What is ISO 50001:2018?

ISO 50001:2018 is the international standard for Energy Management Systems (EMS), providing organizations with a framework to manage energy performance smoothly. It establishes policies, objectives, and processes that help organizations systematically monitor and reduce energy use, cut costs and minimize environmental impact.
Energy consumption represents one of the largest operating costs for businesses worldwide. Rising energy prices, climate change, and regulatory expectations have made energy management a priority for industries of all sizes. ISO 50001:2018 enables companies to integrate energy management into daily operations, reducing waste while improving sustainability. To get started with ISO 50001:2018 certification, contact support@pacificcert.com.
What is the Purpose of ISO 50001:2018?
The purpose of ISO 50001:2018 is to help organizations establish the systems and processes necessary to improve energy performance, including efficiency, consumption, and intensity. Unlike voluntary conservation programs, ISO 50001:2018 provides a globally recognized and certifiable framework that organizations can implement across sectors.
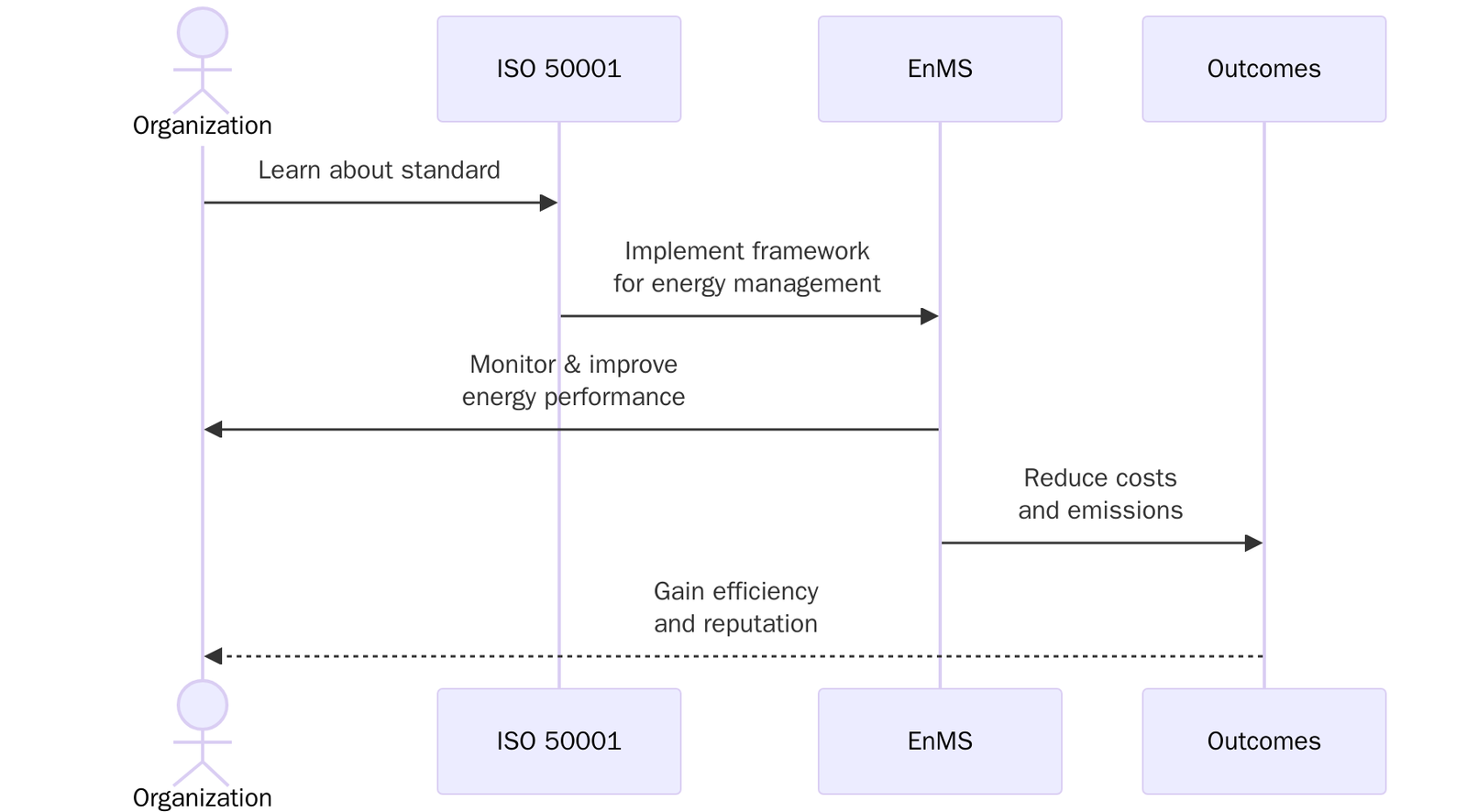
The standard supports organizations in adopting a structured approach to continually monitor and reduce energy use. It also provides a tool for compliance with energy-related regulations and sustainability commitments. By doing so, ISO 50001:2018 allows organizations to achieve measurable results, reduce carbon emissions and improve competitiveness in increasingly energy-conscious markets.
Scope and Applicability
ISO 50001:2018 applies to all organizations regardless of size, industry, or geographic location. It can be implemented in manufacturing plants, commercial buildings, government institutions, healthcare facilities and service-based organizations.
The standard is applicable to both energy-intensive industries such as oil and gas, steel, and chemicals, as well as smaller enterprises seeking operational cost savings. ISO 50001 covers all types of energy, including electricity, natural gas, oil, steam, renewables, and fuel. It is particularly relevant in industries where energy costs account for a significant portion of production expenses and where reducing energy use contributes directly to profitability and sustainability.
Key Definitions
- Energy Performance: Measurable results related to energy efficiency, consumption, and use.
- EMS (Energy Management System): A set of policies and processes designed to achieve continual improvement in energy performance.
- Baseline: A reference point used to compare energy performance over time.
- Significant Energy Use (SEU): Energy consumption that has a major impact on an organization’s performance and requires monitoring.
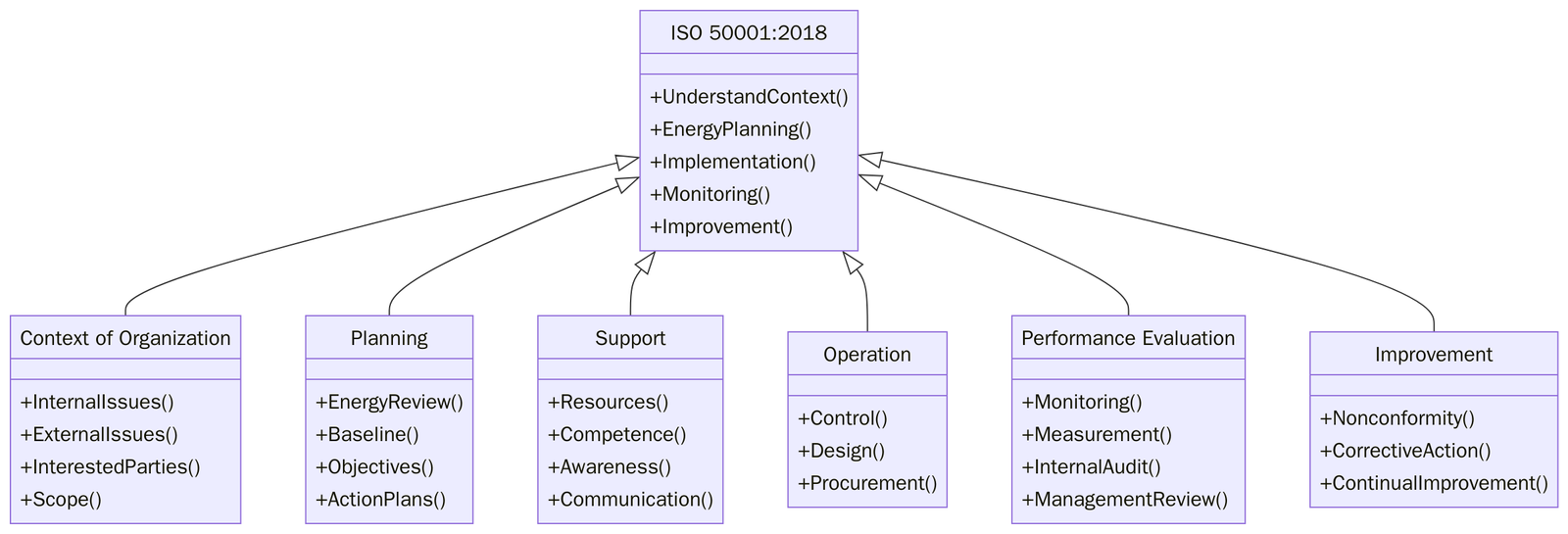
ISO 50001 Clauses-wise Structure
Clause | Title | Description |
1 | Scope | Defines applicability of the standard. |
2 | Normative References | Lists related ISO standards. |
3 | Terms and Definitions | Provides terminology for consistency. |
4 | Context of the Organization | Understanding internal and external factors that affect energy performance. |
5 | Leadership | Outlines management’s role in establishing energy policies and objectives. |
6 | Planning | Identifying risks, opportunities, and significant energy uses. |
7 | Support | Ensures resources, competence, and communication. |
8 | Operation | Establishes operational controls for energy performance. |
9 | Performance Evaluation | Monitoring, measuring, and analysing energy performance. |
10 | Improvement | Requirements for continual improvement and corrective action. |
What are ISO 50001 requirements?
To implement ISO 50001, organizations must meet a range of requirements that ensure systematic energy management. The requirements focus on developing an energy policy, setting measurable objectives and integrating energy management into organizational processes. Below are the main ISO 50001 requirements:
- Conduct an initial energy review to identify baseline energy performance and significant energy uses.
- Establish an energy policy approved by top management.
- Define measurable energy objectives and targets aligned with the policy.
- Implement an energy data collection and monitoring system.
- Ensure resources and staff training are available to support the EMS.
- Integrate energy management into operational controls and maintenance programs.
- Conduct regular internal audits and management reviews to ensure system effectiveness.
- Maintain documented information including energy plans, performance indicators, and compliance records.
To integrate ISO 50001:2018 requirements into your operations, contact support@pacificcert.com.
What are the ISO 50001:2018 benefits?
Implementing ISO 50001 provides organizations with both financial and environmental benefits. The benefits extend across cost savings, regulatory alignment and corporate responsibility, making the standard attractive to industries worldwide. Below are the key ISO 5001 benefits:
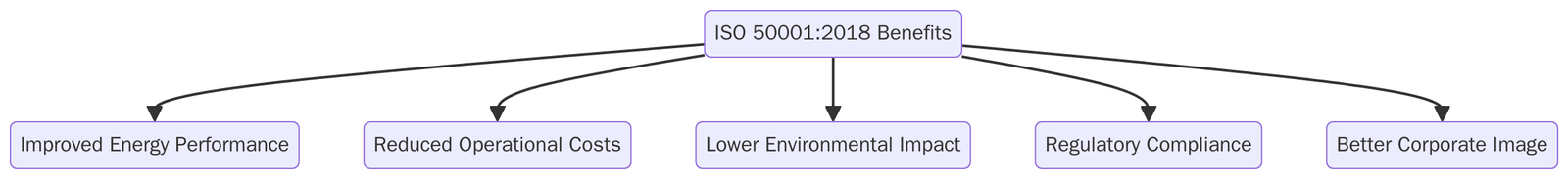
- Continuous monitoring and control systems help organizations identify waste and reduce energy bills significantly, often delivering savings of 10–20% in the first years.
- By reducing energy use and integrating renewable energy sources, organizations contribute directly to global climate change goals and carbon neutrality targets.
- ISO 50001 helps organizations meet government energy efficiency laws and reporting requirements, reducing the risk of fines and penalties.
- Many companies use ISO 50001 as a foundation for broader sustainability and ESG reporting, showing commitment to environmental responsibility.
- Lower operational costs translate into more competitive pricing and improved profitability in energy-intensive sectors.
- Governments and financial institutions often provide tax benefits, grants, or low-interest loans to organizations with ISO 50001 certification.
- By involving employees in energy-saving initiatives, companies build a culture of responsibility and innovation. Workers become more conscious about energy use in daily operations.
- Certification communicates to customers, regulators, and partners that the organization actively manages its environmental impact.
- ISO 50001 prepares organizations for volatile energy prices, supply disruptions, and stricter climate policies. It ensures operational continuity and energy security.
- As an ISO standard, certification is recognized worldwide, giving multinational companies consistency across operations and strengthening international credibility.
Another key trend is the link between ISO 50001:2018 and sustainability reporting frameworks such as ESG disclosures, where energy efficiency is a critical indicator. Organizations adopting ISO 50001:2018 not only save costs but also position themselves as leaders in responsible energy management.
Certification Process
Certification to ISO 50001:2018 follows a structured process. Below is a step-by-step outline:
- Gap Assessment: Review current practices against ISO 50001 requirements.
- Planning: Define energy policy, objectives, and significant energy uses.
- Implementation: Establish monitoring, measurement, and operational controls.
- Training and Awareness: Provide training for employees and integrate energy management responsibilities.
- Internal Audit: Conduct audits to verify compliance and identify gaps.
- Management Review: Top management evaluates performance and decides improvements.
- Stage 1 Audit: Certification body reviews documented policies and processes.
- Stage 2 Audit: Certification body assesses actual implementation and energy performance improvements.
- Certification Decision: If requirements are met, ISO 50001 certification is awarded.
- Surveillance Audits: Annual audits verify ongoing compliance and continual improvement.
ISO 50001 Audit Checklist
- Is there a documented and approved energy policy showing commitment to continual improvement?
- Has the organization identified significant energy uses (SEUs) and established a baseline?
- Are measurable energy objectives and performance indicators (EPIs) in place with action plans?
- Have all applicable energy-related legal and regulatory requirements been identified and documented?
- Are operational procedures for SEUs documented, implemented, and maintained?
- Is energy performance monitored, measured, and compared against baseline and EPIs?
- Are staff trained and aware of their roles in energy management?
- Does procurement consider energy efficiency when purchasing equipment and services?
- Are internal audits conducted regularly with findings recorded and corrective actions taken?
- Does top management review the EMS performance, objectives, and opportunities for improvement?
How much does ISO 50001 Certification Cost?
The cost of ISO 50001:2018 certification depends on organizational size, energy complexity, and geographic location. Key cost components include initial energy review, implementation of monitoring systems, staff training, and certification body audit fees.
For small organizations, costs may be moderate, focused mainly on consulting and certification audits. For large energy-intensive industries, costs are higher due to extensive monitoring systems, complex processes, and site audits. However, these costs are typically offset by significant reductions in energy bills and improved access to funding or government incentives tied to energy efficiency.
Certification Timeline
The timeline for ISO 50001:2018 certification varies depending on organizational readiness and complexity. Preparation Phase includes conducting energy review and setting objectives may take 2–3 months. Next is the implementation Phase which requires establishing monitoring systems, controls and documentation often takes 3–6 months. Lastly, we have certification Audits, which include Stage 1 and Stage 2 audits and it takes around 1–2 months.
In total, most organizations achieve certification within 6–12 months. Larger enterprises may require more time if multiple facilities or energy-intensive processes are involved.
Training and Courses
Training is important for staff to understand and implement ISO 50001 effectively. Key courses include:
- Lead Auditor Training– For professionals conducting certification audits of EMS.
- Lead Implementer Training– For managers and energy officers responsible for deploying ISO 50001:2018.
- Internal Auditor Training– For in-house teams to maintain compliance through regular audits.
Pacific Certifications provides accredited training programs. If your organization is seeking ISO 50001:2018 training, contact support@pacificcert.com.
How Pacific Certifications Can Help?
Pacific Certifications supports organizations in achieving ISO 50001:2018 certification through independent audits and training. Our services include:
- Gap assessments for energy management readiness.
- Certification audits by accredited auditors.
- Integration support with ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 management systems.
- Training programs for staff and managers.
To get ISO 50001:2018 certified and strengthen your energy management framework, contact support@pacificcert.com.
FAQs – ISO 50001:2018 Energy Management Systems (EnMS) Certification
What is ISO 50001:2018 certification?
ISO 50001:2018 is an international standard for establishing an Energy Management System (EnMS). It provides a framework for organizations to improve energy performance, reduce energy consumption, and enhance sustainability through efficient energy management practices.
Who should get ISO 50001 certification?
ISO 50001 certification is ideal for organizations of all sizes and sectors that aim to improve energy efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and cut energy costs. It is particularly beneficial for manufacturing units, industrial facilities, and energy-intensive businesses.
What are the benefits of ISO 50001:2018 certification?
Reduces energy costs and carbon emissions
Enhances energy performance and operational efficiency
Ensures compliance with energy regulations and sustainability goals
Improves corporate image and stakeholder trust
Supports continual improvement in energy management
Is ISO 50001 mandatory?
ISO 50001 is not mandatory by law in most countries but is often encouraged or required by clients, partners, or government energy programs. It demonstrates a proactive approach to sustainable energy management.
How long does it take to get ISO 50001 certified?
Depending on the organization’s size and current energy management practices, it typically takes 3 to 6 months to fully implement the Energy Management System and achieve certification.
How does ISO 50001 help with sustainability and ESG goals?
By improving energy efficiency and reducing greenhouse gas emissions, ISO 50001 contributes significantly to sustainability objectives and strengthens an organization’s Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) performance.
Can ISO 50001 be integrated with other management systems?
Yes, ISO 50001 follows the Annex SL structure, making it easy to integrate with other standards like ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 9001 (Quality Management).
Do small businesses benefit from ISO 50001:2018?
Yes, energy savings and reduced costs apply to organizations of all sizes.
Does ISO 50001:2018 apply only to manufacturing?
No, it applies to any organization including services, healthcare, and government.
How often are audits required?
Annual surveillance audits and full recertification every three years.
Contact Us
If you need support with ISO ISO 50001 certification, contact us at support@pacificcert.com.
Read More at: Blogs by Pacific Certifications






