What is HACCP Certification?

HACCP stands for Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points. It is a food safety system that identifies, evaluates and controls hazards that are significant for food safety. Originally developed by NASA and food safety experts in the 1960s, HACCP has since become a globally accepted framework used across the food industry.
Today, HACCP Certification is widely recognized by food processors to regulators. It focuses on preventing hazards rather than relying only on finished product inspection.
To begin your HACCP certification process or learn more, contact us at support@pacificcert.com
What is the Purpose of HACCP Certification ?
The purpose of HACCP Certification is to prevent foodborne illness by managing risks from biological, chemical and physical hazards during production, handling and distribution. HACCP encourages preventive actions at key steps rather than corrective actions after problems arise. This approach supports better control across raw material sourcing, processing, packaging and delivery.
What is Scope and Applicability of HACCP Certification?
HACCP applies to all organizations involved in the food chain, from farm to fork. These include:
- Food manufacturers and processors
- Packaging and ingredient suppliers
- Cold chain logistics and transport operators
- Hotels, restaurants and catering units
- Retail food outlets and wholesale distributors
- Bottled water and beverage plants
HACCP Certification is suitable for any business that handles food for human consumption, regardless of size. It can be applied to fresh, frozen, cooked or packaged products. Some countries require HACCP certification by law, while others use it as a best practice model alongside ISO 22000 or GMP standards.
Key Definitions
Hazard: A biological, chemical or physical agent with potential to cause illness or injury when present in food.
Critical Control Point (CCP): A step where control can be applied to prevent or eliminate a hazard.
Critical Limit: A measurable value (like time, temperature or pH) that must be met at a CCP.
Monitoring: Regular checks or observations to ensure CCPs are under control.
Corrective Action: Steps taken when a critical limit is not met.
Verification: Activities to confirm the HACCP system is working as intended.
Record Keeping: Documentation that proves hazards were controlled throughout the process.
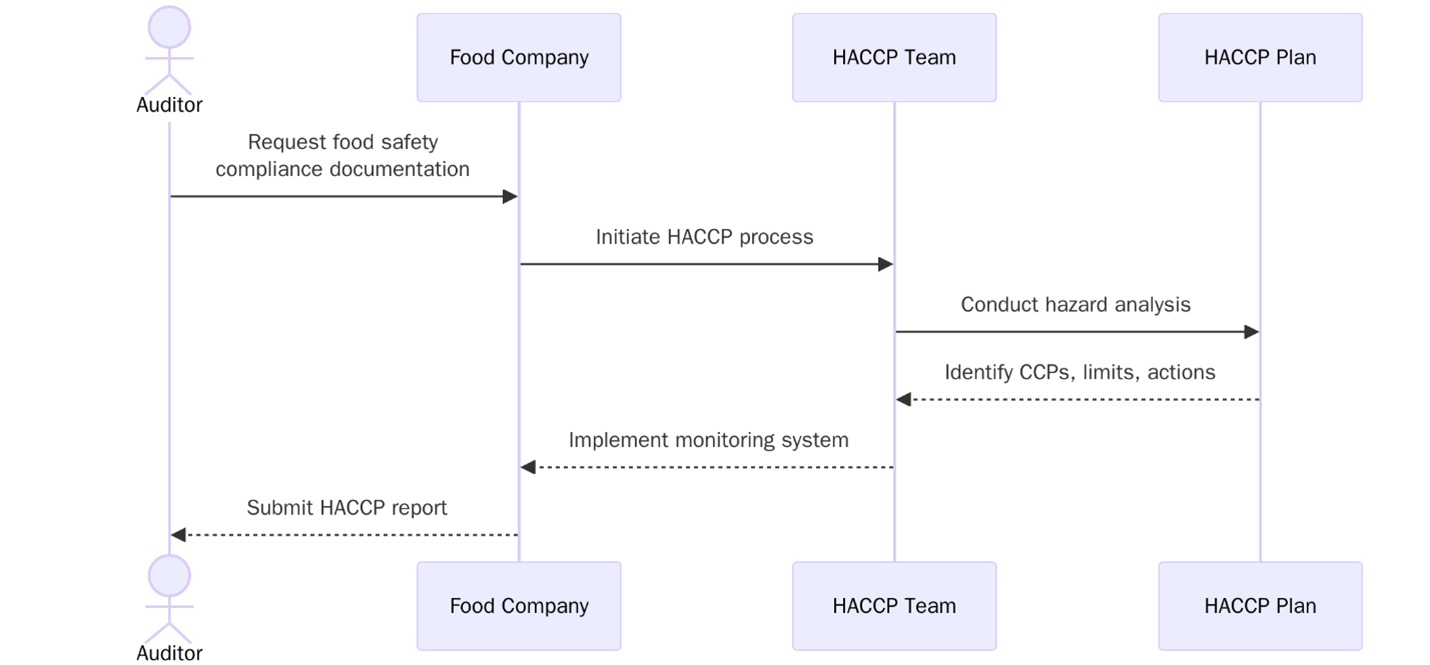
What is the Structure of HACCP System?
Step | Title | Description |
1 | Assemble HACCP Team | Select a cross-functional group familiar with operations |
2 | Describe Product | Define ingredients, packaging, storage and distribution |
3 | Identify Intended Use | State how the product will be used and by whom |
4 | Construct Flow Diagram | Create a step-by-step flow of the production process |
5 | On-site Confirmation | Verify the accuracy of the flow diagram in practice |
6 | Conduct Hazard Analysis | Identify potential hazards at each step |
7 | Determine CCPs | Choose steps where control is essential for food safety |
8 | Establish Critical Limits | Set values that define safe limits at each CCP |
9 | Monitor CCPs | Define how, when and who checks each CCP |
10 | Take Corrective Actions | Describe actions if CCPs exceed critical limits |
11 | Verify the System | Use audits or checks to confirm HACCP effectiveness |
12 | Keep Records | Maintain documentation to support system control |
What are the HACCP Certification Requirements?
To implement HACCP, a food business must follow structured steps that support hazard identification and control.
Below are the main HACCP Certification Requirements:
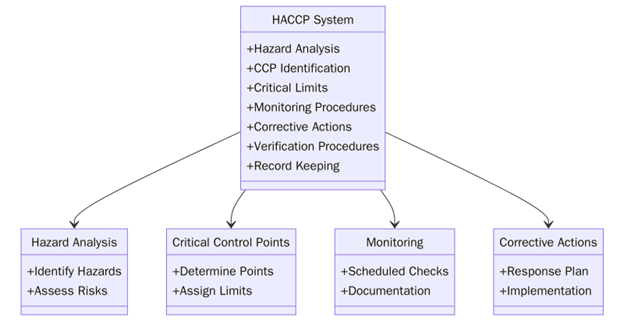
- Build a multidisciplinary HACCP team familiar with operations.
- Develop product descriptions and usage profiles.
- Map out all processing steps with a flowchart.
- Conduct a hazard analysis for each step in the process.
- Identify critical control points where safety hazards must be managed.
- Set critical limits for temperature, time or pH values at CCPs.
- Establish monitoring methods such as temperature logs or inspections.
- Create corrective actions if critical limits are breached.
- Verify the HACCP plan through internal audits and third-party review.
- Maintain records of all monitoring, verifications and corrective actions.
What are the benefits of HACCP Certification?
HACCP certification helps companies in the food sector build reliable safety systems, improve quality and gain trust across supply chains. It supports brand credibility and market growth.
Key benefits of HACCP Certification include:
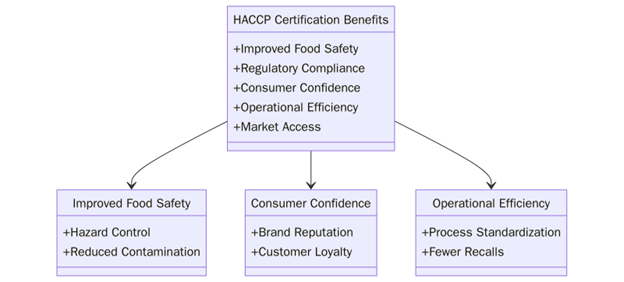
- Reduces food safety risks during production and distribution
- Builds trust among customers, regulators and buyers
- Supports market access for exports and large-scale contracts
- Improves traceability and raw material control
- Lowers incidents of food recalls or consumer illness
- Supports structured staff roles during food safety audits
- Aligns with ISO 22000, FSSC 22000 and GMP practices
- Enhances buyer confidence during supplier approval processes
HACCP systems are shifting toward digital, data-driven practices across the global food industry. Businesses are adopting IoT sensors to track temperature and other critical points in real time, while cloud-based platforms are replacing paper logs to improve documentation and audit readiness.
What is the Eligibility Criteria of HACCP Certification?
Any food business that handles, processes, packages or transports food products is eligible for HACCP certification. This includes farms, processing plants, restaurants and delivery operators. Both small businesses and large multinationals apply HACCP, especially when supplying to regulated or export markets. Having ISO 9001 or ISO 22000 in place can make it easier to implement HACCP systems by building on existing controls.
Whar is HACCP Certification Process?
- Gap Assessment – Evaluate current food safety practices and identify missing elements.
- Team Formation & Planning – Assign trained staff and plan implementation timelines.
- Hazard Analysis – Map the full process, identify hazards and determine CCPs.
- HACCP Plan Development – Finalize control points, critical limits and monitoring procedures.
- Training & Awareness – Educate staff on HACCP steps and recordkeeping needs.
- Trial Runs – Begin pilot monitoring and corrections based on sample batches.
- Internal Audit – Conduct a pre-certification review of all HACCP controls.
- Final Audit – Undergo third-party audit and submit technical documents for review.
HACCP Certification Timeline
The certification process usually takes 4 to 10 weeks depending on company size, product range and documentation readiness. For businesses with previous food safety systems, the timeline can be shorter. Seasonal products, multi-line processing or high-risk food categories may extend the timeline. Prompt record updates and management participation improve audit speed.
What is the HACCP Certification Cost?
HACCP Certification Cost depends on the complexity of the food operation, number of CCPs, training needs and audit scope. Single-product businesses with simple processes may require lower investment, while multi-line plants or exporters may need broader analysis. Additional expenses may include internal training, lab testing and third-party audit fees. Having ISO or GMP records already in place can lower the time and effort required.
How can Pacific Certifications Help?
Pacific Certifications offers HACCP audit and certification services across food and beverage, hospitality, catering, and packaging industries. We work with production teams and quality leads to ensure safety risks are addressed through clear and verifiable methods.
Our services include:
- Conducting gap assessments of existing food safety procedures
- Assisting with hazard identification and CCP determination
- Reviewing HACCP plans and supporting record templates
- Auditing monitoring logs and verification records
- Coordinating audits with ISO 22000 or GMP where needed
- Providing certification backed by ABIS accreditation
Training and Courses
Lead Auditor Training
Trains professionals on HACCP audits, documentation checks and CCP verification steps.
Lead Implementer Training
Prepares staff to create and manage HACCP systems across the full food chain.
Internal Auditor Training
Covers internal monitoring methods, audit planning and record checks under HACCP.
Pacific Certifications provides accredited training programs. If your organization is looking for HACCP training, our team is equipped to help you. Contact us at support@pacificcert.com
FAQs
What is HACCP?
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point) is a science-based, preventive system for identifying, evaluating, and controlling food-safety hazards across the whole food chain, focusing on prevention rather than end-product testing.
How many principles are there in HACCP?
Seven: (1) hazard analysis, (2) determine CCPs, (3) set critical limits, (4) monitor CCPs, (5) corrective actions, (6) verification, and (7) documentation/records.
How do you get HACCP certification?
Design and implement a HACCP plan per Codex principles, train your team, operate and keep records, then undergo an independent audit by a certification body that offers HACCP certification.
Is HACCP mandatory?
It depends on your market and product. In the U.S., HACCP is mandated for seafood (FDA) and meat/poultry (USDA-FSIS). In the EU, most food businesses must run procedures based on HACCP principles (Regulation (EC) 852/2004, Article 5).
What is a “critical limit” in a HACCP program?
A critical limit is the maximum and/or minimum value (e.g., time, temperature, pH, aw) that must be met at a CCP to prevent, eliminate, or reduce a hazard to an acceptable level, i.e., the line between safe and unsafe operation.
How is HACCP different from ISO 22000?
HACCP is the core hazard-control method; ISO 22000 is a full food-safety management system standard that embeds HACCP principles within broader management requirements (policy, leadership, planning, performance evaluation, etc.).
Do we need to test every product?
No. Effective HACCP relies on preventive controls and verification; regulators note that little end-product testing is needed when controls are validated. Finished-product testing has limits and is not sufficient to prove safety on its own.
Can small food businesses get certified?
Yes. HACCP systems can be scaled to the nature and size of the business, and certification bodies audit small operators too.
Who checks HACCP records?
Your own team verifies them (Principle 6), and regulators/auditors review them. e.g., USDA-FSIS inspectors and FDA guidance both require review of monitoring, corrective-action, and verification records.
What is true about HACCP?
It’s preventive, risk-based, and systematic. It applies at every stage from raw materials to distribution; and it depends on documented monitoring, corrective actions, and verification, not just final testing.
Ready to get ISO certified?
Contact Pacific Certifications to begin your certification journey today!
Suggested Certifications –
Read more: Pacific Blogs






