What is Good Distribution Practices (GDP)?

Good Distribution Practices (GDP) refer to the guidelines and standards for the proper storage, transportation, and distribution of products, particularly pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and food products. GDP ensures that products are handled, stored and distributed in conditions that maintain their quality, safety and efficacy throughout the supply chain.
GDP is critical for maintaining the integrity of sensitive products that could be damaged by improper storage conditions or mishandling during transit. The guidelines ensure that products are distributed in a manner that complies with regulatory standards, ensuring that they reach customers in the condition they were intended.
For more information, contact us at support@pacificcert.com.
Purpose of Good Distribution Practices
The purpose of GDP is to ensure that the distribution of products, especially those that are sensitive or regulated (e.g., pharmaceuticals, medical devices), is conducted safely, consistently and in compliance with relevant laws and regulations. GDP ensures that products are not exposed to conditions that could compromise their quality or safety during the distribution process, from manufacturer to end-user.
By implementing GDP, organizations can reduce the risks of product contamination, degradation and tampering, ensuring that consumers receive products in the best possible condition.
Scope and Applicability
Good Distribution Practices (GDP) are applicable to any organization involved in the distribution, storage, or transportation of products, particularly those that are sensitive or regulated, such as pharmaceuticals, medical devices, food products, and cosmetics. GDP guidelines are relevant to a wide range of industries, including pharmaceuticals, where strict control over storage conditions and transport routes is essential to ensure the quality and safety of medicines. Similarly, food and beverage industries rely on GDP to maintain product integrity and prevent contamination during transportation and distribution.
GDP is essential in ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and maintaining product integrity, which ultimately protects consumers.
Key Definitions
- Good Distribution Practices (GDP): A set of guidelines to ensure that products, especially sensitive items, are stored, handled, and transported in a way that maintains their quality and compliance with regulatory standards.
- Cold Chain: A temperature-controlled supply chain used for transporting perishable products, such as pharmaceuticals or food, to ensure they remain within the required temperature range.
- Supply Chain Management: The process of managing the movement of goods from the manufacturer to the end consumer, ensuring compliance with legal, safety, and quality standards.
- Traceability: The ability to track and trace products throughout the distribution process to ensure their authenticity and integrity.
What are the requirements of Good Distribution Practices (GDP)?
To comply with GDP regulations and achieve certification, businesses must meet specific requirements. These guidelines ensure the safe and smooth handling, storage and transportation of products throughout the supply chain. The following key requirements must be met to maintain compliance with GDP:
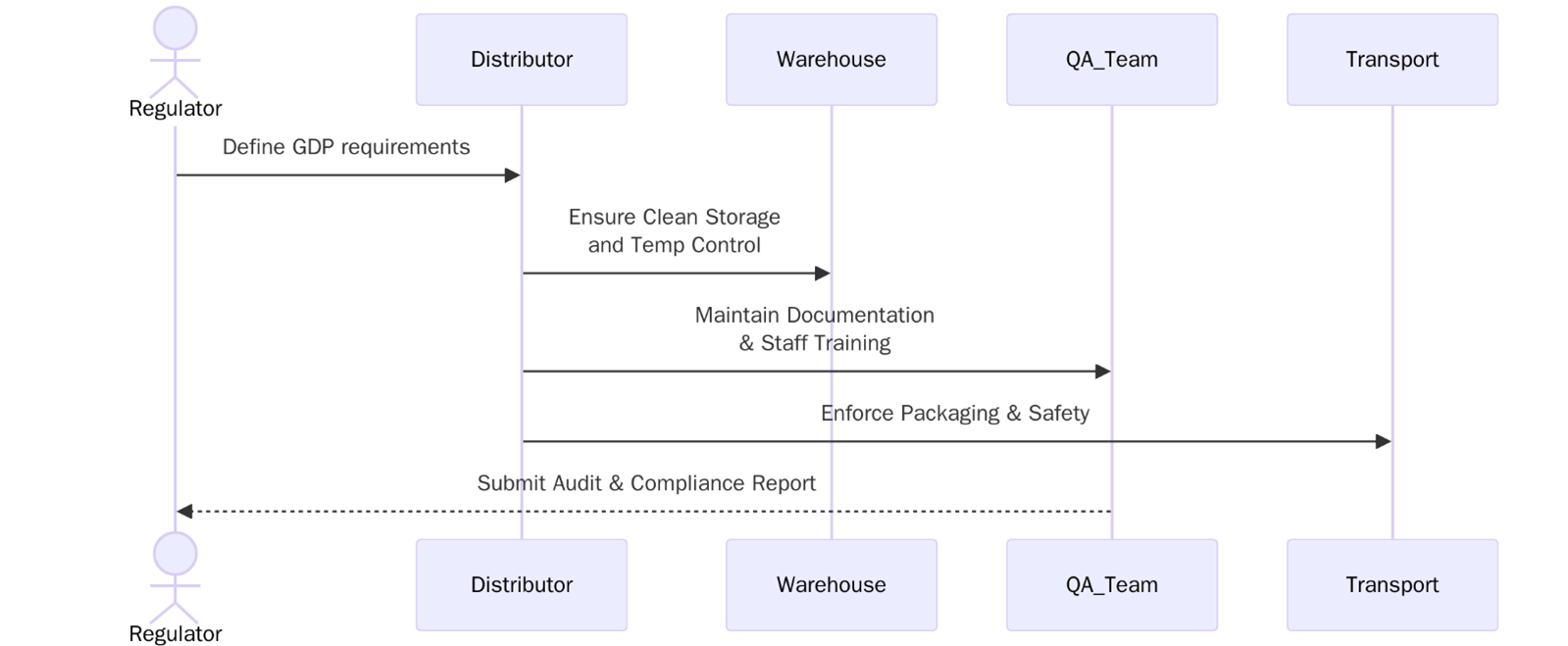
- All GDP-related activities must be documented, including manufacturing processes, inspections, and audits. Proper record-keeping ensures traceability and accountability.
- Organizations must implement a robust QMS to ensure product quality and regulatory compliance across all stages of distribution.
- Employees involved in the distribution process must be trained in GDP practices and aware of the importance of handling products safely and in compliance with regulations.
- Distribution centres must maintain appropriate conditions to ensure products are not exposed to contaminants or inappropriate storage conditions. Proper cleanliness and maintenance are critical.
- Many products, especially pharmaceuticals and perishable goods, require strict temperature and environmental controls to maintain product integrity. This includes cold chain management for temperature-sensitive products.
- Proper protocols for the handling, packaging, and transport of products must be in place to avoid damage or contamination.
For more information, contact us at support@pacificcert.com.
Good Distribution Practices (GDP) Certification: Audit Checklist
The audit checklist for Good Distribution Practices (GDP) certification typically includes the following:
- Have cloud roles and responsibilities between the provider and customer been clearly defined and documented?
- Is virtual machine configuration securely managed and isolated in multi-tenant cloud environments?
- Are procedures in place for the secure return, deletion, or migration of customer assets after contract termination?
- Is administrative access by cloud service customers properly controlled and monitored by the provider?
- Are cloud-specific security requirements addressed in the service agreement (data location, jurisdiction etc.)?
- Is customer activity within the cloud environment logged, monitored, and reviewed for anomalies?
- Are customers informed of any changes that may affect cloud service security controls or SLAs?
- Are measures implemented to segregate and protect customer data in shared infrastructure setups?
- Is there a documented process for handling cloud-specific incidents and notifying affected parties?
What are the benefits of Good Distribution Practices (GDP) Certification?
GDP certification ensures the safety, quality, and compliance of distribution processes, leading to greater operational efficiency and consumer trust. The benefits of certification include:
- Certification ensures that products are handled, stored, and transported according to the highest standards, maintaining their quality and safety.
- GDP certification helps organizations comply with local and international regulations, reducing the risk of fines and penalties.
- Certification show a commitment to quality, increasing consumer confidence in the products and services provided.
- By streamlining distribution practices, businesses can reduce waste, optimize resources, and improve overall efficiency.
- Good Distribution Practices (GDP) certification opens access to new markets by showing compliance with industry standards and regulatory requirements.
Recent trends in supply chain and distribution management emphasize the growing role of technology and automation in ensuring compliance with GDP. The use of IoT devices for real-time monitoring of temperature, humidity, and storage conditions is becoming more widespread, ensuring better control and tracking of products throughout the supply chain.
Countries around the world are tightening their regulations around temperature-sensitive goods and ensuring that distribution networks meet the highest standards of safety and quality. As a result, GDP certification will become essential for businesses aiming to maintain their competitive edge in the global market.
Certification Process for Good Distribution Practices (GDP)
The certification process for GDP typically includes the following stages:
- Pre-Certification Assessment: Conducting an internal audit or gap analysis to identify areas for improvement and assess readiness.
- Documentation Review: Reviewing operational procedures, product tracking, and storage conditions to ensure they meet GDP standards.
- Stage 1 Audit: An initial audit to review the organization’s compliance with GDP guidelines and assess system readiness.
- Stage 2 Audit: A overreaching audit to evaluate the actual implementation of GDP practices, focusing on product handling, storage, and transportation.
- Certification Decision: Certification is awarded based on the results of the audit and confirmation that all requirements are met.
- Ongoing Surveillance: Regular audits to ensure continued compliance with GDP guidelines.
Timeline for GDP Certification
The timeline for Good Distribution Practices (GDP) certification can vary depending on the organization’s readiness. The initial pre-assessment and documentation review usually takes about 1-2 months. The Stage 1 audit takes 1 month, and the Stage 2 audit, which is more overreaching, can span from 1 to 2 months. Certification is generally issued within 3-6 months, depending on audit findings and the organization’s readiness.
What is the Cost of Good Distribution Practices (GDP) Certification?
The cost of GDP certification depends on various factors, including the size of the organization, the complexity of its distribution network and the number of locations involved.
Audit Fee is the Fee for the certification body’s audit process. Training costs are the costs for educating staff on GDP Certification and the necessary processes for compliance. Ongoing maintenance are the costs for regular audits and recertification required every 3 years.
How Pacific Certifications Can Help?
At Pacific Certifications, we provide overreaching auditing and certification services for Good Distribution Practices (GDP) compliance. Our team will guide you through the entire certification process, ensuring that your distribution practices meet the highest standards. Our services include:
- Stage 1 and Stage 2 audits to evaluate your distribution processes and ensure compliance with GDP guidelines.
- Objective conformity assessments based on GDP standards.
- Certification issuance upon successful completion of the audit.
- Ongoing surveillance audits to ensure continued GDP compliance.
- Support for multi-site or global operations.
For audits and certification, contact support@pacificcert.com.
ISO 9001 and GDP Training and Courses
Various training courses are available to help organizations comply with Good Distribution Practices (GDP), including:
- Lead Auditor Training – Equips professionals to conduct external third-party audits.
- Lead Implementer Training – For those responsible for planning and executing ISO 9001 implementation.
- Internal Auditor Training – Preparing internal auditors for certification audits
Pacific Certifications provides accredited training programs. If your organization is looking for GDP training, our team is equipped to help you. Contact us at support@pacificcert.com.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How long does it take to get Good Distribution Practices (GDP) certification?
The certification process typically takes 3–6 months, depending on the organization’s preparedness and audit outcomes.
Is Good Distribution Practices (GDP) certification mandatory for all distributors?
GDP certification is not legally required, but it is highly recommended for businesses in industries like pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and food, where safety and quality are paramount.
What are the main benefits of Good Distribution Practices (GDP) certification?
GDP certification ensures product integrity, improves consumer confidence, ensures regulatory compliance, and improves operational efficiency.
Can I apply for GDP certification without a formal QMS in place?
No, a formal QMS must be in place before applying for GDP certification to ensure compliance with GDP standards.
How often do I need to renew GDP certification?
GDP certification is valid for three years, after which recertification is required.
Ready to get Good Distribution Practices (GDP) certified?
Contact Pacific Certifications to begin your certification journey today!
Suggested Certifications –
Read more: Pacific Blogs






