What is FDA Registration?
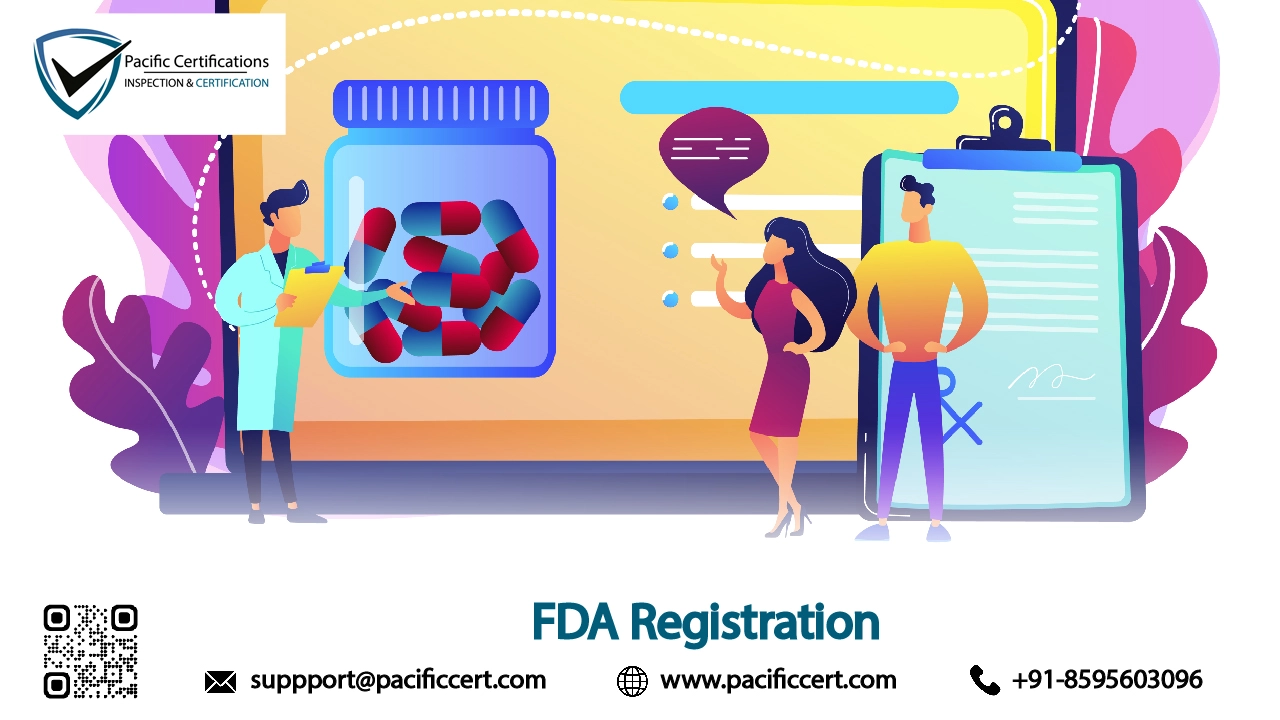
FDA Registration is the process of registering certain types of businesses with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to ensure compliance with federal regulations. This process is required for companies that manufacture, distribute or import food, drugs, medical devices, cosmetics, dietary supplements and certain other products that are regulated by the FDA.
FDA registration ensures that companies comply with safety and quality standards, protecting public health and ensuring that products meet the FDA’s regulatory requirements. Registration allows the FDA to keep track of businesses that produce products covered under its jurisdiction and monitor compliance with its rules.
For more information, contact us at support@pacificcert.com.
Purpose of FDA Registration
The purpose of FDA registration is to ensure that manufacturers, importers, and distributors are complying with FDA standards, which are designed to protect public health. Registration allows the FDA to monitor companies, enforce laws, and inspect businesses to verify that they are adhering to safety and quality guidelines.
For instance, for pharmaceuticals, It ensures that drugs are produced and tested according to the necessary standards. For food products, it guarantees that food manufacturers comply with proper sanitation and safety practices. The goal is to provide consumers with safe, effective and high-quality products.
Scope and Applicability
FDA registration is applicable to a wide range of industries. Manufacturers, processors and distributors must register with the FDA to ensure food safety and compliance with labelling standards. Companies that manufacture drugs or biologics must register with the FDA and follow stringent regulatory requirements for safety and efficacy. Manufacturers of medical devices, including diagnostic and therapeutic devices, must register with the FDA to ensure compliance with safety and performance standards.
While not mandatory, FDA registration can be beneficial for cosmetic manufacturers to show compliance with safety and labelling guidelines. Companies that produce and distribute dietary supplements must follow FDA rules on labelling, ingredients, and good manufacturing practices (GMP).
It ensures that products within these sectors meet the required safety standards, protecting both consumers and businesses from regulatory violations.
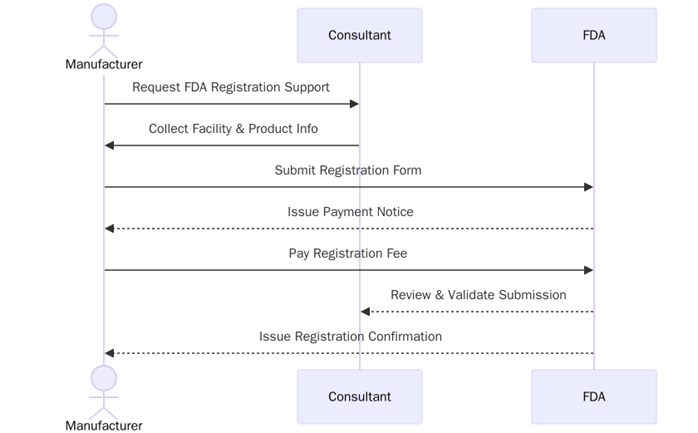
Key Definitions
- FDA Registration: The process of registering a business with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to ensure compliance with federal regulations for specific products.
- FDA-Approved: Indicates that a product has undergone FDA review and has been found to meet the required safety and efficacy standards.
- Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP): Regulations enforced by the FDA that require manufacturers to follow guidelines to ensure the consistent production of safe and effective products.
- FDA-Listed: Indicates that a facility or product is listed with the FDA, which includes basic information about the manufacturer and product.
What are the requirements for FDA Registration?
To comply with FDA regulations and achieve registration, businesses must meet certain specific requirements. These requirements are designed to ensure that organizations are following proper processes for producing safe, high-quality products. Here are the key requirements for FDA registration:
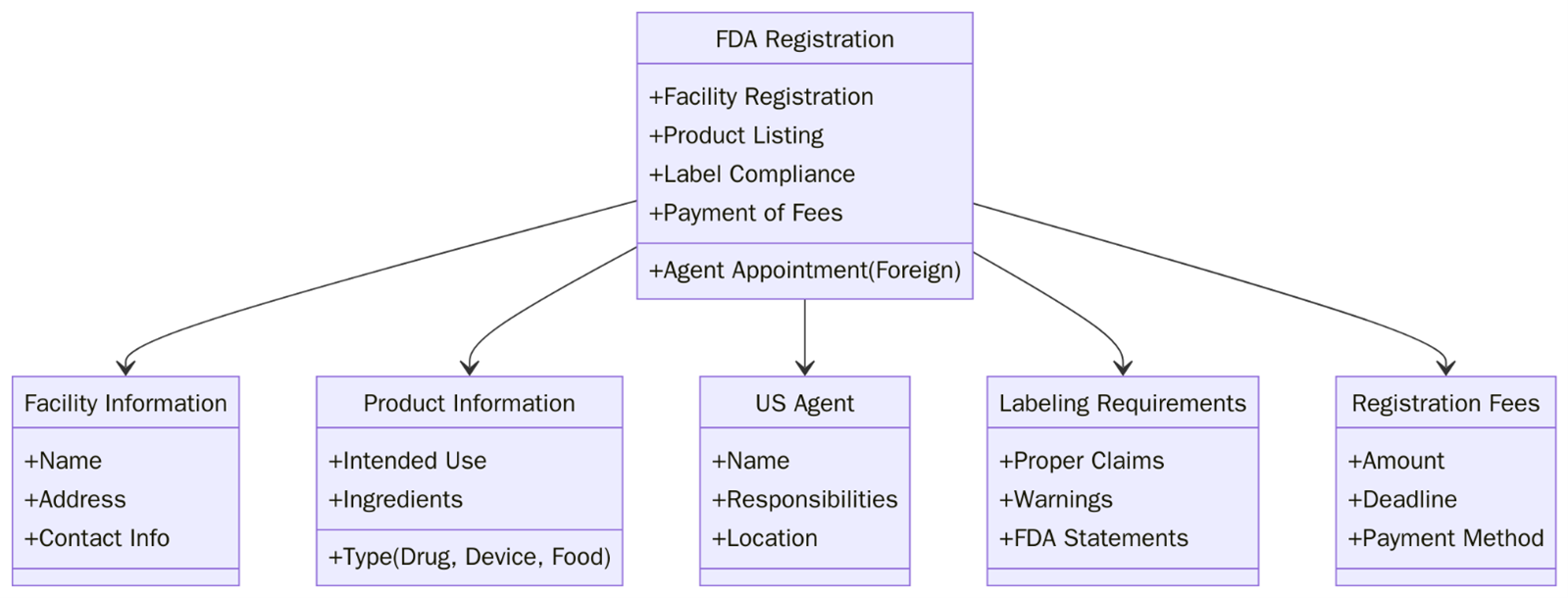
- The business must complete and submit the necessary application forms based on the product category (e.g., food, drug, medical device).
- Companies must establish a quality management system to ensure products are manufactured according to safety and regulatory standards.
- Products must be labelled in accordance with FDA requirements, including proper ingredient listing, claims, and usage instructions.
- Businesses may be subject to periodic FDA inspections to ensure they are complying with current good manufacturing practices (GMP).
- Companies must maintain and provide records of manufacturing, testing, and distribution processes when required by the FDA.
- FDA registration must be renewed annually to ensure continued compliance with the standards.
For more information, contact us at support@pacificcert.com.
FDA Registration: Audit Checklist
The FDA audit checklist includes the following elements to ensure that businesses comply with FDA requirements:
- Have cloud roles and responsibilities between the provider and customer been clearly defined and documented?
- Is virtual machine configuration securely managed and isolated in multi-tenant cloud environments?
- Are procedures in place for the secure return, deletion, or migration of customer assets after contract termination?
- Is administrative access by cloud service customers properly controlled and monitored by the provider?
- Are cloud-specific security requirements addressed in the service agreement (data location, jurisdiction etc.)?
- Is customer activity within the cloud environment logged, monitored, and reviewed for anomalies?
- Are customers informed of any changes that may affect cloud service security controls or SLAs?
- Are measures implemented to segregate and protect customer data in shared infrastructure setups?
- Is there a documented process for handling cloud-specific incidents and notifying affected parties?
What are the benefits of FDA Registration?
FDA Registration offers several key benefits for businesses, including:
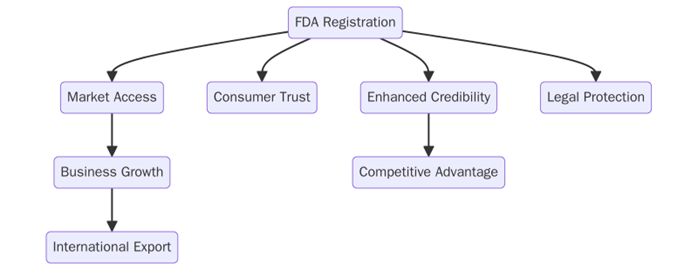
- Ensures that your products meet the necessary legal standards for safety and efficacy, reducing the risk of fines or legal action.
- FDA registration is often required for selling products in the U.S. market. It also improves your company’s credibility and access to international markets where FDA registration is recognized.
- It assures customers that your products are safe and meet the FDA’s rigorous standards, building trust in your brand.
- By complying with FDA guidelines, businesses reduce the risk of product recalls, safety incidents, or regulatory violations.
- Registration ensures your business is subject to FDA oversight, which helps maintain consistent product quality and safety.
With increasing global focus on consumer safety and regulatory compliance, the importance of FDA registration has gained significant attention. More businesses, especially those in the food, medical device and pharmaceutical sectors, are embracing FDA standards to improve product quality and meet international regulations. The FDA is also enhancing its monitoring capabilities, with improved digital systems for product tracking, allowing for faster responses to safety concerns.
The demand for FDA is expected to increase globally as more countries adopt stricter product safety regulations. In the recent years, businesses around the world will need FDA registration to access the U.S. market, especially in high-demand sectors such as medical devices and biotechnology. Regulatory bodies in other regions are likely to harmonize their standards with the FDA’s, making this registration even more critical for global trade. Additionally, the growing emphasis on sustainability and transparency in supply chains will drive further adoption of FDA-certified practices.
Certification Process
The FDA registration process involves several important steps:
- Pre-Registration Assessment: Conducting an internal review of processes to ensure compliance with FDA standards.
- Application Submission: Submitting the required application forms, product details, and facility information to the FDA.
- Inspection: Undergoing an FDA inspection of your manufacturing facility to verify compliance with GMP and other relevant regulations.
- Approval: The FDA reviews your application, inspection results, and any other necessary documentation before granting approval.
- Certification Issuance: Once compliance is confirmed, the FDA issues the necessary registration and approval for your products.
- Ongoing Compliance: Regular FDA inspections and documentation submissions are required to maintain registration status.
Timeline
The typical timeline for FDA registration depends on various factors, including the type of product and the complexity of the organization. The registration process generally spans several weeks.
The pre-assessment and preparation phase generally takes 1-2 months, during which the organization reviews its current processes and makes necessary adjustments. The Stage 1 audit lasts about 1 month, focusing on documentation and readiness. The Stage 2 audit, which involves a overreaching review of processes and software development practices, takes 1-2 months. Certification issuance happens within 3-6 months, depending on the audit findings and the organization’s readiness for certification.
What is the Cost of FDA Registration?
The cost varies depending on the type of business and product.
FDA registration fees are paid annually for the FDA to maintain the registry. If an on-site inspection is required, additional fees may apply for the review and evaluation of your facility known as inspection fee. Training costs is the fees for educating staff on FDA compliance and GMP practices. Ongoing compliance costs for maintaining FDA compliance through regular audits and recertification processes
How Pacific Certifications Can Help?
At Pacific Certifications, we provide overreaching auditing and certification services for FDA registration. Our team will guide you through the entire registration process, ensuring that your products meet the FDA’s rigorous standards. Our services include:
- Stage 1 and Stage 2 audits to evaluate your manufacturing processes and quality management systems.
- Objective conformity assessments based on FDA regulations.
- Registration issuance upon successful completion of the process.
- Ongoing surveillance audits to ensure continued FDA compliance.
- Support for multi-site or global operations.
For audits and certification, contact support@pacificcert.com.
ISO 9001 and FDA Training and Courses
Various training courses are available to help organizations comply with FDA regulations, including:
- Lead Auditor Training – Equips professionals to conduct external third-party audits.
- Lead Implementer Training – For those responsible for planning and executing ISO 9001 and FDA.
- Internal Auditor Training – Preparing internal auditors for certification audits
Pacific Certifications provides accredited training programs. If your organization is looking for FDA registration training, our team is equipped to help you. Contact us at support@pacificcert.com.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How long does it take to get FDA registration?
The FDA registration process takes 1-6 months, depending on your product type, complexity, and readiness.
Is FDA registration mandatory for all businesses in the U.S.?
FDA registration is required for businesses that produce, distribute, or import regulated products such as food, drugs, and medical devices.
What are the main benefits of FDA registration?
Registration ensures compliance with U.S. regulations, improves product credibility, opens access to global markets, and increases consumer trust.
Can I apply for FDA registration without meeting GMP standards?
No, businesses must comply with GMP standards to be eligible for FDA registration.
How often do I need to renew FDA registration?
FDA registration must be renewed annually to maintain compliance.
Ready to get ISO certified?
Contact Pacific Certifications to begin your certification journey today!
Suggested Certifications –
Read more: Pacific Blogs






