What is ISO 13485:2016?

ISO 13485 certification is the global standard for Medical Devices Quality Management Systems (MDQMS), also known as ISO 13485:2016. It defines the requirements for organizations involved in the manufacturing, design, and distribution of medical devices to consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements. ISO 13485 is customized to the medical device industry, with a strong focus on risk management, traceability and compliance with global health regulations.
ISO 13485 certification has become more important due to increasing regulatory enforcement, the implementation of EU MDR 2017/745, IVDR and stricter post-market surveillance expectations worldwide. Moreover, authorities such as Health Canada, FDA, TGA (Australia), and Japan’s PMDA often require ISO 13485 certification for product approvals.
Whether you’re manufacturing Class I surgical tools, Class III implants or in vitro diagnostics, ISO 13485 offers a customized framework, it also supports organizations participating in Medical Device Single Audit Program.
If you are looking for ISO 13485 certification, contact us at support@pacificcert.com!
Scope and Applicability of ISO 13485:2016
ISO 13485:2016 is designed for any organization involved in the design, production, installation or servicing of medical devices. It applies across the entire medical device supply chain including those offering technical documentation or support services related to medical devices.
The standard places strong focus on risk management and keeping the quality management system (QMS) effective throughout the product lifecycle. It’s flexible and can be used by organizations of any size, whether they are directly manufacturing devices or supporting the process.
ISO 9001 vs ISO 13485
Both ISO 13485:2016 and ISO 9001:2015 serve different purposes. ISO 9001 is a generic standard and focuses on customer satisfaction and continuous improvement. ISO 13485 is specifically designed for the medical device industry, with a strong emphasis on compliance, risk management, and patient safety. Below are the key differences:
Feature | ISO 13485:2016 | ISO 9001:2015 |
Industry Focus | Medical devices | General quality management (all sectors) |
Risk Management | Embedded across lifecycle | Primarily at the strategic level |
Regulatory Compliance | Mandatory and detailed | Implied or optional |
Continuous Improvement | Encouraged, but less emphasized | Strong emphasis (PDCA) |
Documentation Requirements | Prescriptive (including records & SOPs) | Flexible |
Post-Market Surveillance | Required (vigilance, complaints) | Not mandatory |
ISO 13485 Clauses-wise Structure
ISO 13485:2016 provides a clear framework for compliance and performance assurance. The table below summarizes clauses:
Clause | Title | Description |
1 | Scope | Defines the scope and applicability of the standard for organizations involved in the medical device lifecycle and related services. |
2 | Normative References | Lists referenced standards that are essential for the application of ISO 13485:2016. |
3 | Terms and Definitions | Provides definitions of key terms used throughout the standard to ensure consistent interpretation and implementation. |
4 | Quality Management System | Establishes general QMS requirements including documentation, quality manual, control of documents, and records management. |
5 | Management Responsibility | Outlines top management’s responsibilities for quality policy, planning, customer focus, internal communication, and management review. |
6 | Resource Management | Covers resource allocation including human resources, training, infrastructure, and work environment needed to ensure product conformity. |
7 | Product Realization | Details requirements for planning, design and development, purchasing, production, and service provision, with a strong focus on risk management. |
8 | Measurement, Analysis, and Improvement | Defines how to monitor, measure, analyze, and improve the QMS and product quality, including CAPA, internal audits, complaints, and data analysis. |
ISO 13485 Requirements Checklist
ISO 13485 requirements checklist is given below:
- QMS and documentation control (Quality Manual, procedures, records, medical device file)
- Management responsibility (policy, objectives, planning, management review)
- Resource management (competence, infrastructure, work environment/contamination control)
- Risk management throughout the lifecycle
- Design and development controls (planning, inputs/outputs, reviews, V&V, transfer, changes)
- Purchasing & supplier control
- Production and service provision (process validation, sterilization/cleanliness, software validation, installation/servicing, preservation)
- Identification & traceability; status of product
- Monitoring & measuring resources (calibration/maintenance)
- Control of nonconforming product
- Corrective and preventive action (CAPA)
- Feedback, complaints, and reporting as required
- Internal audits; measurement, analysis, and improvement
How to Implement ISO 13485:2016 Certification in Your Organization?
Implementing ISO 13485 certification involves establishing a structured Quality Management System to ensure your medical devices consistently meet safety and regulatory requirements. Below are the steps to follow:
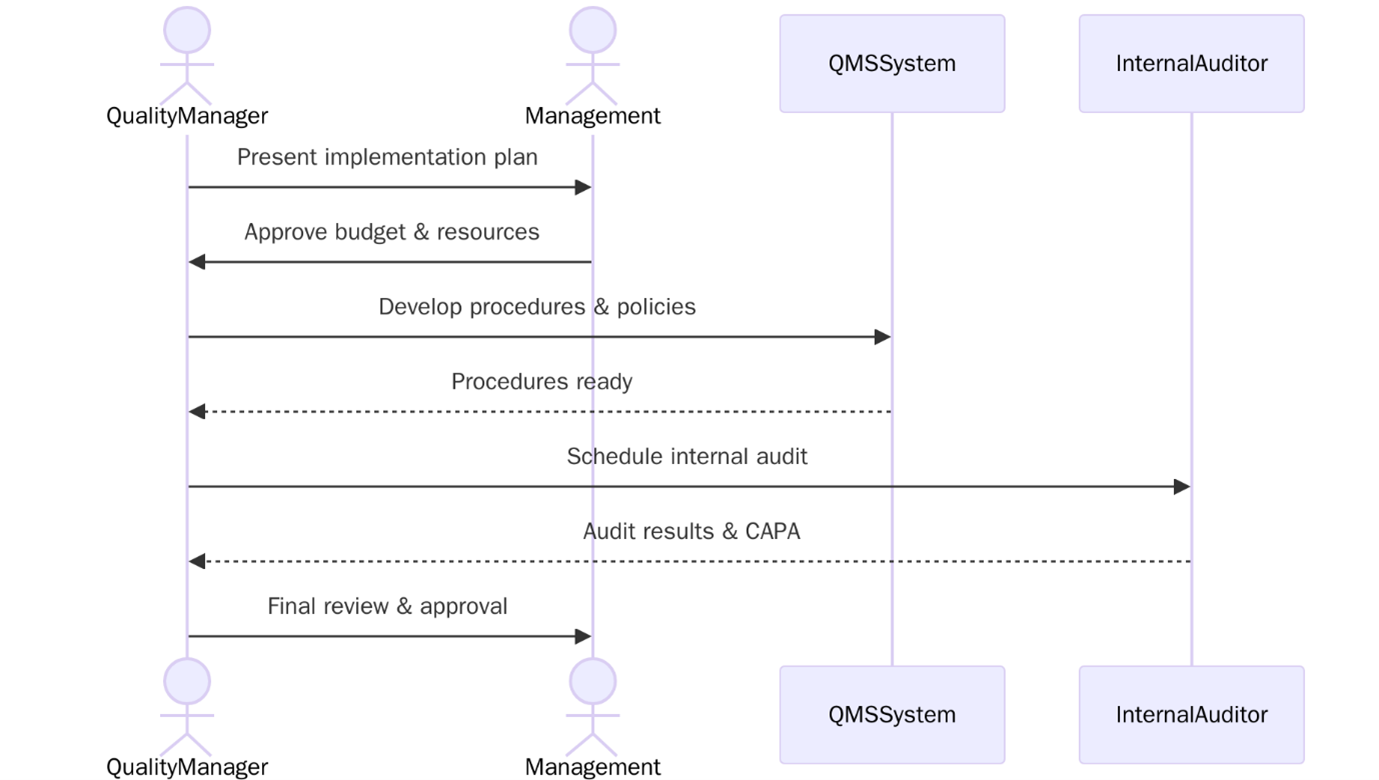
- Review ISO 13485:2016 to understand its clauses, terminology, and regulatory focus.
- Perform a gap analysis to identify where your current system falls short.
- Gain commitment from top management to support resources and quality initiatives.
- Define the QMS scope, including sites, products, and applicable regulatory markets.
- Develop documentation such as Quality Manual, SOPs, risk plans, and technical files.
- Implement key processes including design, production, validation, CAPA, and audits.
- Train employees on their roles, procedures, and compliance responsibilities.
- Conduct internal audits to check conformity and identify improvement needs.
- Hold management reviews to assess QMS performance.
- You are ready for the certification audit
ISO 13485:2016 Audit Checklist
The ISO 13485 audit checklist covers key areas such as design & document control. The checklist below helps identify gaps:
- Is there a documented Quality Management System (QMS) in place that defines all key processes?
- Has top management demonstrated commitment through a quality policy and measurable objectives?
- Are document control and record retention procedures established and effectively implemented?
- Are roles, responsibilities, and authorities—including a designated management representative, clearly defined?
- Are risk management activities applied throughout the design and product realization stages?
- Are supplier evaluation and purchasing controls in place to ensure product conformity?
- Are processes validated where output cannot be verified by subsequent inspection or testing?
- Is there an effective system for handling complaints, adverse events, and regulatory reporting?
- Are internal audits conducted regularly, with documented findings and follow-up actions?
- Are nonconformities and corrective actions managed through a documented CAPA process?
ISO 13485:2016 Certification Process
Understand the ISO 13485:2016 standard and align internal goals with its core requirements, follow the steps below:
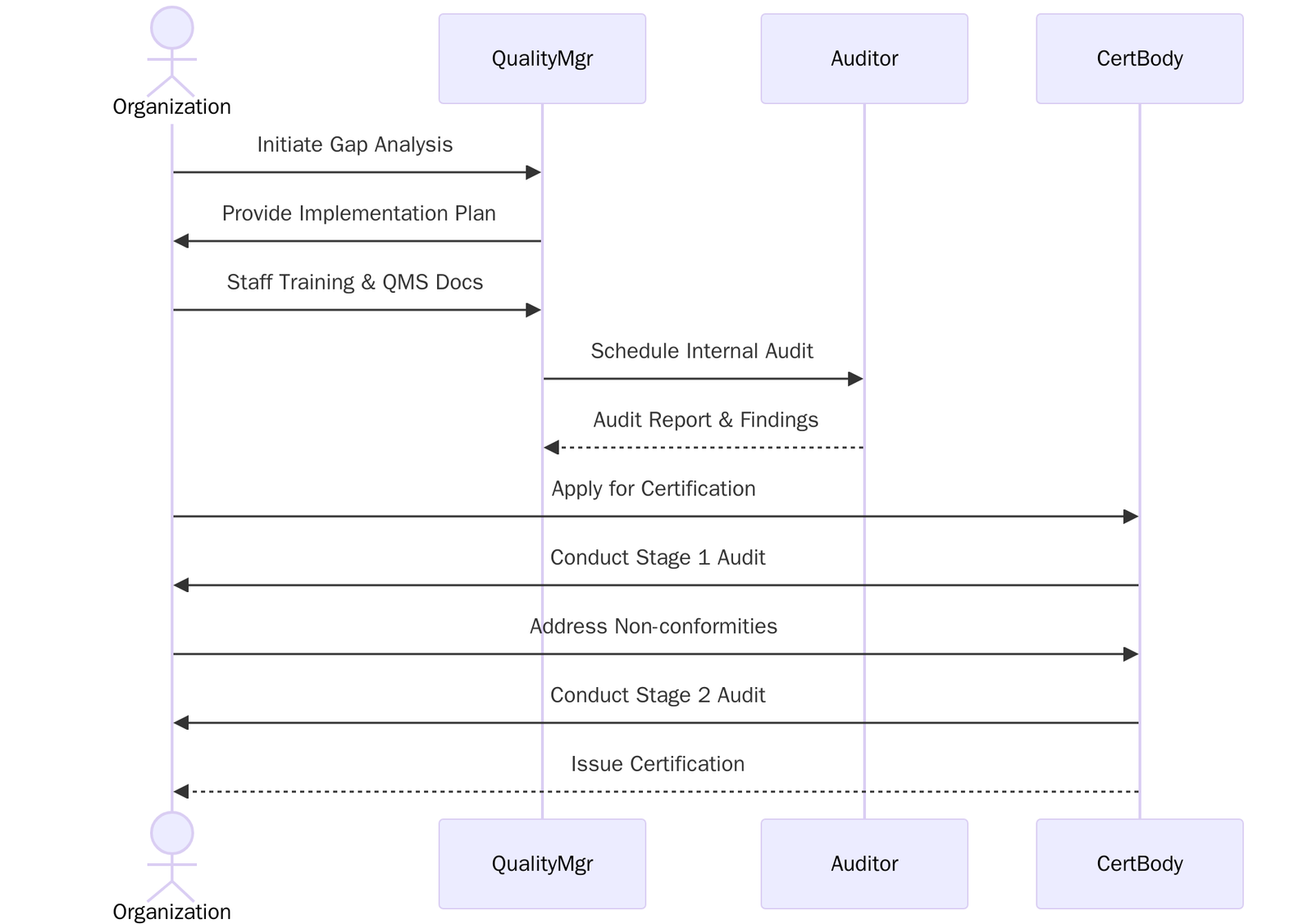
- Fill out and submit the application form to the certification body with scope and company details.
- Review and accept the quotation and certification terms.
- Audit Planning– Certification body schedules Stage 1 and Stage 2 audits.
- Stage 1 Audit– Review of documentation, QMS readiness, and regulatory alignment.
- Stage 2 Audit– On-site/online assessment of implementation and compliance.
- Address any nonconformities identified during audits.
- Final review and approval by the certification body.
- ISO 13485:2016 certificate issued, valid for 3 years.
- Surveillance audits to maintain certification.
What are the ISO 13485 benefits?
ISO 13485:2016 certification offers strategic advantages for organizations involved in the medical device sector. Below are the ISO 13485 key benefits:
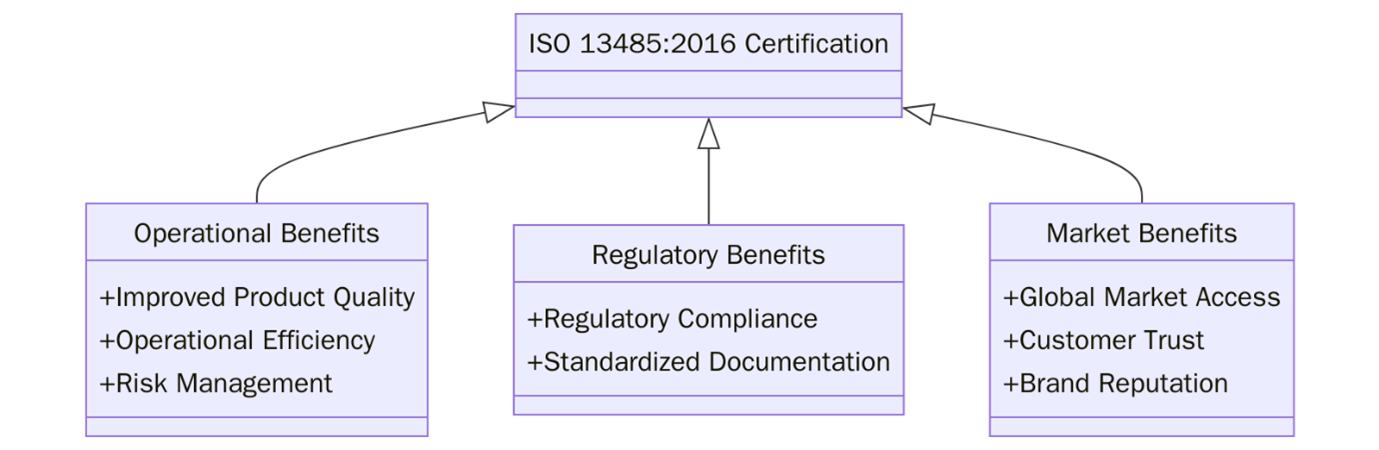
- Regulatory compliance is streamlined by aligning with international requirements.
- Enhanced product safety ensures that medical devices are consistently safe and meet user needs.
- Global market access is enabled as ISO 13485 is recognized across major regulatory jurisdictions worldwide.
- Customer confidence increases due to validated quality practices.
- Improved risk management throughout the device lifecycle helps prevent failures and post-market issues.
- Operational efficiency grows through standardized procedures and minimized waste.
- Stronger supplier relationships are built via controlled purchasing and clearly defined quality expectations.
- Facilitated audits and inspections with documented processes that meet notified body and regulatory expectations.
- Brand credibility and reputation are elevated by demonstrating a commitment to quality and patient safety.
- Support for innovation and growth through a structured framework that enables safe design and development.
Recent Trends
A recent global survey by Emergo by UL found that over 75% of medical device companies see ISO 13485 certification as essential for getting regulatory approval in the EU, Canada, Australia, and Japan.
The COVID-19 pandemic and stricter post-pandemic regulations have pushed companies to adopt stronger quality controls and risk management, making ISO 13485 a must-have for compliance and market access.
If you are looking for ISO 13485 certification audit, contact us at support@pacificcert.com!
What is the timeline ISO 13485:2016 Certification?
The timeline for ISO 13485 certification varies based on the size, complexity, and readiness of the organization. Below is a general timeline:
Phase | Timeline (Approx.) | Activities Included |
Preparation & Gap Analysis | Weeks 1–3 | Understand ISO 13485:2016, assess existing systems, and identify gaps |
Planning & Documentation | Weeks 4–8 | Develop QMS documents (Quality Manual, SOPs, risk files, etc.) |
QMS Implementation | Weeks 9–16 | Implement documented processes, train staff, and record evidence of compliance |
Internal Audit & Review | Weeks 17–20 | Conduct internal audits, perform corrective actions, and hold management review meetings |
Stage 1 Audit (Readiness) | Weeks 21–22 | Certification body reviews documentation and system preparedness |
Stage 2 Audit (Certification) | Weeks 25–28 | Full audit of implementation, effectiveness, and compliance with ISO 13485:2016 |
Corrective Actions (if needed) | Weeks 29–32 | Address any nonconformities identified during the audit |
Certification Issued | Weeks 33–36 | Certification body issues ISO 13485:2016 certificate upon successful audit closure |
To know your certification timeline or roadmap, contact us at support@pacificcert.com.
What is ISO 13485 certification cost?
ISO 13485 certification cost is not fixed and varies depending on several key factors, including the size of the organization, number of employees, number of sites, and the complexity of manufacturing processes.
To receive a customized quote for ISO 13485 certification cost, contact Pacific Certifications at support@pacificcert.com.
Who needs ISO 13485:2016 certification?
The importance of ISO 13485 has grown significantly with the rise of global healthcare regulations like FDA 21 CFR Part 820 (QSR) and EU MDR. In fact, ISO 13485 is often treated as a prerequisite for market access. Without this certification, manufacturers face severe obstacles when participating in tenders.
ISO 13485 is essential for medical device manufacturers, contract manufacturers, original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), sterilization and packaging providers, distributors, and import/export agencies that deal with Class I, II, or III medical devices, including surgical instruments, implants, IVDs, and diagnostic equipment.
How Pacific Certifications can help?
Pacific Certifications is an accredited certification body; we offer globally recognized ISO 13485:2016 certification services for organizations operating in the medical device industry. We conduct impartial audits that help our clients to validate compliance. We verify your system’s effectiveness and ensure compliance maintaining our accreditation integrity.
Our Services Include:
- Stage 1 Audit: We assess your quality manual, procedures, and documented controls
- Stage 2 Audit: We verify practical implementation of processes
- Surveillance Audits
- Recertification Audits
- Combined audits, ISO 13485:2016 with ISO 9001, ISO 14971, or ISO 14001
We cater to organizations across the full medical device lifecycle, ensuring your QMS aligns with requirements such as EU MDR, US FDA, MDSAP etc.
To request a quote or schedule an ISO 13485 audit, reach out to our certification team at support@pacificcert.com.
FAQs for ISO 13485:2016
What is ISO 13485:2016 certification?
It is the international standard for Quality Management Systems (QMS) specific to the medical device industry, focusing on regulatory compliance and risk management.
Who needs ISO 13485 certification?
Manufacturers, suppliers, OEMs, sterilization providers, distributors, and software developers involved in medical devices.
What are the benefits of ISO 13485:2016 certification?
It improves product safety, supports regulatory compliance, builds trust, and enhances access to global markets.
Is ISO 13485 mandatory?
It is not legally mandatory everywhere, but it is a prerequisite for regulatory approval in many countries like the EU, Canada, Australia, and others.
What are the main requirements of ISO 13485:2016?
Key requirements include:
Continual improvement and internal audits
Implementation of a documented QMS
Risk management and design control processes
Validation of processes, including sterilization and software
Product traceability and complaint handling
What is the difference between ISO 13485 and ISO 9001?
While both are quality standards, ISO 13485 is specifically for medical devices, with stricter focus on risk management, regulatory compliance, and traceability.
How long does it take to become ISO 13485 certified?
Typically, 8 to 16 weeks, depending on your organization’s size, preparedness, and complexity.
How can I start the certification process?
Begin with a gap analysis, implement the required QMS, and contact an accredited certification body.
How to get ISO 13485 certification?
Do a gap analysis, implement and operate an ISO 13485 QMS (include risk and regulatory controls), run internal audits and a management review, then pass Stage 1 and Stage 2 audits with an accredited certification body. Close any findings. Certification is on a three-year cycle with annual surveillance.
How to become ISO 13485 certified?
Put your QMS into practice, apply to an accredited certification body, pass the two-stage audit, fix any nonconformities, receive the certificate, then maintain it via yearly surveillance and recertify every three years.
Contact Us
If you need support with ISO 13485:2016 certification, contact us at support@pacificcert.com.
Read More at: Blogs by Pacific Certifications






