What is EN 1639:2009?

EN 1639:2009 is a European standard that specifies the important requirements for medical devices used in dentistry. It provides guidelines for design, manufacturing, testing, and performance evaluation of dental instruments and devices to ensure safety, reliability, and efficacy. The standard covers devices ranging from diagnostic tools, dental instruments, and equipment for restorative and surgical procedures.
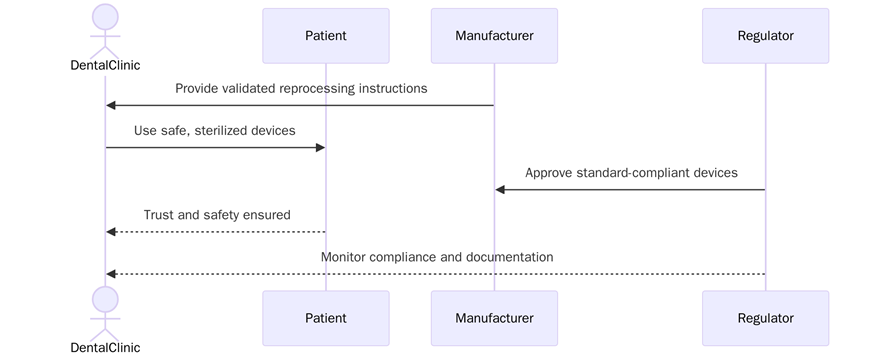
By adhering to EN 1639, manufacturers ensure that their products meet quality standards, minimize risk to patients and dental professionals, and comply with regulatory requirements. This standard serves as a reference for dental device developers, manufacturers and certifying bodies.
For more information, contact our team at support@pacificcert.com.
Purpose
The purpose of EN 1639:2009 is to establish uniform requirements for dental medical devices, ensuring they are safe and fit for intended use. Dental procedures involve instruments that come in contact with patients’ tissues, fluids, and oral cavities. This standard ensures that these devices are manufactured under strict quality guidelines, reducing potential hazards, preventing device failures, and promoting consistent clinical outcomes. EN 1639 supports dental professionals in selecting reliable equipment while providing manufacturers a structured framework to design, produce and test dental devices.
Scope and Applicability
EN 1639 applies to all medical devices used in dentistry, including manual, mechanical, and powered instruments. It covers devices used in clinics, hospitals, and specialized dental laboratories. The standard is relevant for both manufacturers producing new dental instruments and suppliers providing replacement or ancillary components. EN 1639 addresses safety, hygiene, and performance requirements for devices, ensuring that they are compliant with broader European Medical Device Regulations (MDR) and ISO 13485 for quality management in medical devices. Its scope includes risk management, labelling, materials and verification procedures, making it applicable across the dental device lifecycle from design to post-market monitoring.
Key Definitions
- Medical Device: Any instrument, apparatus, appliance, or material used for diagnosis, prevention, monitoring, or treatment in dentistry.
- Manufacturer: Entity responsible for designing and producing dental devices.
- Performance Evaluation: Process to verify that a device meets its intended clinical function safely and smoothly.
- Risk Management: Systematic identification, analysis and control of hazards associated with dental devices.
Clause-wise Structure of EN 1639:2009
| Clause | Title | Description |
| 1 | Scope | Defines the range of dental devices covered and their intended use. |
| 2 | Normative References | Lists related standards such as ISO 13485, ISO 10993, and relevant EN standards. |
| 3 | Terms and Definitions | Provides standardized terminology to maintain consistency. |
| 4 | General Requirements | Outlines general safety, performance, and risk management principles. |
| 5 | Materials | Specifies requirements for materials in contact with patients or dental professionals. |
| 6 | Design Requirements | Covers device design, ergonomics, usability and infection control. |
| 7 | Performance and Functional Requirements | Defines accuracy, durability, and clinical performance parameters. |
| 8 | Testing and Verification | Establishes procedures for inspections, testing and validation of devices. |
| 9 | Labelling and Instructions | Requirements for clear usage instructions, warnings and traceability. |
| 10 | Risk Management | Procedures for hazard identification, risk assessment and mitigation. |
| 11 | Post-market Monitoring | Ensures continued evaluation and reporting of device performance and incidents. |
What are the requirements of EN 1639?
Before implementing EN 1639, organizations should ensure their dental devices meet the following requirements to guarantee safety, reliability, and regulatory compliance. These requirements guide manufacturers in designing, producing, and documenting devices to prevent clinical failures and minimize patient risk.
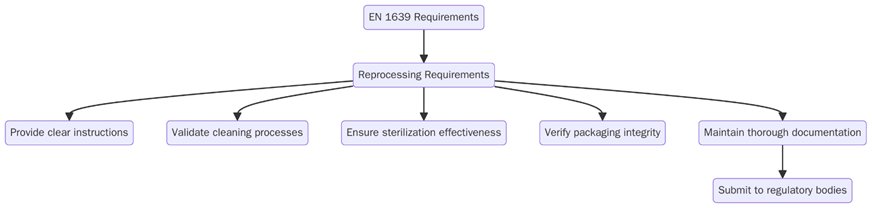
Below are some of the key requirements:
- Use materials that are biocompatible and suitable for contact with oral tissues.
- Design devices that are ergonomic, safe and easy for dental professionals to handle.
- Ensure accuracy, durability, and performance through standardized testing and verification.
- Implement risk management procedures to identify hazards and reduce potential harm.
- Provide detailed labelling, instructions and warnings to support safe use.
- Maintain traceability for all components and materials used in the device.
- Perform functional evaluations and clinical performance assessments.
- Establish post-market surveillance procedures to monitor device performance over time.
- Align with ISO 13485 quality management systems for medical devices.
What are the benefits of EN 1639?
Adhering to EN 1639 helps manufacturers and dental professionals ensure devices are safe, smooth, and trusted. Compliance improves patient outcomes, regulatory alignment and market credibility.
Below are some of the key benefits:
- Improves patient safety by ensuring dental devices meet rigorous quality and performance standards.
- Reduces legal and regulatory risks associated with device failures or non-compliance.
- Supports consistent device performance and reliability for clinical procedures.
- Improves brand credibility and trust among dentists, clinics and distributors.
- Streamlines design, testing, and production processes for dental devices.
- Facilitates compliance with ISO 13485 and European MDR requirements.
- Provides clear labelling, instructions and risk information for safe clinical use.
- Encourages innovation within a structured, risk-managed framework.
Market Trends
The global market for dental medical devices is expanding steadily, driven by rising awareness of oral health, increasing dental procedures and growing adoption of advanced dental technologies. Compliance with EN 1639 has become a key differentiator for manufacturers seeking to access European and international markets, as regulators, distributors and dental professionals demand products that meet stringent safety and performance standards.
Recent trends indicate a strong shift toward minimally invasive dental procedures, digital dentistry, and the integration of advanced materials, all of which require precise design, testing, and labelling in line with EN 1639.
Certification Process for EN 1639 Implementation
While EN 1639 itself is a standard and not certifiable, adherence can be showed through audits or certifications in line with ISO 13485 or MDR requirements. The process includes:
- Evaluate existing dental devices against EN 1639 principles.
- Check design records, material specifications, testing protocols, labelling, and instructions.
- Ensure risk assessments and mitigation measures are in place.
- Conduct performance, functional, and biocompatibility tests.
- Integrate compliance efforts with ISO 13485 or other quality frameworks.
- Establish surveillance, reporting, and corrective action procedures.
- Maintain ongoing evaluation to ensure sustained compliance.
For audits and certification guidance, contact our team at support@pacificcert.com.
What is the certification cost?
The cost of implementing EN 1639 compliance depends on the complexity of the dental devices, the scope of required testing, and integration with existing quality management systems. Organizations may incur expenses for materials verification, performance testing, staff training, documentation updates, and third-party audits. Aligning with ISO 13485 or MDR frameworks may involve additional costs for certification audits and regulatory approvals. Overall, costs vary based on device portfolio size and the level of risk management required.
What is the certification timeline?
The timeline for EN 1639 implementation and alignment depends on the readiness of an organization’s quality management systems and device documentation. For companies already compliant with ISO 13485, alignment can take approximately 2 to 3 months. For organizations establishing new risk management, testing, or labelling procedures, the process may extend to 4 to 6 months. Ongoing post-market surveillance and monitoring continue beyond initial implementation to ensure long-term compliance and device reliability.
How Pacific Certifications Can Help?
Pacific Certifications supports dental device manufacturers in aligning their processes with EN 1639 principles. Our services include:
- Conducting gap assessments to identify areas for improvement.
- Reviewing documentation and design processes for compliance.
- Supporting risk management and post-market surveillance procedures.
- Guiding integration with ISO 13485 or other relevant quality management systems.
- Providing accredited training programs for staff involved in dental device quality and safety.
For guidance or to schedule an audit, contact us at support@pacificcert.com.
Training and Courses
To support the adoption of EN 1639 and related dental device standards, Pacific Certifications offers:
- Lead Auditor Training: Preparing professionals to conduct third-party audits.
- Lead Auditor Training: Equipping staff to plan and implement compliance measures.
- Internal Auditor Training: Training internal teams to maintain quality and safety standards.
Pacific Certifications provides accredited training programs. If your organization is looking for EN 1639 training, our team is equipped to help you. Contact us at support@pacificcert.com.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Which organizations should implement EN 1639?
Any dental device manufacturer, supplier, or laboratory involved in the design, production, or distribution of dental instruments.
Is EN 1639 mandatory?
No, it is a European standard. Compliance helps show safety, performance, and regulatory alignment, and may facilitate approval under ISO 13485 and MDR regulations.
How does EN 1639 improve patient safety?
By ensuring dental devices meet strict design, material, and performance criteria, EN 1639 reduces the risk of device failure, contamination, or injury during dental procedures.
How long does it take to align devices with EN 1639?
For organizations with an existing quality management system, alignment can take 2–3 months. For others, it may take 4–6 months depending on the number and complexity of devices.
Does EN 1639 cover powered dental equipment?
Yes. The standard applies to all dental medical devices, including manual, mechanical, and powered instruments used in clinical and laboratory settings.
What documents are needed for compliance with EN 1639?
Design records, material specifications, performance test reports, labelling and instructions, risk management files and post-market monitoring plans.
Is certification available for EN 1639?
While EN 1639 itself is a standard, compliance can be showed through audits, ISO 13485 certification, or other quality management system certifications.
What are the key benefits for manufacturers?
Compliance improves product reliability, supports market access, improves brand credibility, and reduces potential legal or regulatory risks.
How often should devices be reviewed for continued compliance?
Manufacturers should conduct ongoing post-market surveillance, periodic testing, and risk reassessment to ensure devices continue to meet EN 1639 requirements over their lifecycle.
Ready to get ISO EN 1639 certified?
Contact Pacific Certifications to begin your certification journey today!
Suggested Certifications –
Read more: Pacific Blogs






