What is ISO 45001:2018?

ISO 45001:2018 is the international standard for Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems (OHSMS), it provides a structured framework for organizations to proactively reduce workplace risks and create safer working conditions. ISO 45001 takes a preventive and risk-based approach, it encourages organizations to identify hazards before they result in incidents and to engage all levels of the workforce, from top management to front-line workers, in creating a culture of safety.
Scope & Applicability
ISO 45001:2018 applies to organizations of all types and sizes, across all industries from manufacturing to professional services. The standard helps you to establish and maintain safe working environments and fulfil legal obligations. Its ultimate goal is to reduce work-related injuries/illnesses and fatalities, while promoting well-being at every level of the business.

The standard is designed to be compatible with other ISO management system standards, such as ISO 9001 (Quality) and ISO 14001 (Environmental), making integration into existing systems smoother and more efficient.
Need ISO 45001:2018 certification for your organization? Contact our certification team at support@pacificcert.com to get started!
What is PDCA Cycle in ISO 45001:2018?
ISO 45001 adopts the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle to systematically manage health and safety risks:
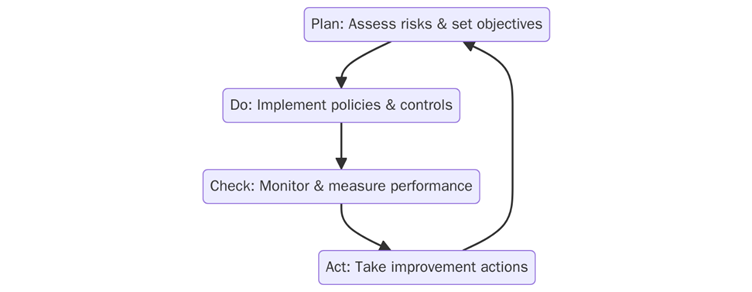
Plan: Identify hazards, assess risks, determine legal requirements, and set OHS objectives.
Do: Implement control measures, training, and resources to manage risks.
Check: Monitor incidents, conduct audits, and review OHS performance data.
Act: Take corrective actions and implement improvements to enhance OHS outcomes.
Key Changes in ISO 45001:2018 Vs OHSAS 18001
- Transition from OHSAS 18001 to an ISO framework with a risk-based approach.
- Emphasis on leadership and worker consultation.
- Requirement to understand the context of the organization and its interested parties.
- Integration with business processes for strategic alignment.
- Focus on both risk and opportunities, not just hazard control.
If you need support with ISO 45001:2018 certification process, please connect with us at support@pacificcert.com!
What are the 7 Principles of ISO 45001:2018?
Continuous Improvement – Enhancing processes based on performance data.
Worker Participation – Active involvement of workers in health and safety decisions.
Leadership Commitment – Top management accountability for a safe workplace.
Hazard Identification and Risk Control – Ongoing assessment and elimination of risks.
Legal Compliance – Meeting legal and other OHS requirements.
Operational Integration – Embedding OHS into business functions.
Performance Measurement – Tracking incidents, audits, and nonconformities.
Clause-wise Structure of ISO 45001:2018
ISO 45001 follows the High-Level Structure (HLS), making it easier to integrate with other systems like ISO 9001 and ISO 14001. Below is a clause-by-clause overview of the standard:
Clause | Title | Description |
4 | Context of the Organization | Understand internal and external OHS influences and interested parties. |
5 | Leadership and Worker Participation | Establish leadership roles and active worker involvement. |
6 | Planning | Identify risks/opportunities, legal requirements, and OHS objectives. |
7 | Support | Provide resources, competence, and communication to maintain the OHSMS. |
8 | Operation | Manage operational risks and emergency preparedness. |
9 | Performance Evaluation | Monitor, measure, and analyze OHS performance. |
10 | Improvement | Continually improve the effectiveness of the OHSMS. |
What are ISO 45001 Requirements?
Implementing ISO 45001, is a proven tool to increase workplace safety and regulatory compliance:
- Learn ISO 45001 clauses, principles, and structure.
- Ensure top management leads and supports the process.
- Compare current practices with ISO 45001 requirements.
- List all applicable OH&S laws and compliance obligations.
- Set system boundaries and draft your safety policy.
- Assess and control workplace health and safety risks.
- Align goals with your policy and risk profile.
- Assign tasks, set timelines, and allocate resources.
- Involve staff in hazard identification and safety improvements.
- Educate employees on roles, responsibilities, and safety practices.
- Maintain procedures, risk registers, and compliance records.
- Use internal audits and KPIs to track performance.
- Conduct management reviews and implement corrective actions.
Audit checklist for ISO 45001:2018
The ISO 45001 audit checklist below covers each clause of ISO 45001 and provides criteria that help to verify documentation and implementation:
- Has the organization defined the scope and context of its OHSMS, including internal and external issues?
- Is there clear leadership commitment and a written OH&S policy aligned with the company’s strategic goals?
- Are roles, responsibilities, and authorities defined and communicated throughout the organization?
- Does the organization identify and assess OH&S risks and opportunities using a structured methodology?
- Are workers and their representatives involved in consultations and decision-making regarding safety?
- Are documented objectives established for OH&S and are they monitored for performance?
- Has the organization identified applicable legal and other requirements and is compliance tracked effectively?
- Are operational controls implemented to eliminate hazards and reduce OH&S risks consistently?
- Are emergency preparedness and response plans documented, tested, and updated based on real scenarios?
- Is there evidence of ongoing performance evaluation, including audits, monitoring, and measurement?
- Are incidents, nonconformities, and corrective actions recorded and analyzed for continual improvement?
- Does top management conduct regular management reviews to assess OHSMS effectiveness and outcomes?
- Is all documentation controlled and accessible to relevant employees and stakeholders as needed?
For audit support and ISO 45001 certification, contact support@pacificcert.com.
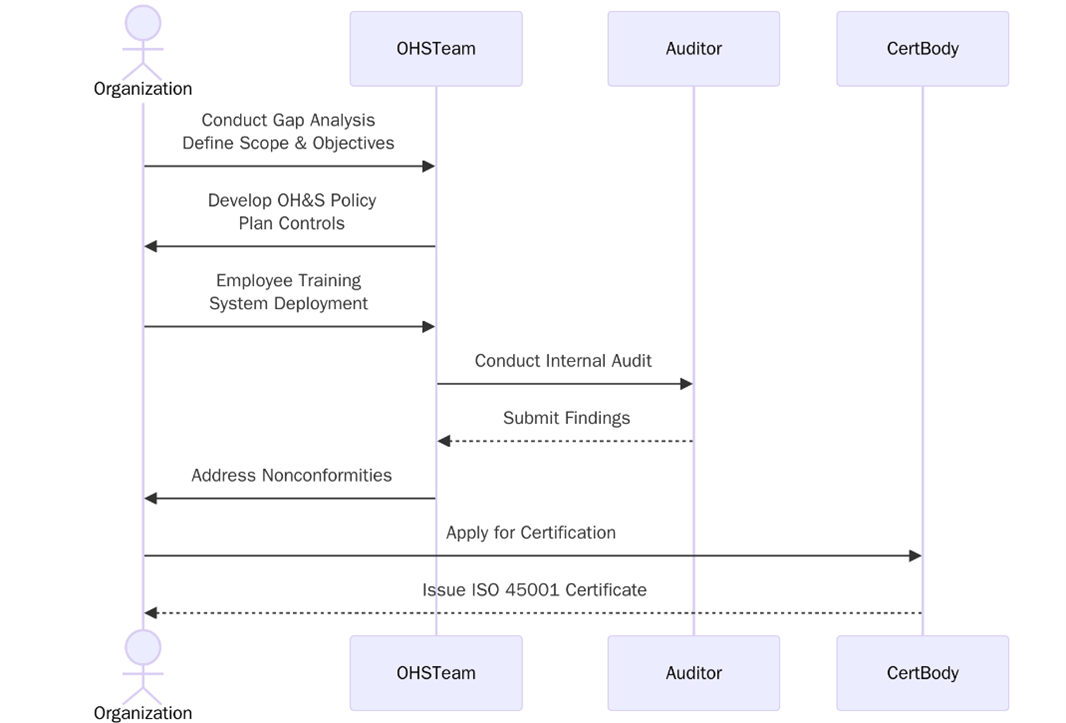
ISO 45001:2018 Certification Process
The ISO 45001 certification process involves a structured audit by an accredited certification body to verify that your system meets all standard requirements. Below are the steps:
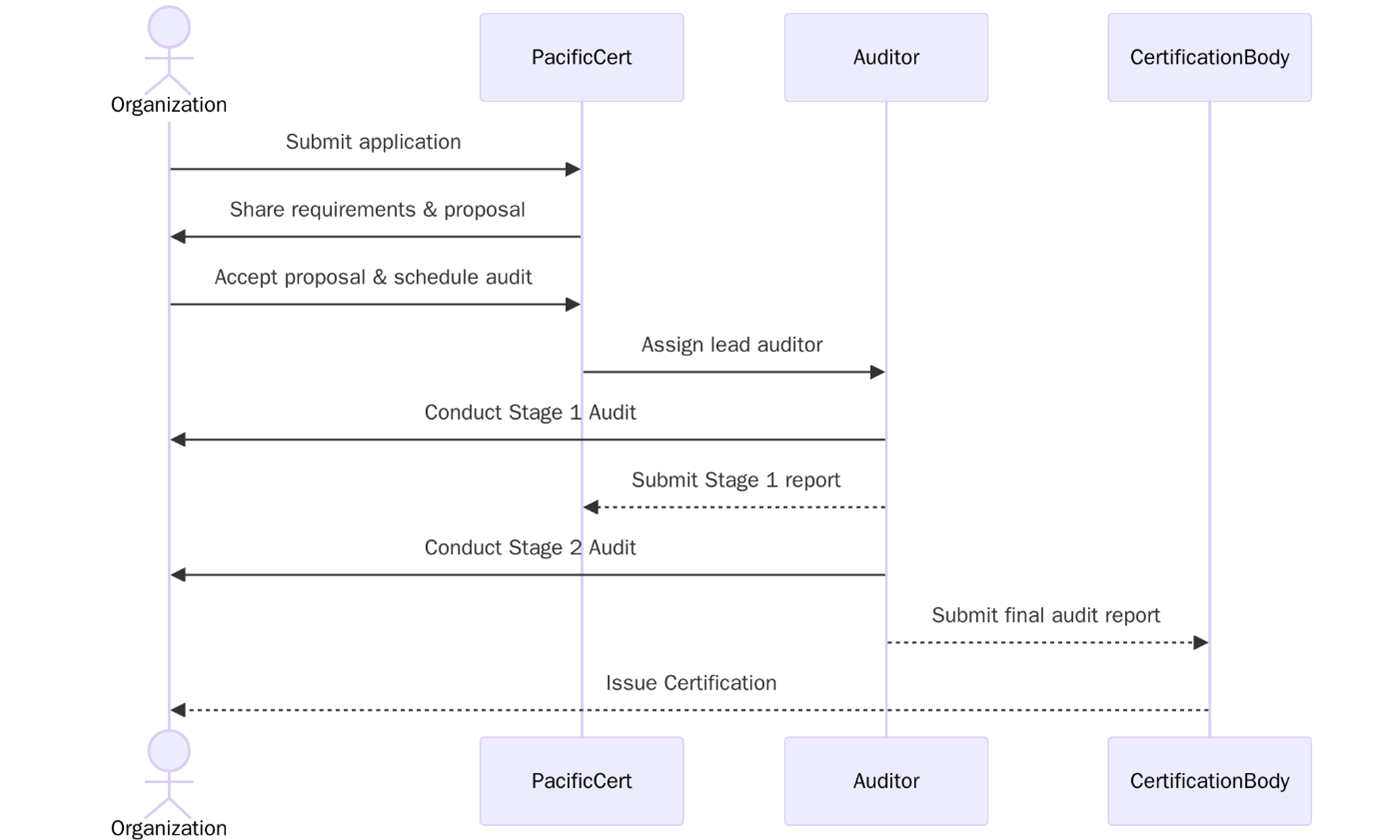
- Organization submits a formal request for ISO 45001 certification with scope and details.
- Certification body reviews application, defines audit scope, and prepares an audit plan.
- Stage 1 Audit: Evaluation of documented OH&S policies, legal compliance, and system readiness.
- Stage 2 Audit (On-Site or Online): Online or on-site audit to verify implementation, staff awareness, and process control.
- If nonconformities are identified, the organization implements corrective actions.
- ISO 45001:2018 certificate is issued, valid for 3 years with annual surveillance audits.
What are the benefits of ISO 45001:2018 Certification?
ISO 45001:2018 certification offers a wide range of benefits to organizations committed to creating a safe and legally compliant work environment. Below are the common benefits:
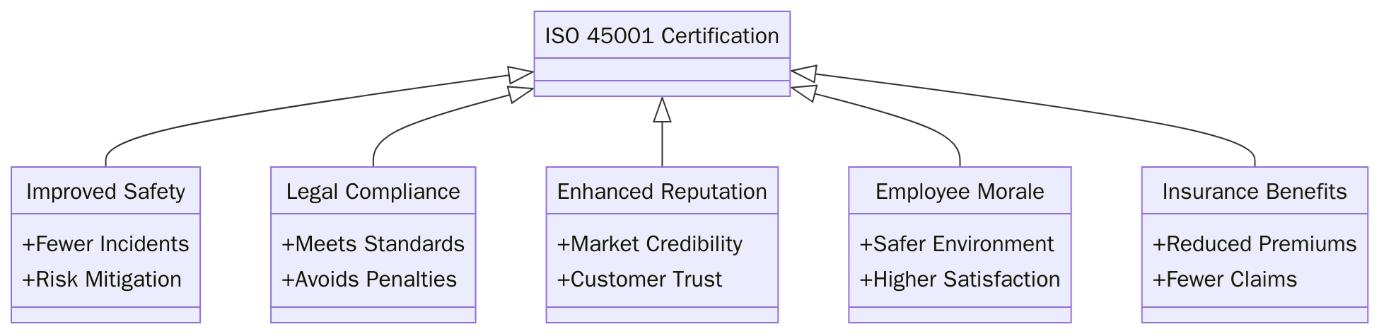
- Reduces workplace injuries and illnesses by identifying hazards and implementing preventive controls across all operations.
- Improves legal and regulatory compliance, helping organizations stay aligned with national and international OH&S laws.
- Enhances employee morale and retention through safer working conditions, involvement, and a strong safety culture.
- Boosts organizational reputation and credibility with customers, regulators, and supply chain partners.
- Supports risk-based decision-making by integrating safety into strategic planning and operational controls.
- Drives continual improvement in health and safety performance through audits, reviews, and employee feedback.
- Lowers insurance premiums and operational costs due to fewer incidents, claims, and associated disruptions.
- Facilitates global market access and business opportunities, as ISO 45001 is recognized and respected worldwide.
- Aligns easily with other ISO standards like ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 for a unified management system approach.
- Demonstrates leadership commitment to safety, reinforcing trust among stakeholders and driving cultural change.
ISO 45001 has been adopted as a national standard by numerous countries, including India, the United States, the United Kingdom among others, for reflecting its global acceptance and applicability. The standard is based on conventions and guidelines of the International Labour Organization (ILO), and national standards, ensuring its alignment with globally recognized occupational health and safety practices.
Moreover, the global ISO 45001 certification demand is experiencing significant growth, projected to expand to USD 57.48 billion by 2033, with a CAGR of about 15.2%.
If your organization is looking to get certified for ISO 45001, contact us at support@pacificcert.com.
What is the ISO 45001 Certification timeline?
The certification process spans 20 to 22 weeks, starting from initial planning to certification issuance. Below is the table with phases:
Week | Phase | Activity Description |
Week 1 | Project Initiation | Define certification scope, assign responsibilities, and conduct kick-off meeting. |
Week 2 | Gap Analysis | Evaluate current OH&S system against ISO 45001 requirements and identify gaps. |
Week 3–4 | Planning | Develop an implementation plan, set OH&S objectives, and allocate resources. |
Week 5–6 | Risk & Compliance Setup | Identify hazards, assess risks, and list all legal and regulatory OH&S requirements. |
Week 7–8 | Policy & Process Development | Draft OH&S policy, procedures, emergency plans, and document controls. |
Week 9–10 | Training & Awareness | Train staff, raise awareness, and assign OH&S roles and responsibilities. |
Week 11–12 | System Implementation | Deploy controls, monitor activities, and maintain documentation. |
Week 13–14 | Internal Audit | Conduct internal audit to verify compliance and prepare for external audit. |
Week 15 | Management Review | Review audit results, OH&S performance, and approve actions for improvement. |
Week 16–17 | Corrective Actions | Address internal audit findings and close any identified nonconformities. |
Week 18 | Stage 1 Audit | Certification body reviews documentation, legal compliance, and readiness. |
Week 19–20 | Stage 2 Audit | On-site audit assessing process implementation, staff involvement, and evidence review. |
Week 21 | Certification Review | Certification body evaluates audit results and finalizes decision. |
Week 22 | Certificate Issuance | ISO 45001:2018 certificate issued upon successful audit completion and approval. |
What is ISO 45001 certification cost?
The ISO 45001 certification cost varies, depending on several factors specific to each organization, depends on the number of employees, the number of sites, the industry’s risk level, and the current state of the organization’s health and safety practices.
For a personalized quotation for the certification process, contact us at support@pacificcert.com.
Why ISO 45001:2018 is important and who needs it?
Organizations certified to ISO 45001 have shown measurable improvements in safety performance. A study analyzing ESG data from 100 large global organizations found that certified companies reported significantly lower Total Recordable Incident Frequency Rates (TRIFR) and Lost Time Injury Frequency Rates (LTIFR) compared to non-certified ones.
Since its launch in 2018, nearly 300,000 organizations across more than 160 countries have adopted ISO 45001, covering close to 400,000 workplaces. Its relevance spans high-risk sectors from manufacturing, construction, mining, oil & gas, chemicals, logistics to energy, where workplace hazards are prevalent and legal obligations are stringent.
However, its structured and preventive approach is equally valuable for low-risk sectors as well, where employee well-being and compliance matter greatly. The standard also improves an organization’s standing in tendering, vendor selection and regulatory assessments,
How Pacific Certifications Can Help?
Pacific Certifications is an accredited certification body; we provide independent and internationally recognized certification services. Our role is to conduct the audit and certify your organization in accordance with ISO 45001, ensuring that it meets all standard requirements, maintaining complete impartiality and integrity in the certification process.
Our Services Include:
- Stage 1 Audit: Assessment of your documented procedures, policies, and readiness for certification.
- Stage 2 Audit: Detailed evaluation of implementation, employee awareness, risk controls, and legal compliance.
- Combined audits with other standards to reduce time and costs.
- Audits for organizations operating across multiple locations.
- Surveillance audits
- Recertification
With industry-experienced auditors and a transparent process, we ensure that your certification journey is smooth and aligned. To get started, contact us at support@pacificcert.com!
FAQs: ISO 45001:2018
What is ISO 45001?
ISO 45001 is the international management-system standard for occupational health and safety. It gives organizations a framework to prevent work-related injury and ill health while improving overall safety performance.
Who should get ISO 45001 certified?
Any organization, regardless of size or industry.
Is ISO 45001 mandatory?
No, it’s voluntary but often required by clients or regulators
How many clauses are in ISO 45001?
There are ten main clauses—from Scope (Clause 1) through Improvement (Clause 10)—with Clauses 4 to 10 containing the requirements that must be met for certification.
How long is the certification valid?
Certification is valid for 3 years, with annual surveillance audits
How long does certification take?
Typically 4–12 weeks, depending on organization size and readiness.
Who issues ISO 45001 certification?
Accredited certification bodies like Pacific Certifications.
Is employee training required?
Yes, training is essential to meet awareness and competence requirements.
Can ISO 45001 be integrated with ISO 9001 or ISO 14001?
Yes, it follows the same High-Level Structure for easy integration.
Why did OHSAS 18001 change to ISO 45001?
The OHSAS specification was replaced so that health-and-safety management could follow the same high-level structure used by other ISO standards such as ISO 9001 and ISO 14001. This makes integration simpler and brings global consensus to what was previously a British-led document.
How do you get ISO 45001 certified?
Close any gaps between your current practices and the standard, run internal audits and a management review, then invite an accredited certification body to perform the two-stage external audit. Once all findings are resolved, the certificate is issued and is subject to annual surveillance visits.
What is the difference between ISO 45001 and ISO 9001?
ISO 45001 focuses on protecting people by managing health and safety risks, while ISO 9001 targets product and service quality. Both share the same structural layout but pursue different objectives.
What are risk and opportunity in ISO 45001?
“Risk” refers to the chance of occupational injury or ill health arising from workplace hazards. “Opportunity” is any circumstance that can improve OH&S performance, such as introducing safer equipment or better training. Both must be identified and addressed within the management system.
Ready to get ISO 45001:2018 certified?
Contact Pacific Certifications to begin your certification journey today!
Suggested Certifications –
Read more: Pacific Blogs






