Good Hygiene Practices (GHP)
GHP is a critical factor in preventing disease transmission and building public trust. In industries where hygiene lapses can result in severe consequences, such as foodborne illness, cross-contamination, or hospital-acquired infections, these practices are indispensable.
GHP is especially vital in:
- Healthcare: Preventing infections and supporting patient recovery
- Food and Beverage: Maintaining product safety from farm to fork
- Hospitality and Retail: Ensuring customer confidence and comfort
- Education and Childcare: Creating safe environments for vulnerable populations
- Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Manufacturing: Avoiding contamination in sensitive products
Want to improve compliance with local or international hygiene regulations? Contact support@pacificcert.com for expert audit services across multiple standards!
What are the requirements of Effective Hygiene Practices (GHP)?
Effective GHP systems require a structured and proactive approach that includes:

- Establishing written hygiene policies and clearly defined roles and responsibilities.
- Routine training programs for staff on hand hygiene, sanitation techniques, and cross-contamination prevention.
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for cleaning, sanitation, personal hygiene, and equipment handling.
- Use of verified cleaning agents and disinfection protocols suitable for the environment or industry.
- Monitoring and verification systems, including visual checks, ATP swabbing, and microbiological testing where required.
- Documentation and record-keeping for hygiene logs, training sessions, and corrective actions.
In formal settings like HACCP or ISO 22000, Good Hygiene Practices are typically pre-requisite programs (PRPs) that must be firmly in place before hazard analysis begins,
What are the benefits of Good Hygiene Practices (GHP)?
In a post-pandemic world, hygiene has become a business imperative, not just a personal responsibility. People are more conscious about how businesses clean, disinfect, and maintain hygienic environments. Below are the benefits of GHP implementation:
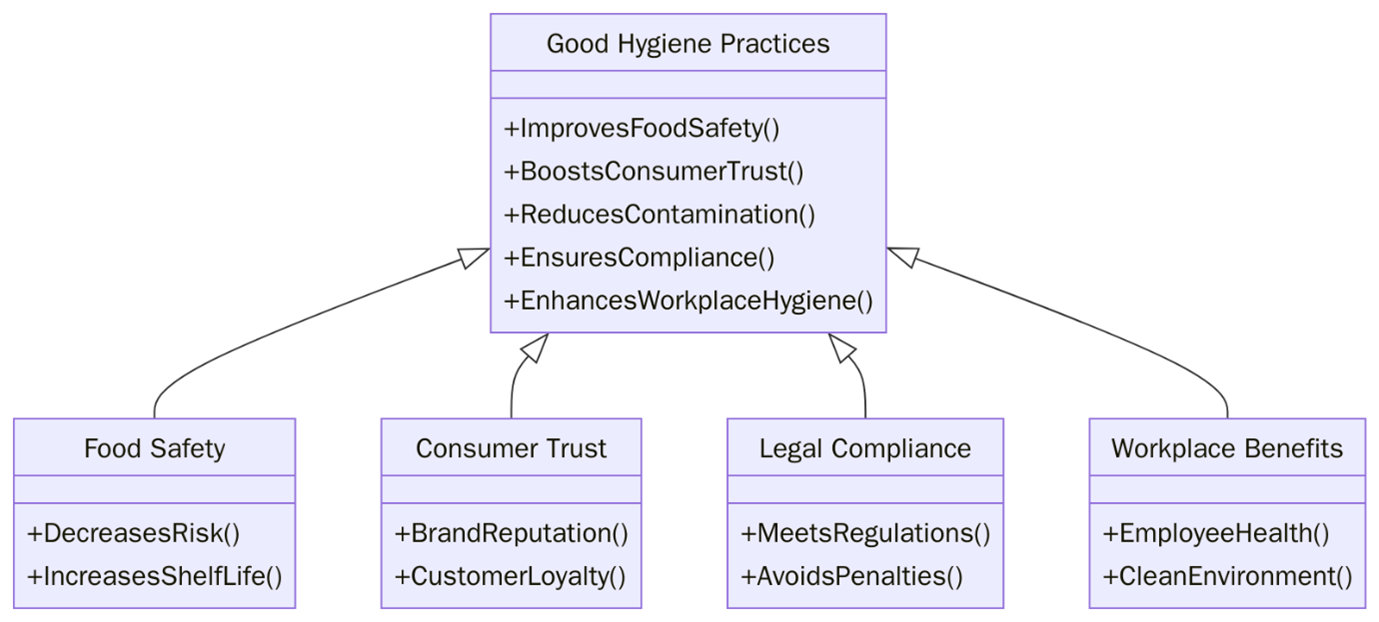
- Minimizes bacteria, viruses, and cross-contamination across people, surfaces, and equipment.
- Meets local health regulations, international food safety requirements, and occupational safety standards.
- Demonstrates a commitment to health, safety, and professionalism.
- Creates a healthier work environment and reduces employee absenteeism.
- Serves as a frontline defense during outbreaks, pandemics, and public health crises.
- Supports requirements for HACCP, ISO 22000, FSSC 22000, GMP, and local food safety laws.
Organizations that fail to meet hygiene standards risk losing customers, facing fines, or dealing with legal consequences.
Globally, there is rising momentum toward:
- Mandatory hygiene training for food handlers and healthcare workers
- Sustainability-linked hygiene practices, such as eco-friendly sanitization
- Digital hygiene tracking systems using IoT and cloud dashboards
- Integration of GHP with ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance) strategies
- Global alignment through Codex Alimentarius, WHO, and ISO guidelines
Countries across Europe, the U.S., Asia, and the Middle East are enforcing stricter hygiene and sanitation laws in food safety, healthcare, hospitality, and cosmetics manufacturing. Having a structured hygiene management system has become a market differentiator and risk mitigator.
Want to make your hygiene practices audit-ready and globally aligned? Contact Pacific Certifications at support@pacificcert.com.
Implementation Timeline
Stage | Estimated Duration |
Staff hygiene awareness training | 1–2 weeks |
Hygiene SOP development | 2–3 weeks |
Implementation of hygiene system | 3–5 weeks |
Internal verification & monitoring | 1–2 weeks |
Optional third-party audit | 2–3 weeks |
Need a phased hygiene implementation roadmap for your industry? Email support@pacificcert.com for a customized plan.
Cost of Implementing Good Hygiene Practices (GHP)
The cost of implementing GHP depends on:
- Industry (food, healthcare, pharma, hospitality, etc.)
- Number of employees and facilities
- Regulatory requirements and third-party audits
- Cleaning, PPE, and equipment investments
For businesses seeking certification (GMP, HACCP), cost considerations also include:
- Consulting or internal resource time
- Training programs
- Documentation and audit fees
How Pacific Certifications Can Help?
Pacific Certifications is an accredited certification body providing audit and certification services for hygiene-related standards such as:
- GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices)
- GHP (Good Hygiene Practices)
- HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points)
- ISO 22000 (Food Safety Management System)
- ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety)
- ISO 9001 (Quality Management with hygiene SOP integration)
We help organizations across industries implement and certify hygiene systems that meet both local regulatory and international compliance standards.
We offer:
- Hygiene audits and documentation reviews
- Training and awareness programs
- Integration with food safety, OHS, or QMS frameworks
- Ongoing surveillance audits and compliance support
Whether you’re feeding customers, treating patients, or producing critical goods, Good Hygiene Practices are the cornerstone of safety, trust, and operational excellence.
Contact Pacific Certifications at support@pacificcert.com to audit, document, or certify your hygiene practices today!
FAQs – GHP
Are Good Hygiene Practices mandatory?
In many regulated industries like food production, healthcare, and cosmetics, GHP is a legal requirement and forms the foundation of compliance with GMP or HACCP.
Can I certify my business for hygiene practices?
Yes. Certifications such as GMP, HACCP, and ISO 22000 include hygiene requirements as a central element. Pacific Certifications can audit and certify your compliance.
How often should hygiene training be conducted?
Regularly—most businesses conduct it at onboarding and annually, with additional refreshers during outbreaks or seasonal risk periods.
What’s the difference between personal hygiene and organizational hygiene systems?
Personal hygiene refers to individual habits like handwashing, while organizational hygiene involves structured systems for sanitation, cleaning schedules, equipment safety, and compliance.
Does GHP apply to office environments?
Yes. While more critical in food or healthcare, maintaining hygiene in any workspace contributes to employee health, morale, and business continuity.
Ready to get GHP certified?
Contact Pacific Certifications to begin your certification journey today!
Suggested Certifications –
Read more: Pacific Blogs








