What is ISO 22000:2018?

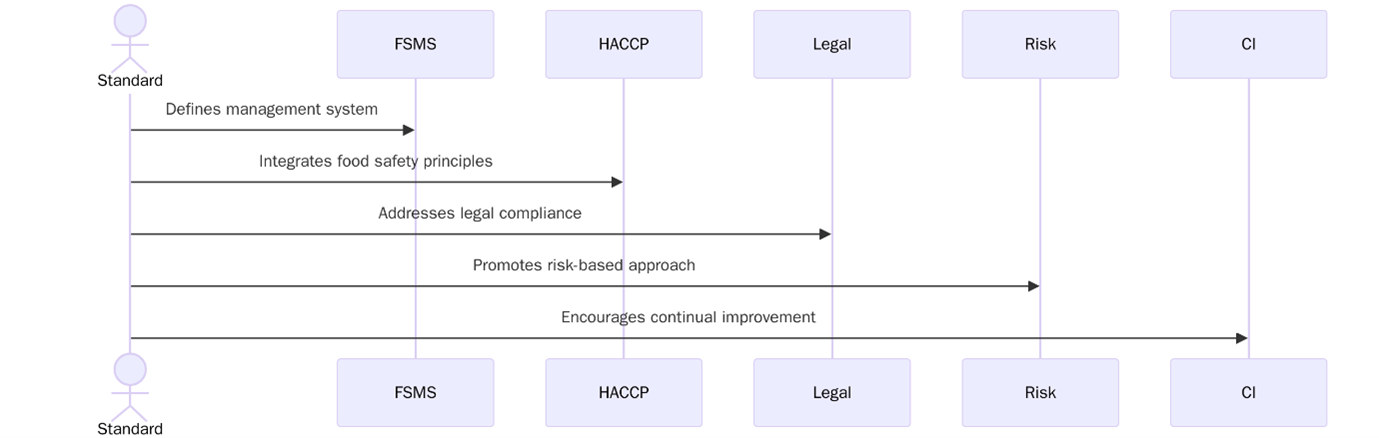
ISO 22000 is an internationally recognized standard for a Food Safety Management System (FSMS), also known as ISO 22000:2018. It provides a framework for organizations involved in the food chain to identify and control food safety hazards, ensuring that food is safe for human consumption. The standard combines with key elements of ISO 9001 and HACCP to create a process-based approach to food safety that emphasizes risk prevention, compliance, and traceability.
Scope & Applicability
The scope of ISO 22000 is broad, making it applicable to all organizations directly or indirectly involved in the food supply chain, regardless of size, complexity, or geographic location. This includes everyone from food manufacturers to cleaning service providers.
For ISO 22000 certification support and audit inquiries, contact support@pacificcert.com.
What is the PDCA Cycle in ISO 22000:2018?
The PDCA Cycle is a foundational concept in ISO 22000 which supports continuous improvement. It helps organizations to systematically plan, implement, monitor, and improve their food safety controls.
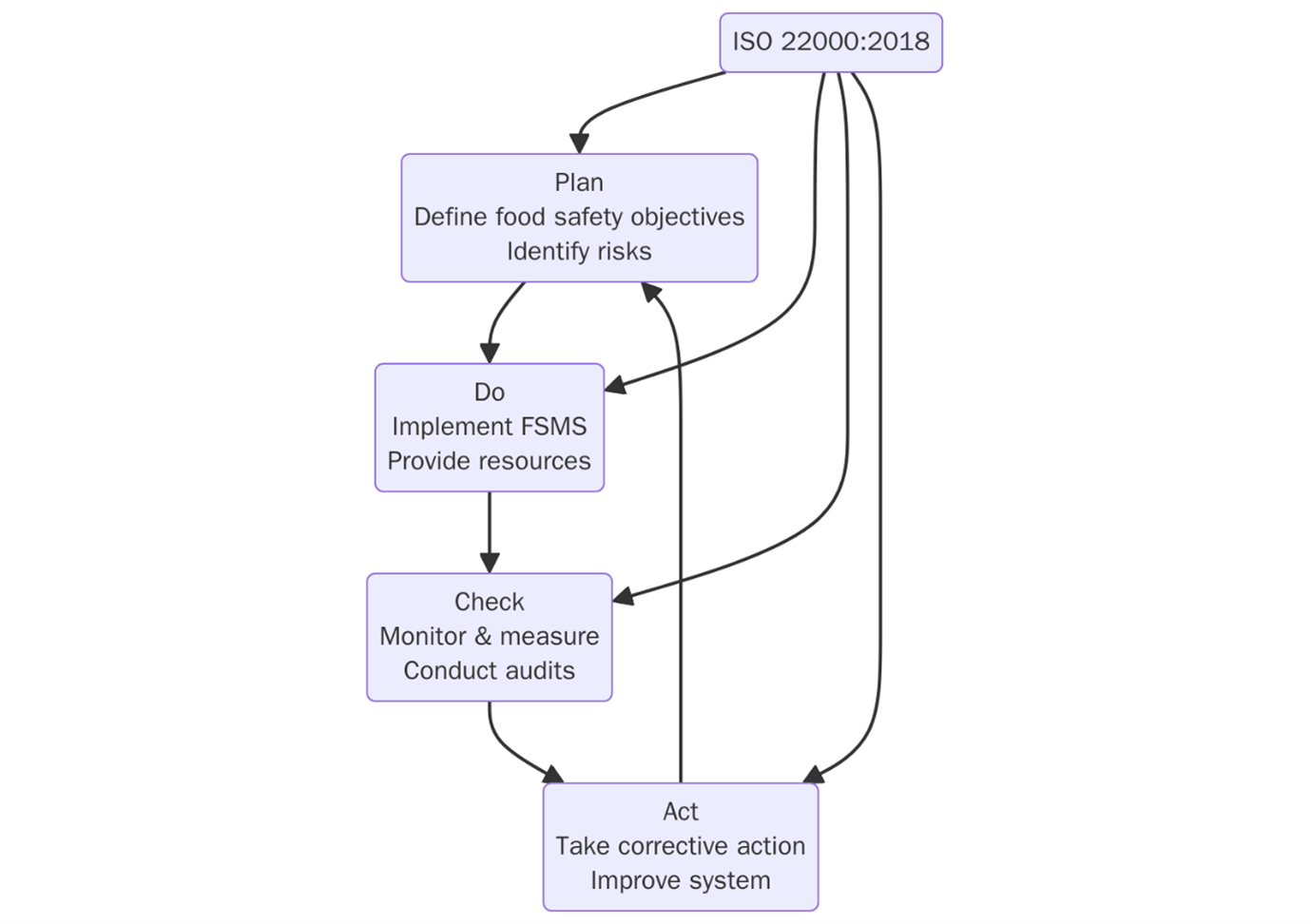
FSMS PDCA model operates on two levels:
- The Organizational Level FSMS
- The Operational Level – managing the PRPs (Prerequisite Programs), OPRPs (Operational Prerequisite Programs), and CCPs (Critical Control Points) within the hazard control plan.
Plan: Define food safety objectives, assess risks, identify hazards, and establish control measures including PRPs, OPRPs, and CCPs.
Do: Implement the FSMS as planned.
Check: Monitor and measure the effectiveness of the FSMS, including verification of PRPs and CCPs.
Act: Take corrective actions based on findings
PDCA creates a culture of continual improvement across all levels of the food chain. Need help with ISO FSMS certification? Contact support@pacificcert.com today!
ISO 22000 Clauses-wise Structure
ISO 22000 follows the Annex SL High-Level Structure, which aligns it with other standards like ISO 9001 and ISO 14001, making integration easier. Below is the table with FSMS clauses:
Clause | Title | Description |
1 | Scope | Defines the applicability and purpose of the FSMS. |
2 | Normative References | Lists referenced documents essential for applying the standard. |
3 | Terms and Definitions | Explains specific terminology used in the context of ISO 22000. |
4 | Context of the Organization | Requires understanding internal/external factors, stakeholder needs, and FSMS scope. |
5 | Leadership | Emphasizes top management’s role in commitment, policy, and assigning roles. |
6 | Planning | Addresses risk-based thinking, FSMS objectives, and planning changes. |
7 | Support | Covers resources, competence, awareness, communication, and documentation. |
8 | Operation | Focuses on PRPs, hazard control plans, traceability, and emergency preparedness. |
9 | Performance Evaluation | Requires monitoring, internal audits, and management reviews of FSMS. |
10 | Improvement | Outlines handling nonconformities and driving continual improvement. |
This structure ensures that ISO is a process-driven and risk-focused standard for managing food safety across the entire supply chain.
What are ISO 22000 Requirements?
ISO 22000 is the international standard for Food Safety Management Systems (FSMS), designed to ensure that food products are safe for consumption throughout the entire food chain. It integrates the principles of HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) with prerequisite programs and a management system approach similar to ISO 9001.
The standard applies to all organisations in the food supply chain, from producers and processors to transporters and retailers, and helps them identify, control, and prevent food safety hazards while meeting legal and regulatory requirements.
The ISO 22000 Requirements include:
- Establish, implement, maintain, and continually improve an FSMS covering all processes in the food chain.
- Demonstrate top management commitment, define a food safety policy, set objectives, and conduct management reviews.
- Provide adequate resources, trained personnel, infrastructure, and work environment to ensure food safety.
- Implement basic hygiene and operational conditions to maintain a safe food production environment.
- Identify food safety hazards, establish critical control points, and define control measures.
- Manage specific operational controls that reduce significant hazards to acceptable levels.
How to Implement ISO 22000:2018 in Your Organization?
The goal of ISO 22000 is to ensure food safety at every stage of the supply chain. Below is a roadmap to help you implement FSMS in your organization:
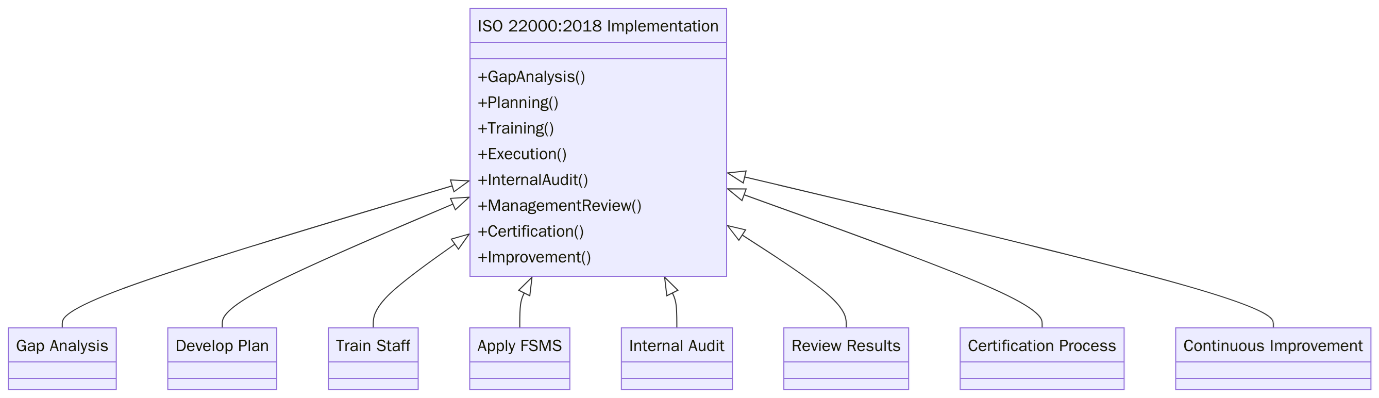
- Study the ISO 22000:2018 standard to understand clause requirements, HACCP integration, and FSMS fundamentals.
- Conduct a gap analysis comparing current food safety practices and identify compliance gaps.
- Define the scope of your FSMS including all products that impact food safety.
- Engage top management to demonstrate leadership commitment and allocate resources.
- Identify applicable legal and regulatory requirements and ensure they are integrated into framework.
- Establish food safety policy and objectives aligned with business goals and food safety risk priorities.
- Form a food safety team with clearly assigned roles and responsibilities for hazard analysis and system management.
- Develop and implement prerequisite programs (PRPs) such as cleaning, sanitation, pest control etc.
- Conduct hazard analysis and define CCPs/OPRPs based on risk assessments and HACCP principles.
- Document all procedures, controls, and records necessary to operate and maintain the FSMS effectively.
- Train employees across all levels to ensure awareness
- Monitor, measure, and verify controls including internal audits, corrective actions, and FSMS reviews.
- Conduct a management review to evaluate FSMS performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Schedule a certification audit with an accredited body
ISO 22000 Audit Checklist
The ISO 22000 audit checklist helps to ensure that all food safety requirements are being effectively implemented and maintained:
- Has the organization clearly defined the scope of its Food Safety Management System?
- Are the internal and external issues that affect food safety performance properly identified and monitored?
- Has top management shown leadership and commitment to the effectiveness of the FSMS?
- Are food safety objectives established, measurable, and reviewed regularly for effectiveness?
- Is there an appointed food safety team leader, and is the team trained and competent?
- Have applicable legal, statutory, and customer food safety requirements been identified and integrated into the FSMS?
- Are Prerequisite Programs (PRPs) effectively implemented to maintain a hygienic environment?
- Has the organization conducted a thorough hazard analysis and identified relevant CCPs and OPRPs?
- Are critical control measures being monitored, validated, and verified as per the food safety plan?
- Are procedures in place for traceability, product withdrawal, and recall in the event of a food safety incident?
- Is internal and external communication related to food safety effectively managed and documented?
- Have internal audits been conducted as per schedule and used to identify and address nonconformities?
- Has management review been carried out to assess the performance and adequacy of the FSMS?
- Are there corrective actions and continual improvement processes in place to manage nonconformities?
- Is the documentation and record-keeping system maintained and accessible as required?
ISO 22000 Certification Process
The ISO 22000 certification process ensures a food business establishes a Food Safety Management System, following:
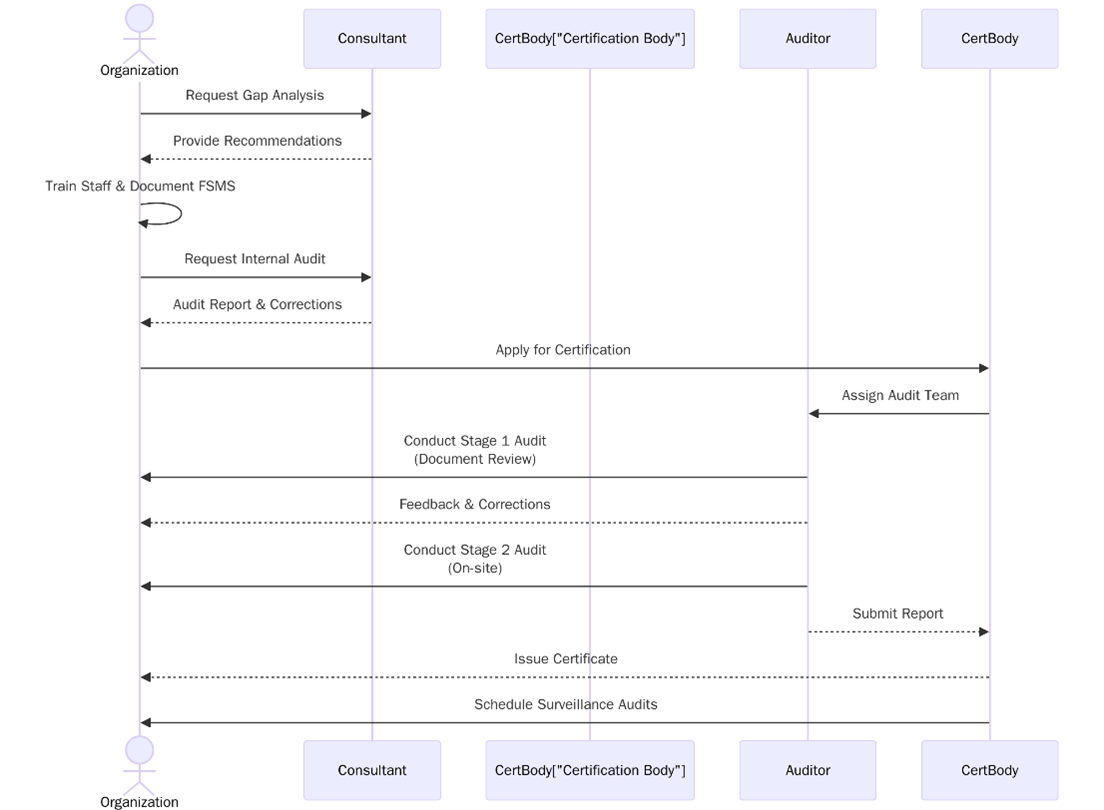
- Submit your organization’s details and FSMS scope to the certification body.
- Receive a proposal, agree on timelines, and finalize the certification contract.
- The certification body schedules and plans the Stage 1 and Stage 2 audits.
- Stage 1 Audit – Documentation review to assess readiness and identify gaps in your FSMS.
- Stage 2 Audit – On-site/Online audit to evaluate the implementation and effectiveness of your FSMS.
- Receive detailed feedback, including any nonconformities.
- Submit corrective action evidence to close any audit findings.
- If approved, your ISO certificate is issued, valid for 3 years.
What are ISO 22000 Certification benefits?
The ISO 22000 certification helps to ensure safe food production and customer confidence. Below are the key benefits:
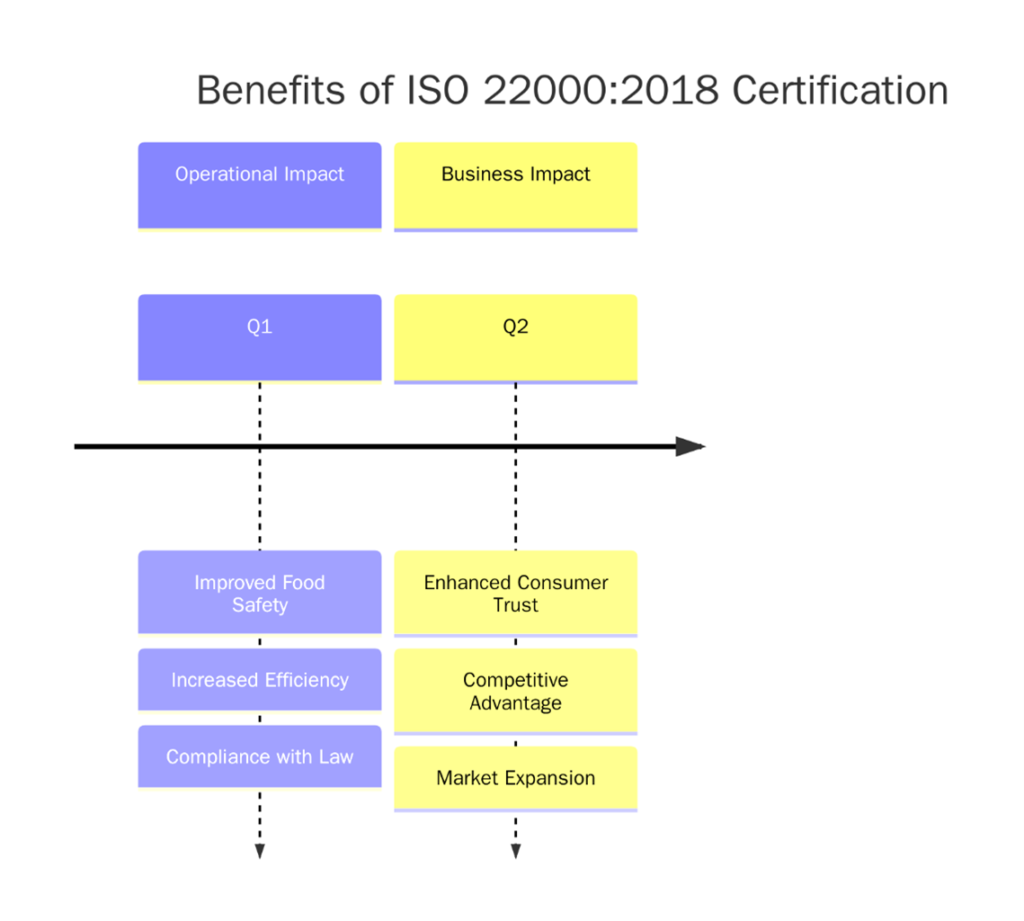
- Enhances food safety and hygiene standards by implementing internationally accepted controls and preventive measures.
- Ensures compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
- Improves customer trust and brand reputation by demonstrating commitment to food safety and responsible practices.
- Supports global market access by aligning with Codex HACCP and being recognized by retailers and regulators worldwide.
- Reduces food safety risks and incidents through structured hazard identification and control processes.
- Integrates easily with other ISO systems for an integrated management system.
- Enhances supply chain communication and traceability, ensuring transparency from raw material to end consumer.
- Boosts efficiency and cost savings by minimizing product recalls and waste.
- Drives continual improvement through performance monitoring and audits
- Promotes staff engagement and awareness with clearly defined roles and training
What is the ISO 22000:2018 Certification timeline?
This timeline depends on your FSMS implemented and readiness for the audit, below is the week wise table:
Week | Stage | Activity Description |
Week 1 | Application & Scope Review | Submit FSMS details; certification body reviews scope and prepares audit plan. |
Week 2 | Quotation & Agreement | Receive and confirm quotation; finalize certification contract. |
Week 3 | Audit Planning | Schedule Stage 1 and Stage 2 audits; plan resources and logistics. |
Week 4 | Stage 1 Audit | Documentation review: check policies, hazard analysis, PRPs, and legal compliance. |
Week 5–6 | Address Stage 1 Findings | Close gaps or nonconformities before the Stage 2 audit. |
Week 7 | Stage 2 Audit | On-site evaluation of FSMS implementation, traceability, CCP/OPRP controls, staff roles. |
Week 8 | Audit Report & Corrective Actions | Review audit findings; submit evidence for any nonconformities found. |
Week 9 | Certification Decision | Final review and decision by the certification body based on audit outcomes. |
Week 10 | Certificate Issuance | ISO 22000:2018 certificate issued |
What is the ISO 22000 certification cost?
The iso 22000 certification cost depends on the size of the organization, number of employees, number of sites, complexity of food processes, and risk level of operations. Organizations that already have a partially implemented food safety system may see reduced costs due to overlapping controls.
Contact us at support@pacificcert.com to get a personalized quote for the certification process!
Key Principles
It is built upon a set of core principles that guide organizations in establishing an effective Food Safety Management System:
- Interactive Communication: Ensures clear, timely exchange of food safety information across the supply chain.
- System Management: Integrates food safety into overall business processes using a structured FSMS.
- Prerequisite Programs (PRPs): Establishes basic conditions and activities to maintain a hygienic environment.
- HACCP Principles: Identifies, evaluates, and controls food safety hazards through a preventive approach.
- Risk-Based Thinking: Promotes proactive identification and management of food safety and system-level risks.
- Continuous Improvement: Uses the PDCA cycle to regularly evaluate and enhance the FSMS.
- Leadership Commitment: Involves top management in driving food safety culture and accountability.
- Evidence-Based Decision Making: Relies on data, monitoring, and analysis for effective food safety decisions.
Why ISO 22000:2018 is important and who needs it?
ISO 22000 is critically important as it provides a framework for managing food safety risks across the entire supply chain. It helps organizations to meet legal obligations and protect public health. It integrates with HACCP, enabling businesses to ensure consistent production of safe food.
Since food safety failures can lead to severe health consequences, it offers a reliable method to mitigate these risks. It also supports better traceability and internal communication, which are all vital to modern food safety operations. According to recent global data, over 40,000 organizations worldwide have adopted this standard to strengthen their food safety.
Any business that impacts food safety can benefit from implementing ISO 22000.
How Pacific Certifications Can Help?
We at Pacific Cert specialize in conducting independent audits to verify whether your FSMS meets all the requirements of the standard. Our audit approach is systematic and ensures regulatory compliance.
Our Services:
- Assessment of your FSMS documentation
- A detailed audit of your implemented system, food safety controls and staff awareness.
- Audits designed for organizations operating across multiple food production sites.
- Combined audits with other ISO standards
- Surveillance audits
- Recertification Audits
Pacific Certifications offers a transparent certification path that builds trust with regulators and consumers. Contact our audit team at support@pacificcert.com.
FAQs: ISO 22000:2018
What is ISO 22000:2018?
It’s a global standard for Food Safety Management Systems that ensures food is safe from production to consumption.
Who needs ISO 22000?
Any organization in the food chain can get ISO 22000.
Is ISO 22000 the same as HACCP?
No, ISO 22000 includes HACCP principles but adds a full management system structure, including risk-based thinking and continual improvement.
How long does certification take?
Typically 10–16 weeks, depending on your readiness and organizational size.
Is ISO 22000 recognized internationally?
Yes, It is accepted and respected by regulatory authorities, retailers, and buyers worldwide.
How long is the certificate valid?
The certificate is valid for 3 years with annual surveillance audits.
Can ISO 22000 be integrated with other ISO standards?
Absolutely, ISO 22000 follows the High-Level Structure (HLS), making it easy to integrate with other standards like ISO 9001 (Quality) or ISO 14001 (Environmental).
What is the validity of an ISO 22000 certificate?
The certificate is typically valid for 3 years, subject to annual surveillance audits by the certification body.
How to get ISO 22000 certification?
Build a food safety management system that meets ISO 22000, train your team, and keep records running. Do a gap review, run internal audits, and hold a management review. Then hire an accredited certification body for a two-stage audit: Stage 1 checks readiness and Stage 2 verifies full implementation. Close any findings and the body issues your certificate. After that you’ll have yearly surveillance audits and a three-year cycle. ISO itself does not certify.
What is the latest version of ISO 22000?
The current edition is ISO 22000:2018. It remains the active version and was confirmed in 2023, with Amendment 1 published in February 2024 adding “climate action” changes.
Contact Us
If you need support with ISO 22000 certification, contact us at support@pacificcert.com.
Read More at: Blogs by Pacific Certifications






